Neo-Perinatal Health Care Delivery: Practices and Procedures 1
Session: Neo-Perinatal Health Care Delivery: Practices and Procedures 1
455 - Impact of Neuromuscular Blockade on Post-intubation Ventilation in Very Low Birthweight Infants: A Multi-Center Study
Friday, April 25, 2025
5:30pm - 7:45pm HST
Publication Number: 455.5190
Meghan Rowe, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA, United States; Sara K. Neches, University of Washington School of Medicine, Shoreline, WA, United States; Natalie Chapkis, Seattle Children's Hospital and University of Washington, Seattle, WA, United States; Sara Khan, University of California, Los Angeles David Geffen School of Medicine, Los Angeles, CA, United States; Blair Weikel, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, CO, United States; Theresa Grover, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, CO, United States; James S. Barry, University of Colorado School of Medicine, centennial, CO, United States; Rebecca Shay, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, CO, United States

Rowe Meghan, MD (she/her/hers)
Fellow
University of Washington School of Medicine
Seattle, Washington, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Premedication, including a paralytic, has been shown to improve success of neonatal tracheal intubation (TI) and decrease adverse events. Post-intubation impairment of ventilation remains a concern. Hypercarbia and acute changes in partial pressure of carbon dioxide (pCO2) are associated with increased pulmonary vascular resistance, fluctuations in cerebral blood flow, and risk for intraventricular hemorrhage. There is a gap in knowledge of the effect of full premedication, including paralysis, on post-intubation ventilation of very-low birthweight (VLBW) infants.
Objective: To investigate differences in post-intubation ventilation for VLBW neonates following intubation with and without full premedication, including paralysis.
Design/Methods: Multicenter, retrospective observational study of non-emergent NICU TI for infants < 1500g at intubation, comparing pre-intubation characteristics and post-intubation outcomes among three premedication groups: Full (atropine, opiate, and paralytic) Partial (atropine and/or opiate) and None. Data was collected from the National Emergency Airway Registry for Neonates (NEAR4NEOs) and retrospective chart review in two academic, level III NICUs with similar premedication protocols at the University of Colorado (UC) and the University of Washington (UW). Primary outcomes include hypercarbia (post-pCO2 > 65 mmHg) or acute change in pCO2 >10 mmHg on pre- and post-intubation blood gases. Data was analyzed using descriptive statistics, ANOVA, Chi-Square, and Fischer’s exact test.
Results: 157 TIs for VLBW infants between June 2019 and June 2021 were analyzed (N=68,43% UC and N=89,57% UW; Table 1). 150(96%) TI encounters had full NEAR4NEOs data; 50(33%) recorded adverse TI-associated events (TIAE) across three premedication groups (None: N=20,13%, Partial: N=21,14%, Full: N=9,6%; p=0.01). 28(18%) TI encounters were missing pre-intubation pCO2 data, and 6(4%) were missing post-intubation pCO2. There was no difference in median post-intubation pCO2 between groups (None: 56mmHg, IQR [45-69], Partial: 53mmHg, IQR [45-64], Full: 61mmHg, IQR [51-72]; p=0.26). Significantly more TI with full premedication had >10 mmHg increase in post-intubation pCO2 (None, N=3,13%, Partial, N=12,22%, Full, N=20,43%; p=0.01; Fig 1). There was no difference between groups with respect to a rise in post-intubation pCO2 >65 mmHg.
Conclusion(s): Full premedication was associated with significantly fewer adverse TIAEs. However, this may be at the expense of an acute increase in post-intubation pCO2. Further studies are needed to evaluate specific minute ventilation parameters for the VLBW population.
