Neonatal Hemodynamics and Cardiovascular Medicine 2
Session: Neonatal Hemodynamics and Cardiovascular Medicine 2
048 - Echocardiographic Detection of Pulmonary Hypertension and Right Ventricular Failure in Infants with Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia: An International Survey of the BPD Collaborative
Saturday, April 26, 2025
2:30pm - 4:45pm HST
Publication Number: 48.5036
Shilpa Vyas-Read, Emory University, Atlanta, GA, United States; Ronald W. Day, Blow By Oxygen Foundation, SALT LAKE CITY, UT, United States; Clifford L. Cua, Nationwide Children's Hospital, Columbus, OH, United States; Roopa Siddaiah, Penn State Children's Hospital, Hershey, PA, United States; Robin McKinney, HASBRO CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL, PROVIDENCE, RI, United States; Philip Levy, Boston Children's Hospital, BROOKLINE, MA, United States; Eric Douglas. Austin, Vanderbilt University School of Medicine, Nashville, TN, United States; Krithika Lingappan, MD, PhD, Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, United States; Kathleen Gibbs, CHOP, Philadelphia, PA, United States; Steve Abman, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Denver, CO, United States; Shazia Bhombal, Children's Healthcare of Atlanta/Emory University, Atlanta, GA, United States

Shazia Bhombal, MD
Associate Professor
Children’s Healthcare of Atlanta/Emory University
Atlanta, Georgia, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Transthoracic echocardiograms (TTE) for detection of pulmonary hypertension (PH) are recommended for infants with moderate and severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD). The clinical and echocardiographic factors used at the bedside to diagnose and manage PH may vary between clinical subspecialists and practice sites.
Objective: To survey members of the BPD Collaborative on the use of TTE and the echocardiographic thresholds for the definition and management of PH and right ventricular failure (RVF) in infants with BPD
Design/Methods: Members of the BPD Collaborative were sent the survey between March – June 2024 by anonymous link using the Qualtrics survey platform. The survey consisted of 33 multiple-choice and rank-order questions and two open-ended questions. Responses were categorized by subspecialty: 1) neonatology, 2) cardiology and PH specialists, 3) multi-disciplinary (nurses, nurse practitioners, respiratory therapy, pharmacists, sonographers), and 4) pulmonology and pediatric intensive care. Responses to open-ended questions were categorized into six themes.
Results: Of the 432 members, 108 participated in the survey (25% response rate): 60% neonatologists, 17% cardiology/PH specialists, 20% pulmonologists/pediatric intensivists, and 11% multidisciplinary. Over 90% of respondents agreed that: 1) their site had a protocol for monitoring infants with BPD for PH; 2) TTE was the most feasible method to identify and serially monitor PH and RVF; and 3) a position paper to describe the most feasible, accurate, and reliable TTE measures to evaluate and monitor PH and RVF is needed. Subspecialty categories differed when asked about the parameters needed to identify PH and RVF, as well thresholds to quantify PH severity (Tables 1 & 2, respectively). Responses to system, patient, and echocardiography-related obstacles to obtaining and interpreting measurements for PH or RVF were classified into six themes that highlighted modifiable factors such as reduction of variability in protocols and image acquisition, and improved communication between subspecialty groups (Table 3).
Conclusion(s): Echocardiography is a recognized, feasible method to monitor PH and RVF among a majority of respondents in the BPD collaborative; however, the parameters and thresholds for their identification and management vary between subspecialties. All respondent groups agreed that a position paper that incorporates the views of key stakeholders would aid in closing knowledge gaps, standardizing practices, and enhancing communication between subspecialties regarding the use of echocardiography in infants with BPD at risk for PH and RVF.
