Neonatal Infectious Diseases/Immunology 4: Immunity in early life
Session: Neonatal Infectious Diseases/Immunology 4: Immunity in early life
064 - Defining Patterns of Lung Injury and Repair Following Perinatal Influenza Virus Infection
Sunday, April 27, 2025
8:30am - 10:45am HST
Publication Number: 64.4106
Jonathan Knowlton, Childrens Hospital of Philadelphia, PHILADELPHIA, PA, United States; Subham Basu, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States; Yun Ying, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States; Edward Morrisey, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA, United States

Jonathan Knowlton, MD PhD (he/him/his)
Neonatology Fellow
Childrens Hospital of Philadelphia
PHILADELPHIA, Pennsylvania, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Viral respiratory infections early in life are associated with significant pediatric morbidity and mortality and have long-term consequences for lung health into adulthood. Despite pediatric respiratory infections being the leading cause of childhood hospitalization, little is known about the injury and repair mechanisms that operate in the lung following illness.
Objective: The primary objective of this study was to define the patterns of lung injury and repair using a neonatal mouse model of influenza virus lower respiratory tract infection.
Design/Methods: Neonatal (p2) CD-1 mice were intranasally inoculated with influenza A virus (H1N1) strain A/PR/8/34 or phosphate-buffered saline under isoflurane anesthesia at various TCID50. Following inoculation, pups were weighed daily and assessed clinically for signs of respiratory distress. Pups were sacrificed if they were moribund, displayed severe respiratory distress, or experienced weight loss. Kaplan-Meier curves were plotted to quantify survival trajectories following infection. Vital signs were monitored using the MouseOX pulse oximeter 7 days post-infection (dpi) to measure heart rate, oxygen saturation, and respiratory rate. To define histological injury patterns, lungs were harvested at various dpi and processed for H&E staining or immunohistochemistry. All statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism software.
Results: Influenza virus infection of neonatal mice was associated with significant mortality at all TCID50 tested (p < 0.0001; log-rank test). Compared to control pups, influenza-infected mice exhibited tachypnea, increased work of breathing, and stagnation in weight gain that reached statistical significance at 6 and 7 dpi (p < 0.05; unpaired t-test). Pulse oximetry of pups with clinical signs of respiratory distress at 7 dpi showed significant hypoxemia compared to controls (mean SpO2 51%, SD 14 vs 99%, SD 1; p < 0.05; unpaired t-test). Histology at 3-5 days post-infection revealed heterogeneous injury patterns, with disparate areas of cellular infiltration, interstitial inflammation, and alveolar simplification. Histology done at 28 dpi showed a resolution of significant cellular infiltration but the persistence of diffuse emphysematous changes in the lung.
Conclusion(s): Neonatal mice develop severe lower respiratory tract disease following influenza virus infection, which is associated with significant architectural changes in the lung. Pathologic histological changes following neonatal influenza infection persist into adulthood, indicating that early-life respiratory tract infections cause long-term damage.
Influenza virus infection causes significant morbidity and mortality in neonatal mice
.png) A) Weight change as a percentage of birth weight for individual mice inoculated with either PBS (mock; black lines) or 0.1 TCID50 of influenza virus (red lines). B) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for neonatal mice inoculated with either PBS (mock) or the indicated TCID50 of influenza virus.
A) Weight change as a percentage of birth weight for individual mice inoculated with either PBS (mock; black lines) or 0.1 TCID50 of influenza virus (red lines). B) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for neonatal mice inoculated with either PBS (mock) or the indicated TCID50 of influenza virus. Influenza virus infection causes hypoxemic respiratory failure in neonatal mice
.png) Continuous pulse oximetry (30 sec) of mice seven days post-inoculation with either PBS (mock; n = 3; shades of orange) or 0.1 TCID50 of influenza virus (n = 3; shade of blue).