Table 1. Intubation Characteristics
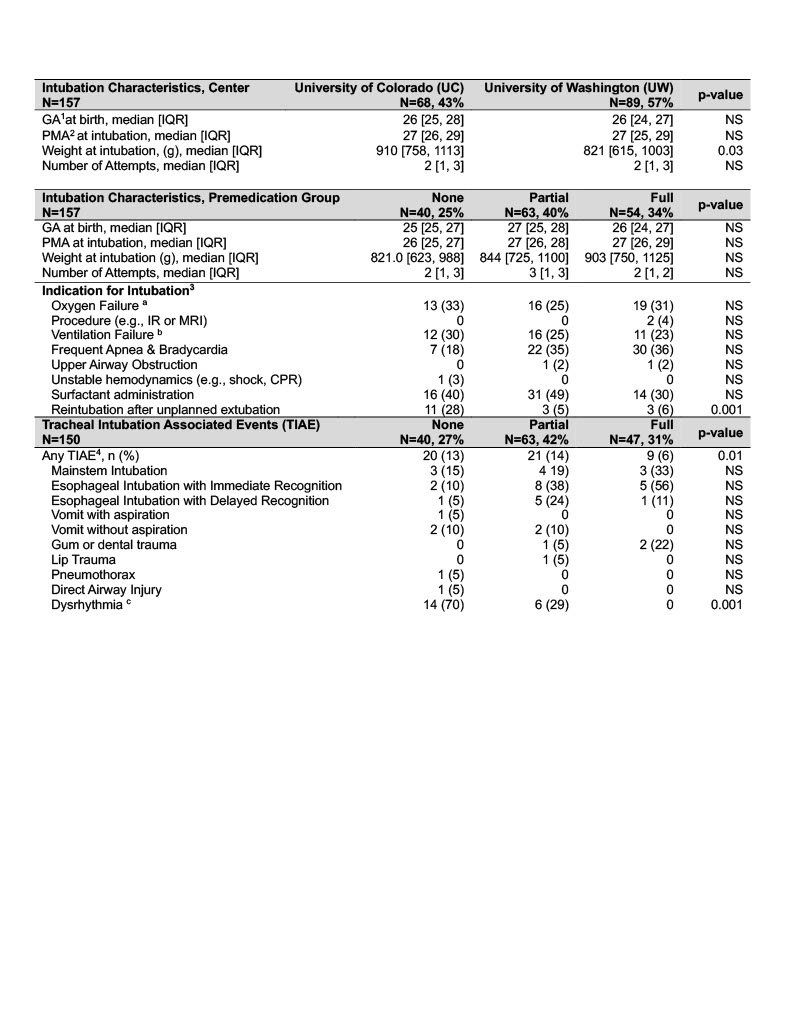 Premedication Groups: None: no premedication; Partial: atropine and/or opiate; Full: atropine+opiate+paralytic
Premedication Groups: None: no premedication; Partial: atropine and/or opiate; Full: atropine+opiate+paralytic 1. GA= gestational Age in Weeks
2. PMA= post-menstrual age at time of intubation in weeks
3. Encounter and first TI course data as defined by the NEAR4NEOs database available for N=150 infants. Percentages may exceed 100% as infants may have more than one indication for intubation
a. oxygen failure includes PaO2 <60 mmHg in FiO2 >0.60 in the absence of cyanotic heart disease
b. ventilation failure includes PaCO2 > 50 mmHg in the absence of chronic lung disease
4. A total of N=50 (33%) of TI encounters reported any TIAE. Percentages for individual TIAEs may exceed 100% as infants may have more than one TIAE during the intubation course.
c. Dysrhythmia includes tachycardia, bradycardia with heart rate <60 bpm, and other arrhythmias
Table 2. Pre- and post-intubation pCO2 data
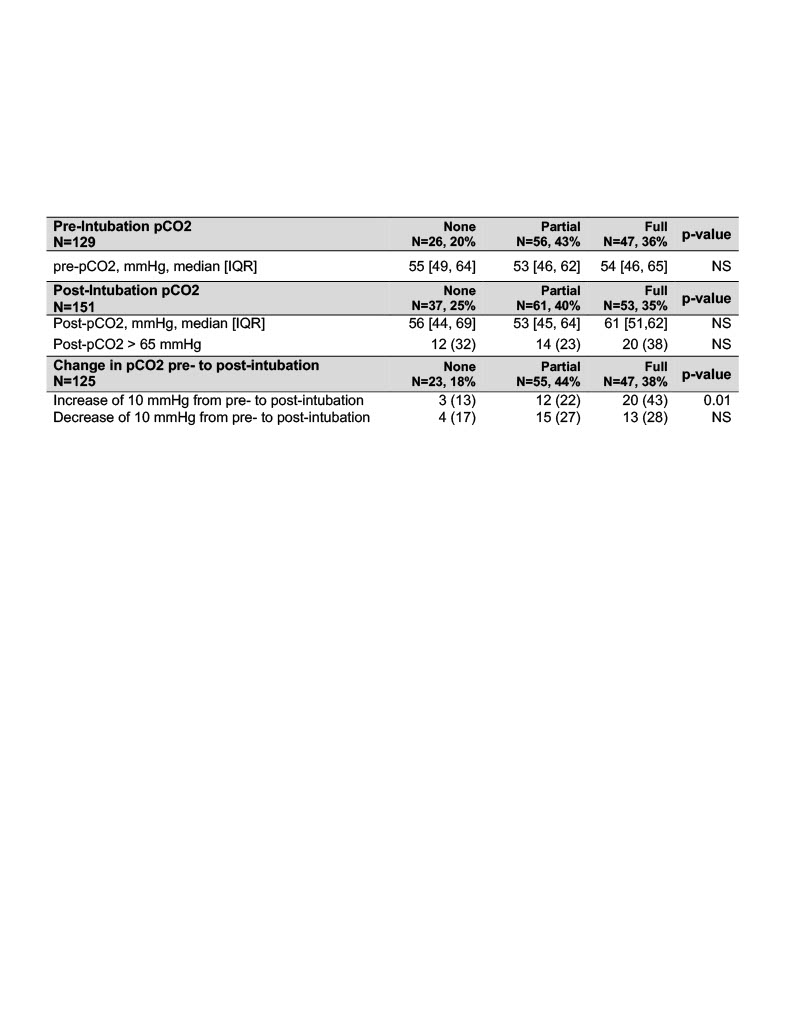 Data for pCO2 was retrospectively collected by chart review from blood gases immediately before and after the intubation encounter. N=129 (82%) of TI encounters had pre-intubation pCO2 data recorded. N=151 (96%) had post-intubation pCO2 data recorded. N=125 (80%) of TI encounters had both pre- and post-intubation pCO2 data recorded.