Survey responses evaluating pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular failure in patients with BPD
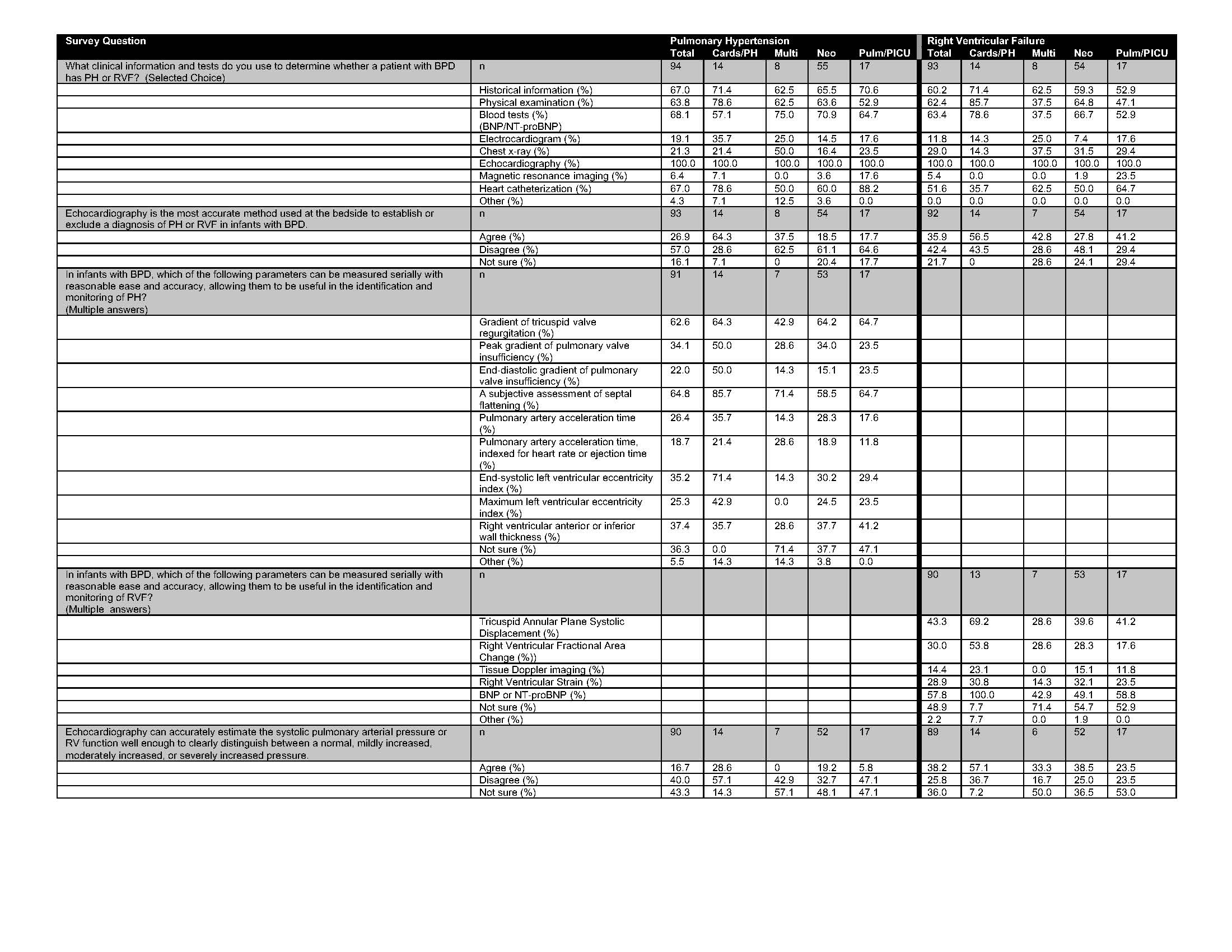 Multiple-choice responses to questions evaluating pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular failure in infants with BPD are shown. The total number of respondents (n) is listed in the top row (gray) and percentage by subspeciality is shown below each question.
