Neonatal General 8: Growth, Nutrition and Feeding
Session: Neonatal General 8: Growth, Nutrition and Feeding
685 - Decrease in Arginine level in preterm infants after discontinuation of TPN
Saturday, April 26, 2025
2:30pm - 4:45pm HST
Publication Number: 685.4551
Zainab Manan, University of Texas Medical Branch School of Medicine, Galveston, TX, United States; Ashraf Aly, Utmb, Galveston, TX, United States; Sunil Jain, University of Texas Medical Branch School of Medicine, Galveston, TX, United States
- SJ
Sunil Jain, MD (he/him/his)
University of Texas Medical Branch School of Medicine
Galveston, Texas, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Arginine (ARG) is the precursor for synthesizing nitric oxide (NO) by NO synthase. Endothelial NO is an anti-inflammatory chemical mediator involved in mucosal integrity, blood flow, intestinal barrier function, and is a pulmonary vasodilator. Preterm infants (PI) are prone to NEC, BPD, and BPD-associated pulmonary hypertension, which could be due to low ARG levels in PI.
Objective: Assess the serum ARG level in PI and the ARG level in preterm breast milk, as this is the primary source of ARG once the infant is no longer receiving TPN.
Design/Methods: In an observational prospective pilot study, we collected blood samples from 18 PI ( < 30 weeks gestation & < 1000 g) on days 1, 3, 7, 14, and 21. All infants were started on TPN on day 1 which was slowly weaned, and enteral feeds (donor or mothers’ own milk) was increased as tolerated. On day 14, all infants were off TPN and were on full enteral feeds. We collected breast milk from mothers with preterm infants. ARG levels were measured by chromatography-mass spectrometry. Data was analyzed by SPSS 21, and mean ARG levels in blood were compared, and p < 0.05 was significant.
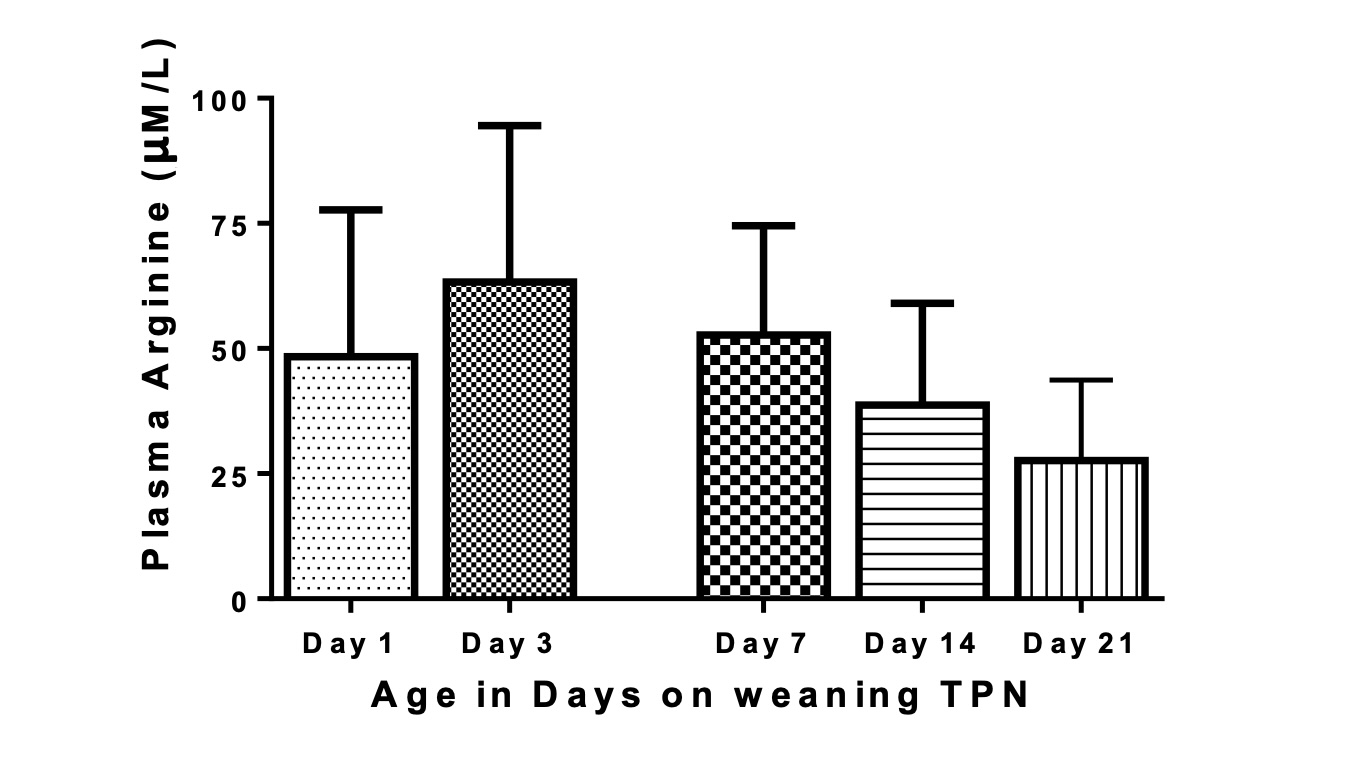
Results: Initially, on day 3, ARG levels increased as infants were almost 100% on TPN. However, ARG levels continued to decrease as enteral feeds were increasing and TPN was decreasing. Arg levels on day 14 (infants were on full enteral feeds) and 21 were significantly lower compared to day 3 (63+5 v/s 38.7+ 4.2µmol/L p < 0.001 and 63 +5 v/s 27 + 3.0µmol/L p < 0.0001 Figure). Breast milk ARG measurements are currently being done.
Conclusion(s): On day 3 ARG levels increased as TPN was the main source of ARG in PI. As the TPN intake went down and breast milk intake increased, ARG levels significantly decreased as seen on day 14 and 21. Breast milk may not be the best source of ARG in PI. This needs to be confirmed. Our data highlights the need for a study on ARG supplementation and neonatal outcomes, particularly NEC, BPD and BPD associated pulmonary hypertension in PI.
Figure 1