Neonatal GI Physiology & NEC 2
Session: Neonatal GI Physiology & NEC 2
722 - Early Total Enteral Feeding (ETEF) versus Conventional Enteral Feeding (CEF) in neonates with birth weight of 750-1250 grams: A Randomized Control Trial
Saturday, April 26, 2025
2:30pm - 4:45pm HST
Publication Number: 722.5088
Sushma Nangia, Lady Hardinge Medical College & Kalawati Saran Children's Hospital, New Delhi, Delhi, India; Kiran Kumar, Lady Hardinge Medical College & Kalawati Saran Childrens Hospital, New Delhi, Delhi, India; Tapas Bandyopadhyay, ABVIMS & Dr. RML Hospital, New Delhi, Delhi, India; Pratima anand, Lady hardinge medical, New Delhi, Delhi, India
- SN
Sushma Nangia, MD, DM (she/her/hers)
Professor
Lady Hardinge Medical College & Kalawati Saran Children's Hospital
New Delhi, Delhi, India
Presenting Author(s)
Background: India accounts for the highest number of preterm births and nutrition is a critical component of their overall management. Uncertainty exists regarding their feeding policy especially on regards to early total enteral feeding (ETEF) use in neonates with birth weight of 750-1250 grams.
Objective: To compare the time of attainment of full enteral feeds and other clinical outcomes in preterm neonates with birth weight of 750-1250 grams receiving ETEF versus conventional enteral feeding (CEF).
Design/Methods: One hundred and twenty-eight preterm neonates with birth weight of 750-1250 grams were randomized to ETEF or CEF group at 2 hour of life. In ETEF group, feeding was initiated on day 1 with 80 ml/kg/day enteral feeds and was advanced by 20 ml/kg/day till full enteral feed of 150 ml/kg/day was reached and sustained for 24 hours. In CEF group, feeding was initiated with 20 ml/kg of enteral feeds on day one and advanced as per pre-defined protocol, till full enteral feed of 150mL/kg was reached and sustained for 24 hours.
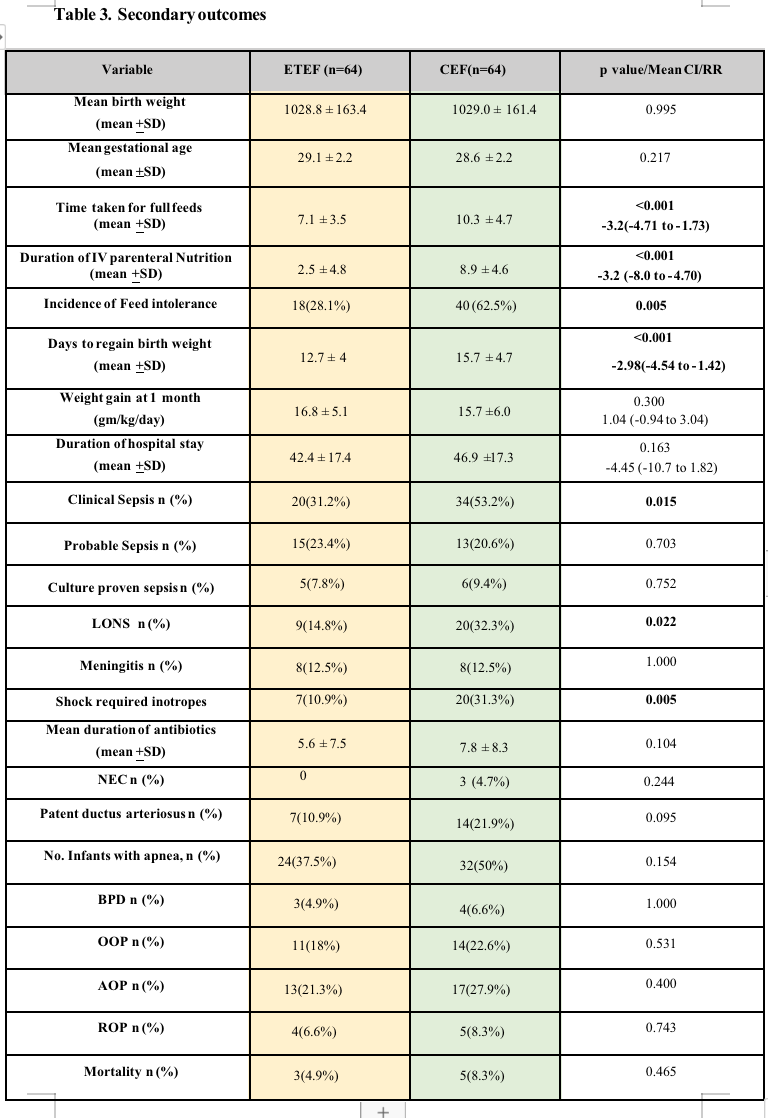
Results: Mean birth weight (grams) and gestation (weeks) of the 128 enrolled neonates was 1028.8 ± 163 and 1029.0 ± 161, and 29.1 ± 2.2 & 28.6 ± 2.2 in ETEF and CEF groups respectively(Table-1). Neonates in ETEF group reached full enteral feeds 3.2 days earlier (mean/SD) (7.1 ± 3.5 days), than in the CEF group (10.3 ± 4.7 days) which was statistically significant (95% CI - 4.71 to -1.73) (p < 0.001). (Table-2)