Multiple-choice responses to questions evaluating pulmonary hypertension and right ventricular failure in infants with BPD are shown. The total number of respondents (n) is listed in the top row (gray) and percentage by subspeciality is shown below each question.Echocardiographic parameters of PH and management
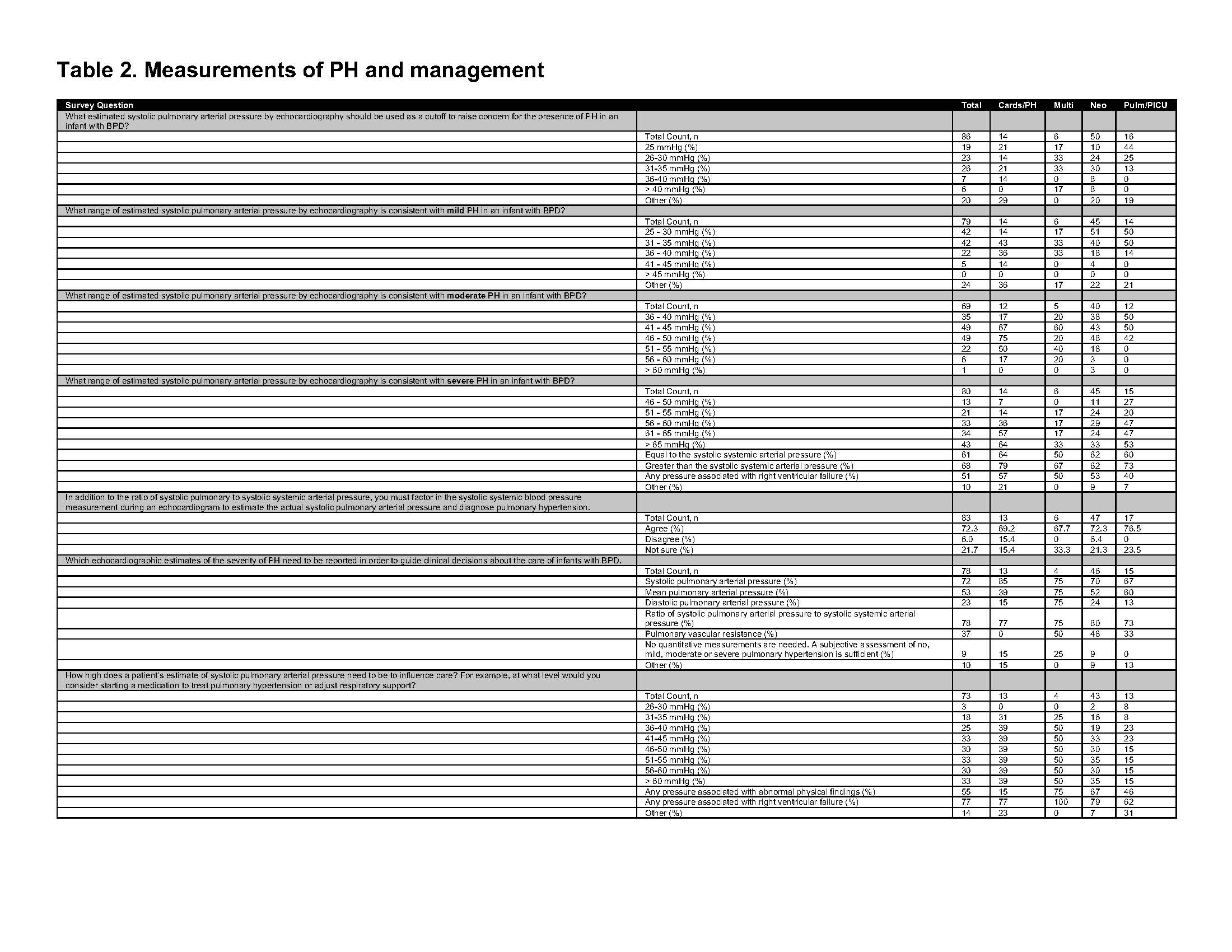 Multiple-choice responses for questions evaluating thresholds for echocardiographic parameters for the diagnosis and treatment of PH and RVF are shown. The total number of respondents (n) are shown in the top row (in gray), and the percentage of respondents by sub-specialty are shown below each question.