Data for pCO2 was retrospectively collected by chart review from blood gases immediately before and after the intubation encounter. N=129 (82%) of TI encounters had pre-intubation pCO2 data recorded. N=151 (96%) had post-intubation pCO2 data recorded. N=125 (80%) of TI encounters had both pre- and post-intubation pCO2 data recorded.Fig. 1 Full premedication was significantly associated with both a decrease in adverse TIAEs (p=0.01) and an increase in pCO2 >10 mmHg (p=0.01) from pre-intubation pCO2 levels
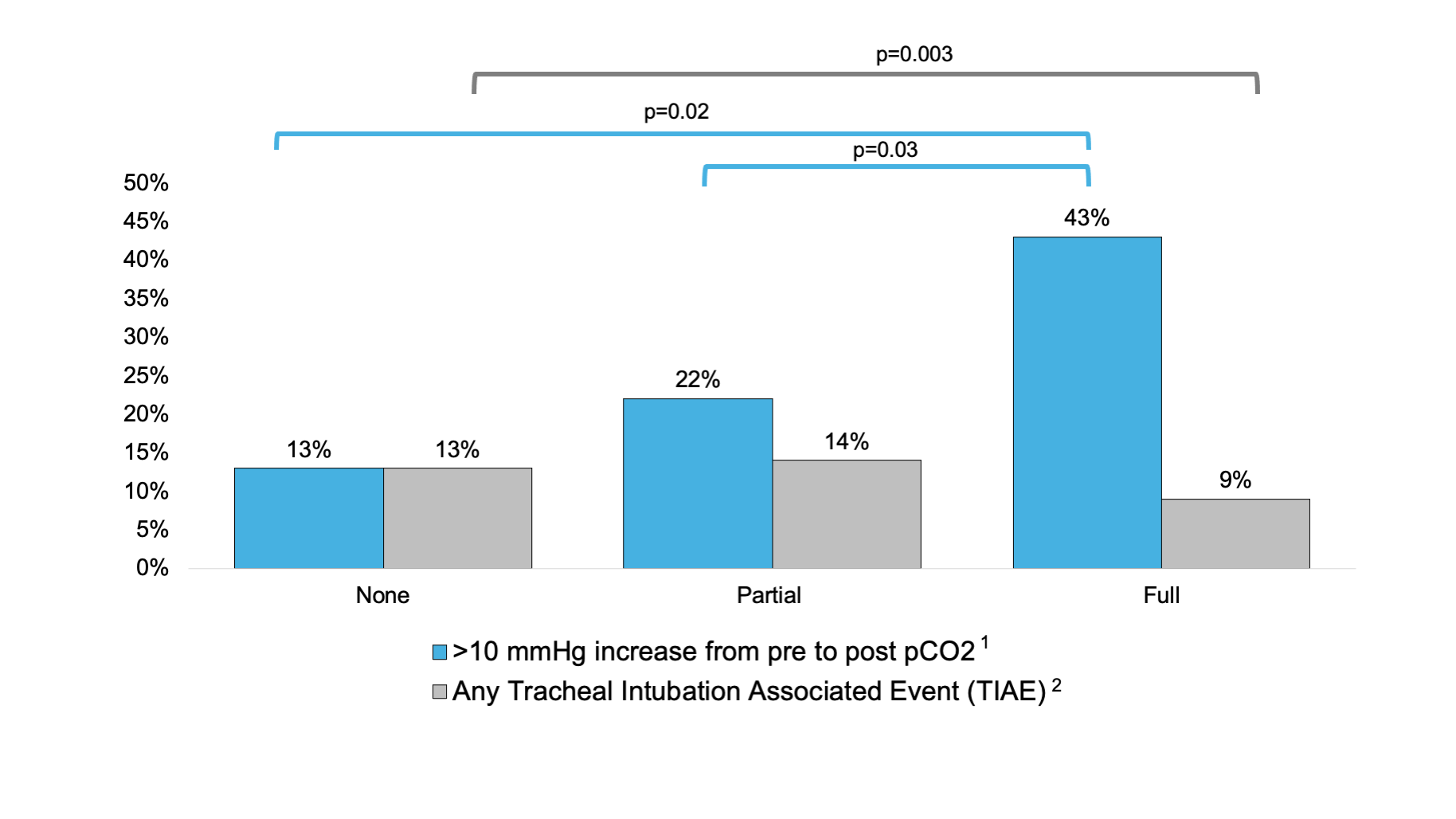 1. TIAEs include: mainstem intubation, esophageal intubation with immediate recognition, esophageal intubation with delayed recognition, vomiting with and without aspiration, gum, dental or lip trauma, direct airway injury, dysrhythmia. N=50 (33%) TI encounters reported any TIAE, however infants may have had multiple TIAE within one encounter.
