Neonatal Infectious Diseases/Immunology 3: Evaluating and preventing infections in NICU
Session: Neonatal Infectious Diseases/Immunology 3: Evaluating and preventing infections in NICU
596 - Organism-Specific Heart Rate Patterns in Neonatal Sepsis: Simplifying Complex Physiology
Friday, April 25, 2025
5:30pm - 7:45pm HST
Publication Number: 596.5665
Sherry Kausch, University of Virginia, Charlottesville, VA, United States; Brynne Sullivan, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, VA, United States; Colm P. Travers, UAB, Birmingham, AL, United States; Zachary A. Vesoulis, Washington University in St. Louis School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, United States; Rakesh Sahni, Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, New York, NY, United States; Douglas E. Lake, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville, VA, United States; Karen D. Fairchild, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Earlysville, VA, United States

Karen D. Fairchild, MD
Professor of Pediatrics
University of Virginia School of Medicine
Earlysville, Virginia, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: A well-described pattern of low variability of heart rate (HR) punctuated by transient decelerations emerges in some preterm infants with late-onset sepsis (LOS). We hypothesized that HR patterns would differ based on organism group and mortality.
Objective: Compare changes in 4 HR mathematical moments (mean, standard deviation, skewness, kurtosis) around the time of LOS with Gram-negative, Coagulase-negative Staphylococcus and other Gram-positive bacteria (GN, CONS, OGP).
Design/Methods: The cohort includes very-low-birthweight infants at 4 NICUs that prospectively archive continuous every-2-second HR data (NIH grant HD072071). We calculated HR mean, standard deviation (reflecting variability), skewness (asymmetry of HR histogram, more negative skewness reflecting more decelerations), and kurtosis (tailedness of HR histogram). These were calculated in 10-minute windows, averaged hourly, in the 96-hour period surrounding diagnosis of LOS (positive blood culture >72h from birth and at least 5 days antibiotics). For each organism group, we plotted hourly HR characteristics as a function of time. We calculated the number of hours prior to LOS diagnosis when each metric changed significantly compared to the baseline value 24 hours before diagnosis. Mortality within 7 days of LOS in relation to HR patterns was analyzed using Wilcoxon rank sum testing.
Results: In total, 369 infants (mean GA 25.5 weeks, 55% male) had HR data available around the time of LOS (79 GN, 222 CONS, 68 OGP) (Table 1). HR mean and SD increased in the hours leading up to LOS diagnosis, but skewness and kurtosis did not change significantly. Compared to baseline 24h prior to LOS, mean HR rose significantly for each organism group, with a more prominent and earlier rise for GN. (Figure 1) The significant rise in HR over infants’ baseline started 9 hours prior to diagnosis of GN, 2 hours before CONS, and 1 hour before OGP. Standard deviation of HR also increased significantly for each group, 2 hours prior to diagnosis of GN LOS, 5 hours before CONS, and 2 hours before OGP. Death occurred within 7 days of the positive blood culture in 33 cases and was more common in GN LOS (mortality 22% GN, 4.5% CONS, 8.8% OGP). Survivors had higher standard deviation and skewness of HR (p < 0.01) but no difference in HR mean or kurtosis (Figure 2)
Conclusion(s): Infants with GN sepsis had an earlier rise in HR compared to those with CONS or OGP sepsis, but other HR changes were not significantly different among the 3 organism groups. Better HR variability and fewer decelerations at the time of LOS diagnosis were associated with survival.
Infant characteristics and outcomes of LOS, by organism group
.jpg)
Heart rate characteristics 48 hours before and after the time of LOS, by organism group.
