Emergency Medicine 4
Session: Emergency Medicine 4
245 - Demographic Factors Leading to Disparities in Sexually Transmitted Infection Screening, Testing, and Treatment in the Pediatric Emergency Department
Saturday, April 26, 2025
2:30pm - 4:45pm HST
Publication Number: 245.4101
Elizabeth W. Perry, University of Texas Southwestern Medical School, Carrollton, TX, United States; Nakia N. Gaines, University of Texas Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, TX, United States; Jo-Ann O. Nesiama, University of Texas Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, TX, United States; Joan Reisch, University of Texas Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, TX, United States; Sing-Yi Feng, UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, United States
- EP
Elizabeth W. Perry, MD (she/her/hers)
Pediatric Emergency Medicine Fellow
University of Texas Southwestern Medical School
Carrollton, Texas, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are prevalent in adolescents. Obtaining a sexual history in the pediatric emergency department (PED) can improve STI screening however is difficult due to time constraints, agreeability and confidentiality concerns, and cost of testing and treatment. Previous studies have evaluated factors resulting in varying rates of STI screening but there have been no studies reviewing rates of STI screening based on language spoken.
Objective: To compare rates of STI screening based on age, sex, race, ethnicity, language spoken, and patient acuity in adolescent patients presenting to a large volume PED
Design/Methods: Retrospective chart review of adolescent patient encounters between 5/2022-4/2023. Age, sex, race, ethnicity, language spoken, and patient acuity were analyzed. Patients who were non-verbal due to medical condition or presenting complaint and patients presenting for trauma or emergent acuity were excluded.
Results: Of 10,130 patients, 16.9% had a sexual history documented. 30.96% of patients with a sexual history documented were tested for STIs (17.26% treated). 63.39% of patients with positive sexual history were tested for STIs (36.29% treated). 9.93% of females were screened for STIs compared to 4.78% of males; more females were treated for STIs compared to males (7% vs. 5.9%, p< 0.001). Older adolescents were more likely to be tested and treated for STIs (p < 0.001). Patients with unknown race were more often tested (25%) and treated (12.5%) than other races (p < 0.001). There was no significant difference in testing between non-Hispanic Whites and Hispanic patients, however non-Hispanic White patients were more likely to be treated than Hispanic patients (9.01% vs. 7%, p< 0.001). Acuity was directly proportional with STI testing and treatment (p < 0.001). STI testing was more frequent in English speaking patients (8.34% vs. 6.57%) but treatment rates did not differ between English and Spanish speaking patients (6.82% vs. 5.89%, p< 0.001). There was no significant difference in sexual history documentation, STI testing, or treatment based on use of a language interpreter.
Conclusion(s): This large retrospective study demonstrates a low rate of STI screening in the PED, consistent with previous studies. The documentation of a sexual history results in an increased likelihood of STI screening. In our language resource rich institution, there was no significant difference in sexual history documentation or STI screening between racial groups, ethnic groups, or preferred language, however this may not be true in PEDs without ready access to language interpreters.
Screening Rates for STIs by Demographic and Clinical Variables
.png) This table summarizes the number and percentage of individuals screened for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) compared to those not screened, segmented by age, gender, race, ethnicity, emergency severity index (ESI) level, sexual history documentation, sexual activity documentation, use of language interpreters, and language spoken. Statistical significance is indicated with p-values for each category.
