Pulmonology
Session: Pulmonology
099 - Disruption of the surfactant protein A receptor isoform SP-R210L in alveolar macrophages alters the toll-like receptor pathway
Friday, April 25, 2025
5:30pm - 7:45pm HST
Publication Number: 99.4302
Tram N. Van, Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine, Vestal, NY, United States; Brycen Aldrich, Pennsylvania State University College of Medicine, Hershey, PA, United States; Zissis C. Chroneos, Penn State College of Medicine, Hershey, PA, United States; Chintan K. Gandhi, Penn State Hershey College of Medicine, Hershey, PA, United States

Chintan K. Gandhi, MBBS, MD (he/him/his)
Associate Professor
Penn State Hershey College of Medicine
Hershey, Pennsylvania, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Surfactant protein A activates and helps clear pathogens through alveolar macrophages via the receptor SP-R210. SP-R210 exists in two isoforms—SP-R210L (long) and SP-R210S (short)—which are encoded by alternative splicing of the myosin 18A gene. Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are innate immune sensors that recognize viral nucleic acids leading to the activation of antiviral genes.
Objective: To study how SP-R210 isoforms differentially regulate endosomal TLR signaling pathway.
Design/Methods: RAW264.7 macrophages (control, SP-R210L (DN), and SP-R210L (KO)) were treated with Poly(I:C), (pIC, TLR3 agonist), Imiquimod (IM, TLR7 agonist), and ODN1585 (ODN, TLR9 agonist). Cell supernatants were collected at various time points, and TNF-α and IFN-β levels were measured using ELISA (Fig 1).
Results: Fig 2, pIC significantly increased TNF-⍺ production in SP-R210(KO) cells. For IFN-β secretion, pIC-treated SP-R210(KO) cells showed the strongest response. pIC-treated SP-R210(DN) cells had a lower stimulation of IFN-β secretion compared to SP-R210(KO), yet there was a significant difference compared to untreated cells. IM significantly elevated TNF-⍺ production across all three cell lines with the highest level in SP-R210(KO) cells, followed by SP-R210(DN) and control cells. No significant difference was observed in IFN-β secretion across all three cell lines compared to controls. In contrast to pIC and IM, ODN elicited higher TNF-α production in SP-R210(DN) cells compared to SP-R210(KO) cells. No significant difference was observed in IFN-β secretion across all three cell lines upon ODN treatment.
Fig 3, IM was the only treatment that stimulated TNF-⍺ secretion in control cells. No significant difference was observed in IFN-β secretion in control cells across treatments. IM and ODN treatment resulted in robust stimulation of TNF-⍺ secretion in SP-R210L(DN) cells compared to untreated cells. However, no significant difference is observed between pIC-treated versus untreated SP-R210L(DN) cells. All three treatments showed significant IFN-β secretion in SP-R210L(DN) cells at 8h. At later time points, only SP-R210L(DN) cells treated with pIC had a significantly higher IFN-β secretion than untreated cells. All three treatments resulted in significant TNF-⍺ secretion in SP-R210(KO) cells, with IM causing the most robust stimulation, followed by pIC, then ODN. At 8-72h, only IM caused the most robust IFN-β stimulation in KO cells. p < 0.05 between treated versus untreated cells (One-way ANOVA).
Conclusion(s): Disruption of SP-R210L isoform plays distinct roles in inhibiting and activating the endosomal TLR signaling pathway.