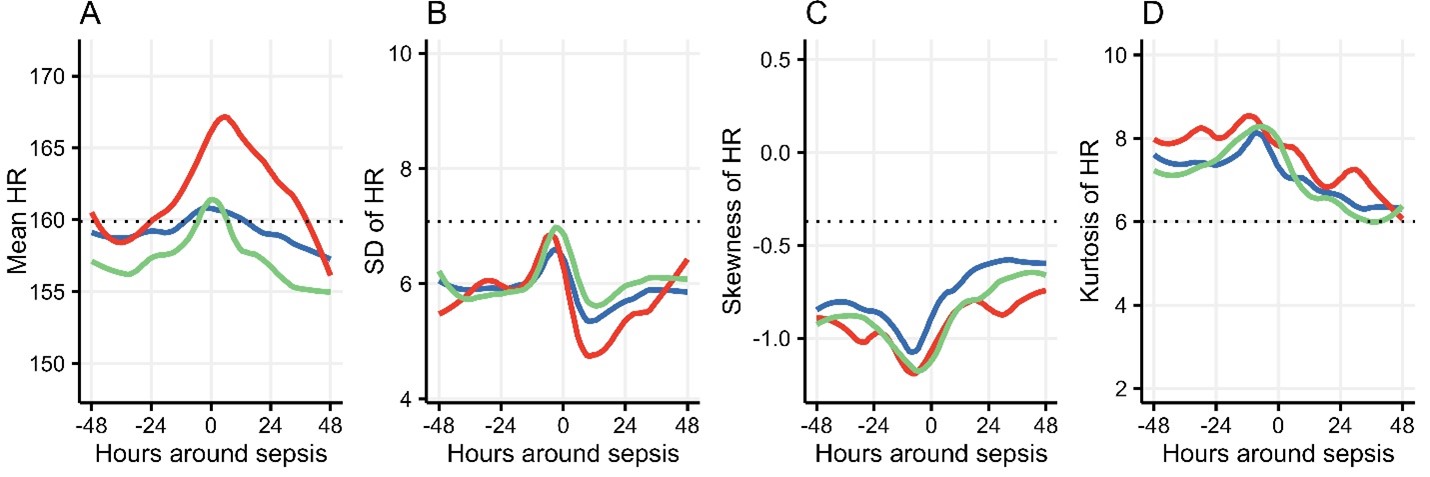 HR data were available for VLBW infants at 4 NICUs around the time of 369 sepsis events. Hourly group mean (A), standard deviation (B), skewness (C), and kurtosis (D) are shown for infants with GN LOS (red, n=79), CONS LOS (blue, n=222), and OGP LOS (green, n=68). The dashed horizontal line represents the mean heart rate characteristic for all VLBW infants at all times. Using sign rank tests, mean HR rose significantly by time zero (time of positive blood culture) compared to 24 hours prior for each group, with the earliest rise and highest peak for the GN group. Standard deviation of HR also increased prior to LOS diagnosis, mirrored by a decrease in skewness reflecting more transient decelerations. There was not a significant change in HR kurtosis around the time of LOS.
HR data were available for VLBW infants at 4 NICUs around the time of 369 sepsis events. Hourly group mean (A), standard deviation (B), skewness (C), and kurtosis (D) are shown for infants with GN LOS (red, n=79), CONS LOS (blue, n=222), and OGP LOS (green, n=68). The dashed horizontal line represents the mean heart rate characteristic for all VLBW infants at all times. Using sign rank tests, mean HR rose significantly by time zero (time of positive blood culture) compared to 24 hours prior for each group, with the earliest rise and highest peak for the GN group. Standard deviation of HR also increased prior to LOS diagnosis, mirrored by a decrease in skewness reflecting more transient decelerations. There was not a significant change in HR kurtosis around the time of LOS.Heart rate characteristics at the time of LOS diagnosis for 7-day survivors and non-survivors
.jpg) Heart rate mean (A), standard deviation (B), skewness (C), and kurtosis (D) are shown for infants for infants that survived (blue, n =33) versus those that died within 7 days of LOS diagnosis (orange, n =336). Horizontal line in the box is median, box bounds are 25th and 75th percentile, whiskers are 5th and 95th percentile, and dots are outliers. Asterisks indicate HR SD and skewness were significantly higher in survivors (p < 0.05).
Heart rate mean (A), standard deviation (B), skewness (C), and kurtosis (D) are shown for infants for infants that survived (blue, n =33) versus those that died within 7 days of LOS diagnosis (orange, n =336). Horizontal line in the box is median, box bounds are 25th and 75th percentile, whiskers are 5th and 95th percentile, and dots are outliers. Asterisks indicate HR SD and skewness were significantly higher in survivors (p < 0.05). 