Feed intolerance was higher in CEF group (62.5 % vs. 28.1% - p 0.005). NEC occurred only in the CEF group and late onset sepsis was higher in CEF group (32% vs.14.8%). Neonates in the ETEF group regained birth weight 3 days earlier and the mean duration of hospital stay (days) were 4 days shorter (42.9 ±17.4 vs. 46.9 ± 17.3). BPD,ROP and AOP were similar in both the groups.Incidence of PDA (21.9% vs 10.9 %) and mortality were higher in CEF arm (7.8% vs 4.7%;RR 0.60(0.15-2.40).(Table-3)
Conclusion(s): Early total enteral feeding in sick preterm neonates with birth weight of 750-1250 grams leads to early attainment of full feeds, earlier regaining of birth weight, shorter hospital stay and reduced incidence of PDA, without increase in incidence of NEC, feed intolerance, sepsis and mortality.
Baseline Characteristics
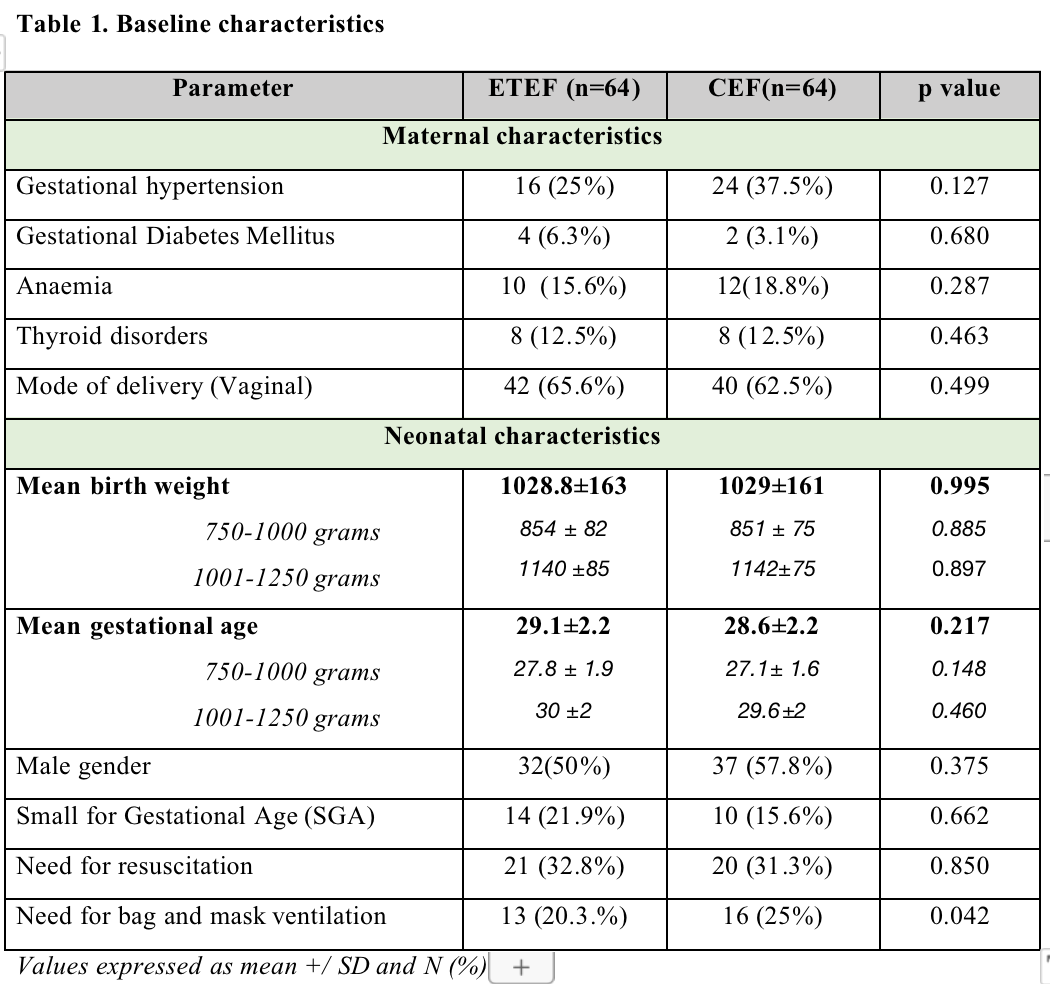
Primary Outcome
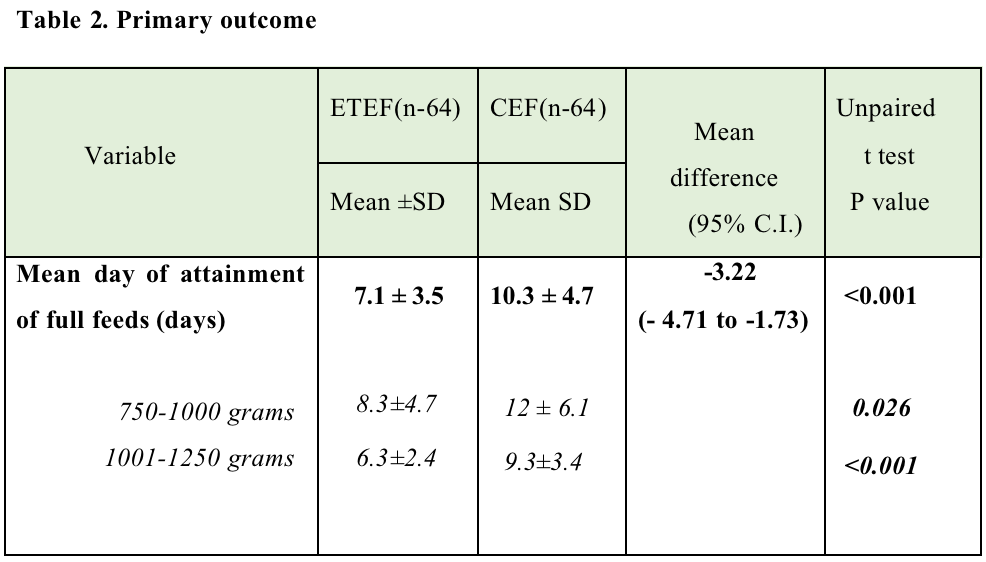
Secondary outcome