Fig 1. Experimental methods
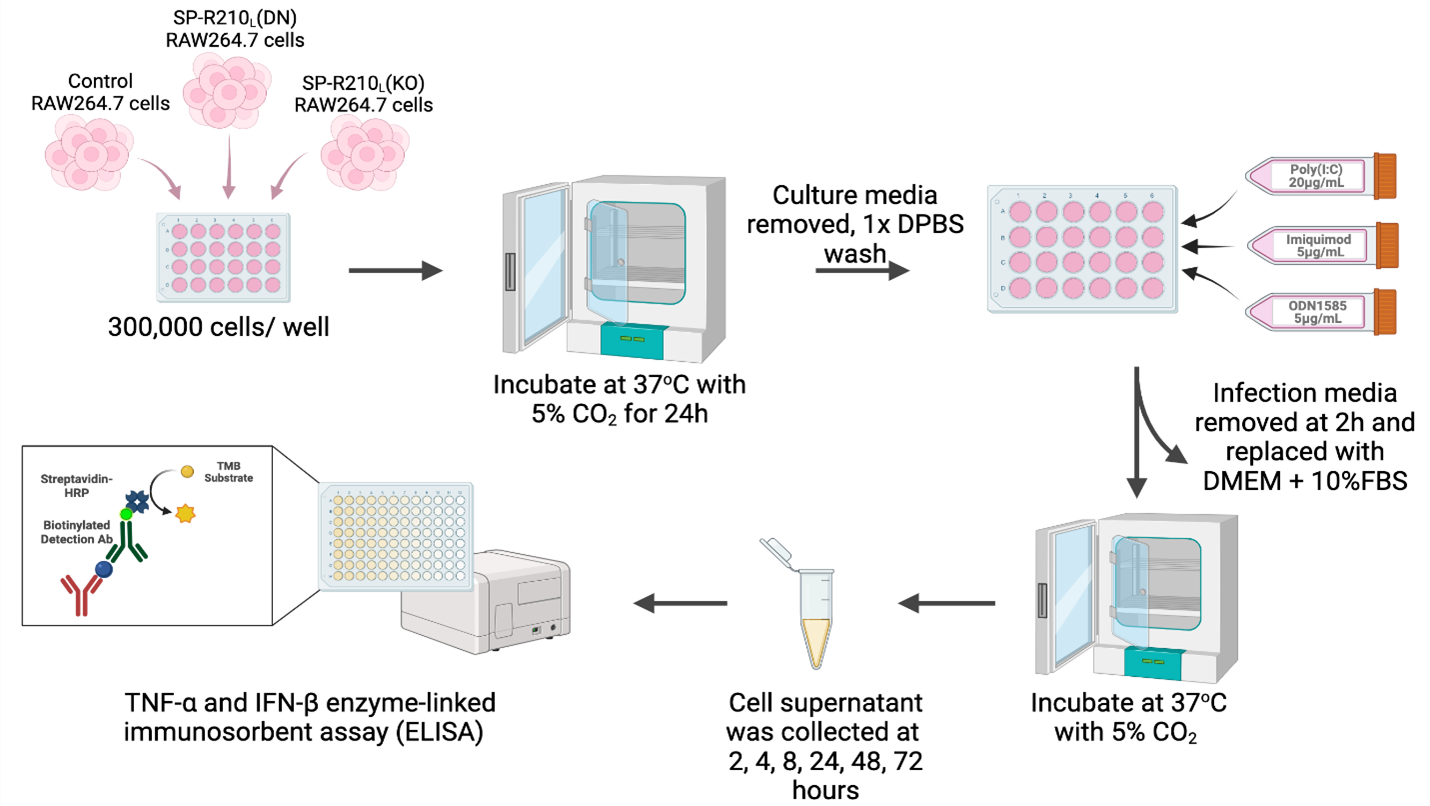
Fig 2. Differential cytokine responses in control and SP-R210-deficient macrophages upon treatment with TLR3, 7, 9 agonists
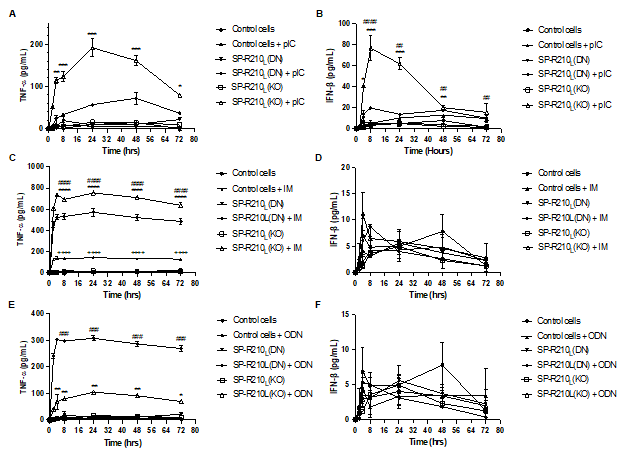 (A) pIC significantly increased TNF-⍺ production in SP-R210(KO) cells (B) For IFN-β secretion, pIC-treated SP-R210(KO) cells showed the strongest response. pIC-treated SP-R210(DN) cells had a lower stimulation of IFN-β secretion compared to SP-R210(KO), yet there was a significant difference compared to untreated cells. (C) IM significantly elevated TNF-⍺ production across all three cell lines with the highest level in SP-R210(KO) cells, followed by SP-R210(DN) and control cells. (D) No significant difference was observed in IFN-β secretion across all three cell lines compared to controls. (E) In contrast to pIC and IM, ODN 1585 elicited higher TNF-α production in SP-R210(DN) cells compared to SP-R210(KO) cells. (F) No significant difference was observed in IFN-β secretion across all three cell lines upon ODN1585 treatment. p < 0.05 between treated versus untreated cells (One-way ANOVA).