This table summarizes the number and percentage of individuals screened for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) compared to those not screened, segmented by age, gender, race, ethnicity, emergency severity index (ESI) level, sexual history documentation, sexual activity documentation, use of language interpreters, and language spoken. Statistical significance is indicated with p-values for each category.Antibiotic Prescription Rates by Demographic and Clinical Variables
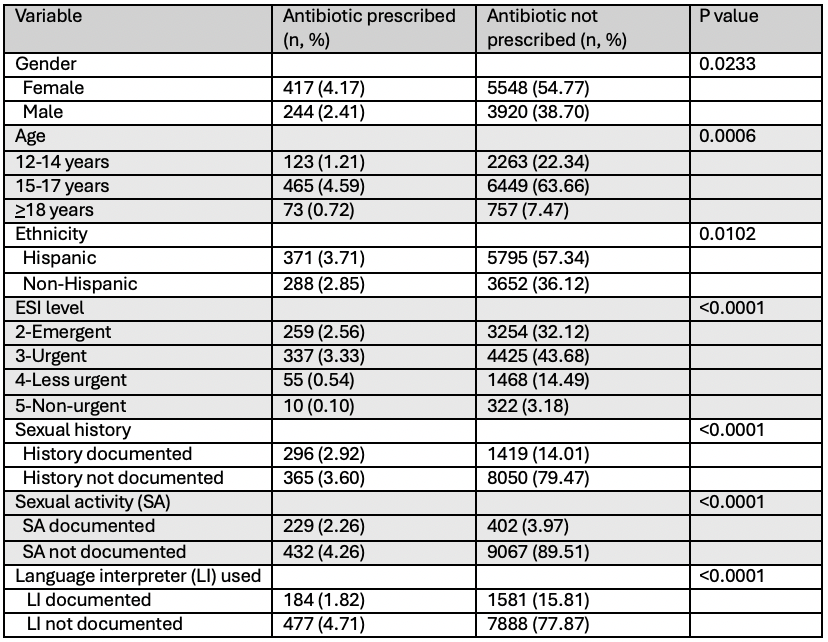 This table outlines the frequency and percentage of patients prescribed antibiotics versus those not prescribed, categorized by gender, age, ethnicity, emergency severity index (ESI) level, documentation of sexual history, sexual activity status, and use of language interpreters. Statistical significance is indicated with p-values for each category.
This table outlines the frequency and percentage of patients prescribed antibiotics versus those not prescribed, categorized by gender, age, ethnicity, emergency severity index (ESI) level, documentation of sexual history, sexual activity status, and use of language interpreters. Statistical significance is indicated with p-values for each category.Language Access Documentation and Its Impact on STI Screening and Antibiotic Prescription
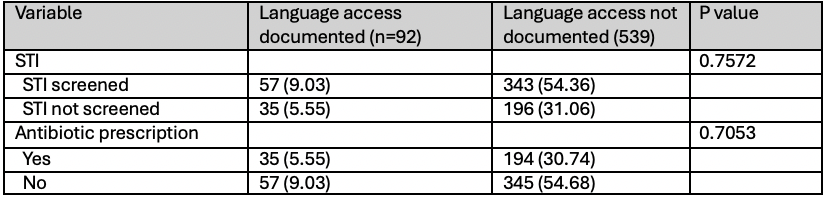 This table compares the number and percentage of patients with documented language access versus those without, focusing on STI screening and antibiotic prescription outcomes. P-values indicate the statistical significance of differences between the two groups regarding screening and prescription rates.
This table compares the number and percentage of patients with documented language access versus those without, focusing on STI screening and antibiotic prescription outcomes. P-values indicate the statistical significance of differences between the two groups regarding screening and prescription rates.Screening Rates for STIs by Demographic and Clinical Variables
.png) This table summarizes the number and percentage of individuals screened for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) compared to those not screened, segmented by age, gender, race, ethnicity, emergency severity index (ESI) level, sexual history documentation, sexual activity documentation, use of language interpreters, and language spoken. Statistical significance is indicated with p-values for each category.
This table summarizes the number and percentage of individuals screened for sexually transmitted infections (STIs) compared to those not screened, segmented by age, gender, race, ethnicity, emergency severity index (ESI) level, sexual history documentation, sexual activity documentation, use of language interpreters, and language spoken. Statistical significance is indicated with p-values for each category.Antibiotic Prescription Rates by Demographic and Clinical Variables
 This table outlines the frequency and percentage of patients prescribed antibiotics versus those not prescribed, categorized by gender, age, ethnicity, emergency severity index (ESI) level, documentation of sexual history, sexual activity status, and use of language interpreters. Statistical significance is indicated with p-values for each category.
This table outlines the frequency and percentage of patients prescribed antibiotics versus those not prescribed, categorized by gender, age, ethnicity, emergency severity index (ESI) level, documentation of sexual history, sexual activity status, and use of language interpreters. Statistical significance is indicated with p-values for each category.Language Access Documentation and Its Impact on STI Screening and Antibiotic Prescription
 This table compares the number and percentage of patients with documented language access versus those without, focusing on STI screening and antibiotic prescription outcomes. P-values indicate the statistical significance of differences between the two groups regarding screening and prescription rates.
This table compares the number and percentage of patients with documented language access versus those without, focusing on STI screening and antibiotic prescription outcomes. P-values indicate the statistical significance of differences between the two groups regarding screening and prescription rates.