Continuous pulse oximetry (30 sec) of mice seven days post-inoculation with either PBS (mock; n = 3; shades of orange) or 0.1 TCID50 of influenza virus (n = 3; shade of blue).Influenza virus infection causes profound architectural damage to the neonatal lung
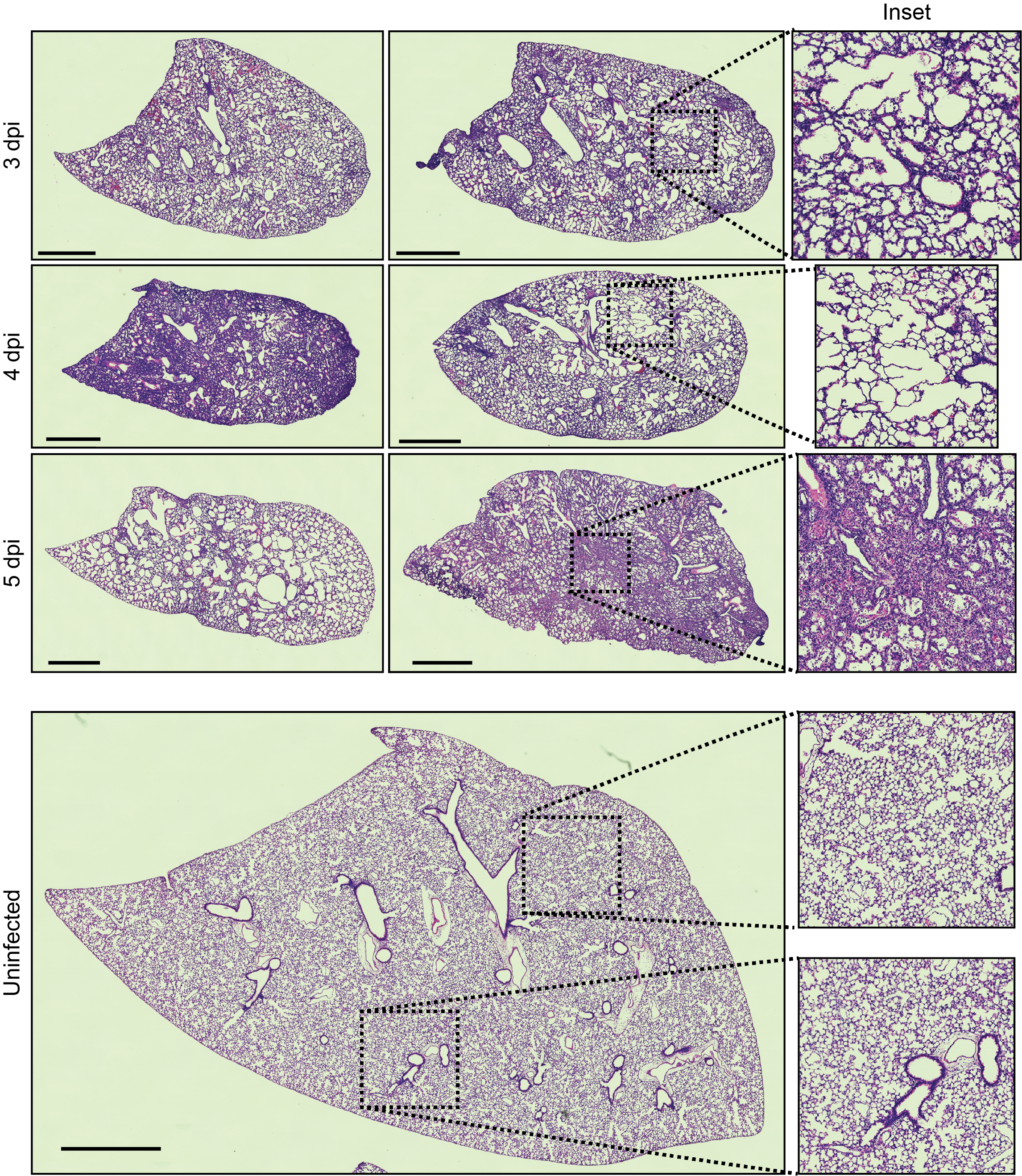 H&E staining of lung sections harvested from neonatal mice at 3-5 dpi (top three rows) or from a control uninfected mouse (bottom row) 14 days post sham (PBS) inoculation. Each H&E section is from a different mouse. Insets on the far right are magnified views representing one square millimeter of tissue area. All scale bars correspond to 1mm.
H&E staining of lung sections harvested from neonatal mice at 3-5 dpi (top three rows) or from a control uninfected mouse (bottom row) 14 days post sham (PBS) inoculation. Each H&E section is from a different mouse. Insets on the far right are magnified views representing one square millimeter of tissue area. All scale bars correspond to 1mm. Influenza virus infection causes significant morbidity and mortality in neonatal mice
.png) A) Weight change as a percentage of birth weight for individual mice inoculated with either PBS (mock; black lines) or 0.1 TCID50 of influenza virus (red lines). B) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for neonatal mice inoculated with either PBS (mock) or the indicated TCID50 of influenza virus.
A) Weight change as a percentage of birth weight for individual mice inoculated with either PBS (mock; black lines) or 0.1 TCID50 of influenza virus (red lines). B) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for neonatal mice inoculated with either PBS (mock) or the indicated TCID50 of influenza virus. Influenza virus infection causes hypoxemic respiratory failure in neonatal mice
.png) Continuous pulse oximetry (30 sec) of mice seven days post-inoculation with either PBS (mock; n = 3; shades of orange) or 0.1 TCID50 of influenza virus (n = 3; shade of blue).
Continuous pulse oximetry (30 sec) of mice seven days post-inoculation with either PBS (mock; n = 3; shades of orange) or 0.1 TCID50 of influenza virus (n = 3; shade of blue).Influenza virus infection causes profound architectural damage to the neonatal lung
 H&E staining of lung sections harvested from neonatal mice at 3-5 dpi (top three rows) or from a control uninfected mouse (bottom row) 14 days post sham (PBS) inoculation. Each H&E section is from a different mouse. Insets on the far right are magnified views representing one square millimeter of tissue area. All scale bars correspond to 1mm.
H&E staining of lung sections harvested from neonatal mice at 3-5 dpi (top three rows) or from a control uninfected mouse (bottom row) 14 days post sham (PBS) inoculation. Each H&E section is from a different mouse. Insets on the far right are magnified views representing one square millimeter of tissue area. All scale bars correspond to 1mm. 