1. TIAEs include: mainstem intubation, esophageal intubation with immediate recognition, esophageal intubation with delayed recognition, vomiting with and without aspiration, gum, dental or lip trauma, direct airway injury, dysrhythmia. N=50 (33%) TI encounters reported any TIAE, however infants may have had multiple TIAE within one encounter. 2. Data for pCO2 was retrospectively collected from blood gases immediately before and after the intubation encounter. N=125 (80%) of TI encounters had both pre- and post-intubation pCO2 data.
Table 1. Intubation Characteristics
 Premedication Groups: None: no premedication; Partial: atropine and/or opiate; Full: atropine+opiate+paralytic
Premedication Groups: None: no premedication; Partial: atropine and/or opiate; Full: atropine+opiate+paralytic 1. GA= gestational Age in Weeks
2. PMA= post-menstrual age at time of intubation in weeks
3. Encounter and first TI course data as defined by the NEAR4NEOs database available for N=150 infants. Percentages may exceed 100% as infants may have more than one indication for intubation
a. oxygen failure includes PaO2 <60 mmHg in FiO2 >0.60 in the absence of cyanotic heart disease
b. ventilation failure includes PaCO2 > 50 mmHg in the absence of chronic lung disease
4. A total of N=50 (33%) of TI encounters reported any TIAE. Percentages for individual TIAEs may exceed 100% as infants may have more than one TIAE during the intubation course.
c. Dysrhythmia includes tachycardia, bradycardia with heart rate <60 bpm, and other arrhythmias
Table 2. Pre- and post-intubation pCO2 data
 Data for pCO2 was retrospectively collected by chart review from blood gases immediately before and after the intubation encounter. N=129 (82%) of TI encounters had pre-intubation pCO2 data recorded. N=151 (96%) had post-intubation pCO2 data recorded. N=125 (80%) of TI encounters had both pre- and post-intubation pCO2 data recorded.
Data for pCO2 was retrospectively collected by chart review from blood gases immediately before and after the intubation encounter. N=129 (82%) of TI encounters had pre-intubation pCO2 data recorded. N=151 (96%) had post-intubation pCO2 data recorded. N=125 (80%) of TI encounters had both pre- and post-intubation pCO2 data recorded.Fig. 1 Full premedication was significantly associated with both a decrease in adverse TIAEs (p=0.01) and an increase in pCO2 >10 mmHg (p=0.01) from pre-intubation pCO2 levels
 1. TIAEs include: mainstem intubation, esophageal intubation with immediate recognition, esophageal intubation with delayed recognition, vomiting with and without aspiration, gum, dental or lip trauma, direct airway injury, dysrhythmia. N=50 (33%) TI encounters reported any TIAE, however infants may have had multiple TIAE within one encounter.
1. TIAEs include: mainstem intubation, esophageal intubation with immediate recognition, esophageal intubation with delayed recognition, vomiting with and without aspiration, gum, dental or lip trauma, direct airway injury, dysrhythmia. N=50 (33%) TI encounters reported any TIAE, however infants may have had multiple TIAE within one encounter. 2. Data for pCO2 was retrospectively collected from blood gases immediately before and after the intubation encounter. N=125 (80%) of TI encounters had both pre- and post-intubation pCO2 data.