(A) pIC significantly increased TNF-⍺ production in SP-R210(KO) cells (B) For IFN-β secretion, pIC-treated SP-R210(KO) cells showed the strongest response. pIC-treated SP-R210(DN) cells had a lower stimulation of IFN-β secretion compared to SP-R210(KO), yet there was a significant difference compared to untreated cells. (C) IM significantly elevated TNF-⍺ production across all three cell lines with the highest level in SP-R210(KO) cells, followed by SP-R210(DN) and control cells. (D) No significant difference was observed in IFN-β secretion across all three cell lines compared to controls. (E) In contrast to pIC and IM, ODN 1585 elicited higher TNF-α production in SP-R210(DN) cells compared to SP-R210(KO) cells. (F) No significant difference was observed in IFN-β secretion across all three cell lines upon ODN1585 treatment. p < 0.05 between treated versus untreated cells (One-way ANOVA). Fig 3. Comparison of the cytokine production level between treatments in each cell type
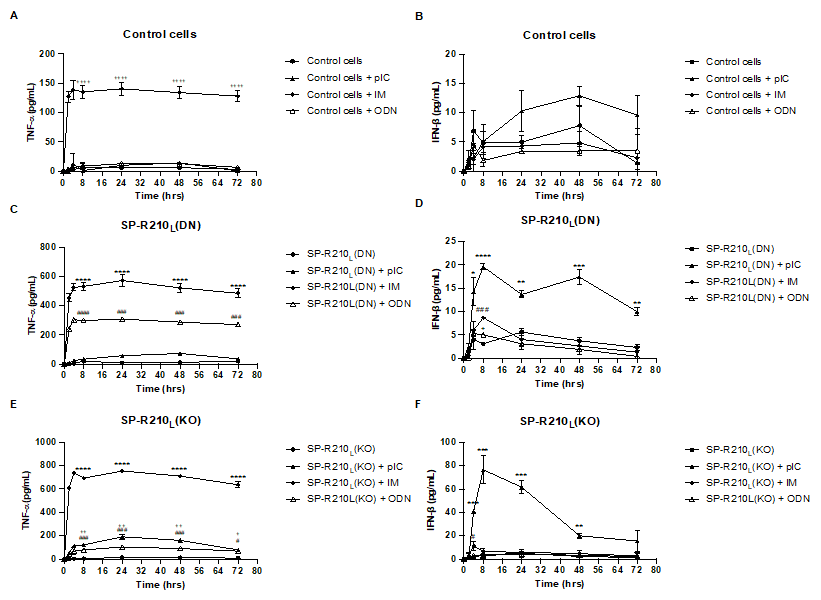 (A) IM was the only treatment that stimulated TNF-⍺ secretion in control cells. (B) No significant difference was observed in IFN-β secretion in control cells across treatments. (C) Both IM and ODN treatment resulted in robust stimulation of TNF-⍺ secretion in SP-R210L(DN) cells compared to untreated cells. However, no significant difference is observed between pIC-treated versus untreated SP-R210L(DN) cells. (D) All three treatments resulted in significant IFN-β secretion in SP-R210L(DN) cells at t = 8h. At later time points, only SP-R210L(DN) cells treated with pIC had a significantly higher IFN-β secretion than untreated cells. (E) All three treatments resulted in significant TNF-⍺ secretion in SP-R210(KO) cells, with IM causing the most robust stimulation, followed by pIC, then ODN. (F) At t = 8-72h, only IM caused the most robust IFN-β stimulation in KO cells. p < 0.05 between treated versus untreated cells (One-way ANOVA).
(A) IM was the only treatment that stimulated TNF-⍺ secretion in control cells. (B) No significant difference was observed in IFN-β secretion in control cells across treatments. (C) Both IM and ODN treatment resulted in robust stimulation of TNF-⍺ secretion in SP-R210L(DN) cells compared to untreated cells. However, no significant difference is observed between pIC-treated versus untreated SP-R210L(DN) cells. (D) All three treatments resulted in significant IFN-β secretion in SP-R210L(DN) cells at t = 8h. At later time points, only SP-R210L(DN) cells treated with pIC had a significantly higher IFN-β secretion than untreated cells. (E) All three treatments resulted in significant TNF-⍺ secretion in SP-R210(KO) cells, with IM causing the most robust stimulation, followed by pIC, then ODN. (F) At t = 8-72h, only IM caused the most robust IFN-β stimulation in KO cells. p < 0.05 between treated versus untreated cells (One-way ANOVA).