Multiple-choice responses for questions evaluating thresholds for echocardiographic parameters for the diagnosis and treatment of PH and RVF are shown. The total number of respondents (n) are shown in the top row (in gray), and the percentage of respondents by sub-specialty are shown below each question.Thematic Analyses of Open-Ended Questions
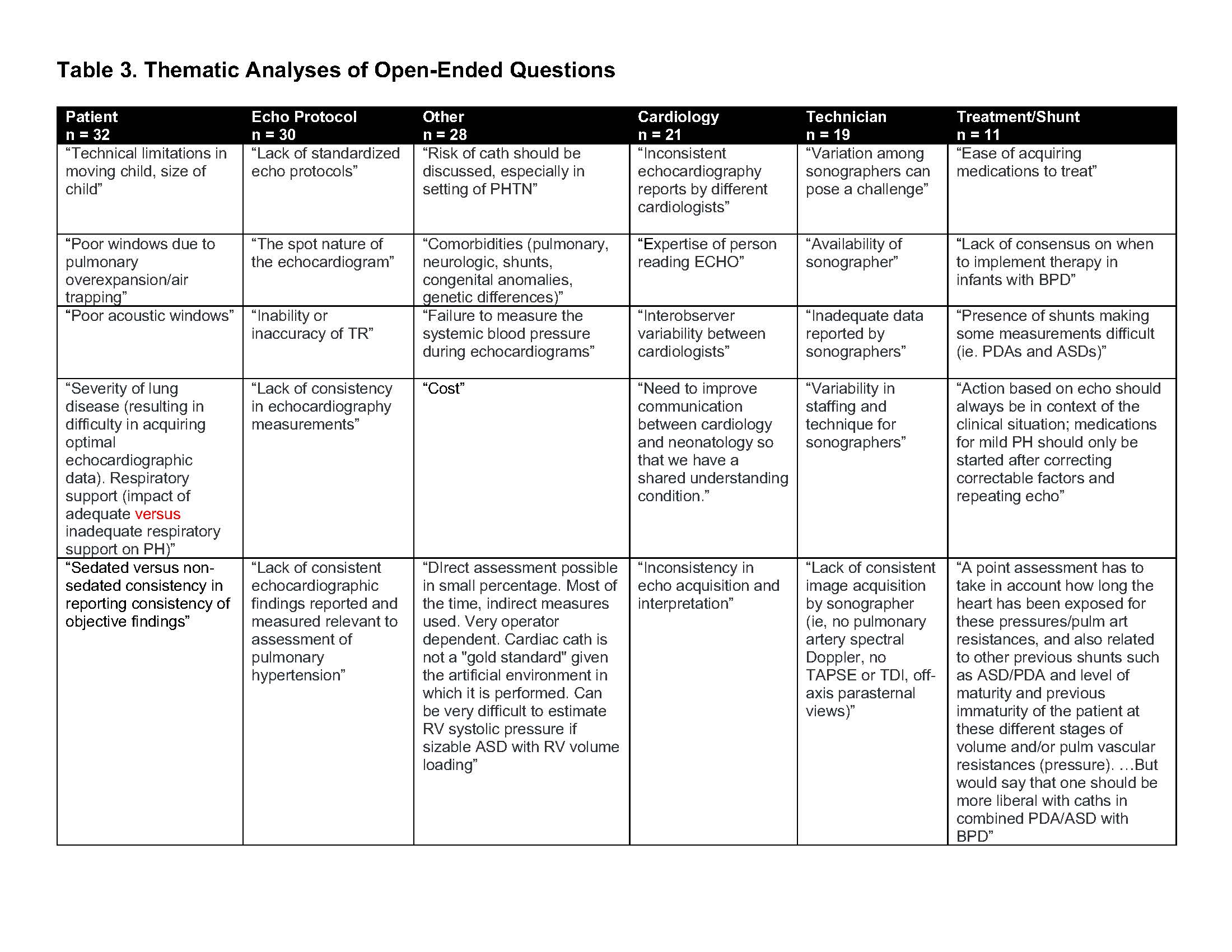 Shown are representative quotations for the six major themes identified through open-ended questions. The total number of responses per theme is indicated in the black heading (n).
Shown are representative quotations for the six major themes identified through open-ended questions. The total number of responses per theme is indicated in the black heading (n).
