Gastroenterology/Hepatology
Session: Gastroenterology/Hepatology
324 - Decreasing Trends in Gastroschisis Across US Regions: The Impact of Smoking
Sunday, April 27, 2025
8:30am - 10:45am HST
Publication Number: 324.4488
Erwin T. Cabacungan, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, United States; Jennifer Schuh, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, United States; Amy J. Wagner, Medical College of Wisconsin, Milwaukee, WI, United States

Jennifer M. Schuh, MD
Research Resident
Medical College of Wisconsin
Milwaukee, Wisconsin, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Gastroschisis (GS) is a common congenital anomaly of the abdominal wall. Despite being linked to several environmental and genetic factors, it still lacks conclusive evidence of its etiology. Smoking during the preconception period, one of the most modifiable risk factors for adverse neonatal outcomes is associated with an increased risk for GS. We hypothesize that with evidenced-based strategies to reduce smoking, particularly among pregnant people, GS prevalence continues to decrease across US regions.
Objective: To determine and compare the yearly regional GS prevalence and its risk factor, smoking, using a national database
Design/Methods: This is a US population-based retrospective cohort study of live births with GS using the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Wide Ranging Online Data for Epidemiologic Research (CDC WONDER) from 2016 to 2023. We compared the four US census regions: Northeast (NE), Midwest (MW), South (S), and West (W). Linear regression compared yearly prevalence, maternal age (MA), race and ethnicity, and tobacco use over time. Population attributable risk (PAR) was calculated to estimate the proportion of GS that could be prevented by eliminating smoking.
Results: The CDC WONDER database, which included 92 million live births, showed a decreasing trend of GS across all four US regions and nationwide, Fig.1. A decreasing trend of GS by maternal age was observed across regions: NE (MA 15-19 and 20-24 years), MW (20-24 and 25-29 years), S (25-29 years) and W (30-34 years), Table 1A. Also, a decreasing trend was observed among the White population across all four regions and the W Hispanic population, Table 1B. Although tobacco use during pregnancy decreased across all four regions, only MW and S showed reduced tobacco use among mothers of GS infants, Figures 2A-2D. PAR trends for tobacco use showed significant declines in the NE (5.5% to 2.5%), MW (6.8% to 2.6%), and S (4.1% to 1.5%).
Conclusion(s): This study shows decreasing GS rates across the US regions and among certain maternal age groups and the white population. As indicated by PAR trends, the decline in tobacco use’s impact on GS underscores the effectiveness of public health measures. Targeted public health efforts must continue to sustain and further enhance progress, particularly in the W.
Figure 1: Decreasing Prevalence of Gastroschisis per 10,000 Births by US Census Regions and Nationwide, 2016 to 2023
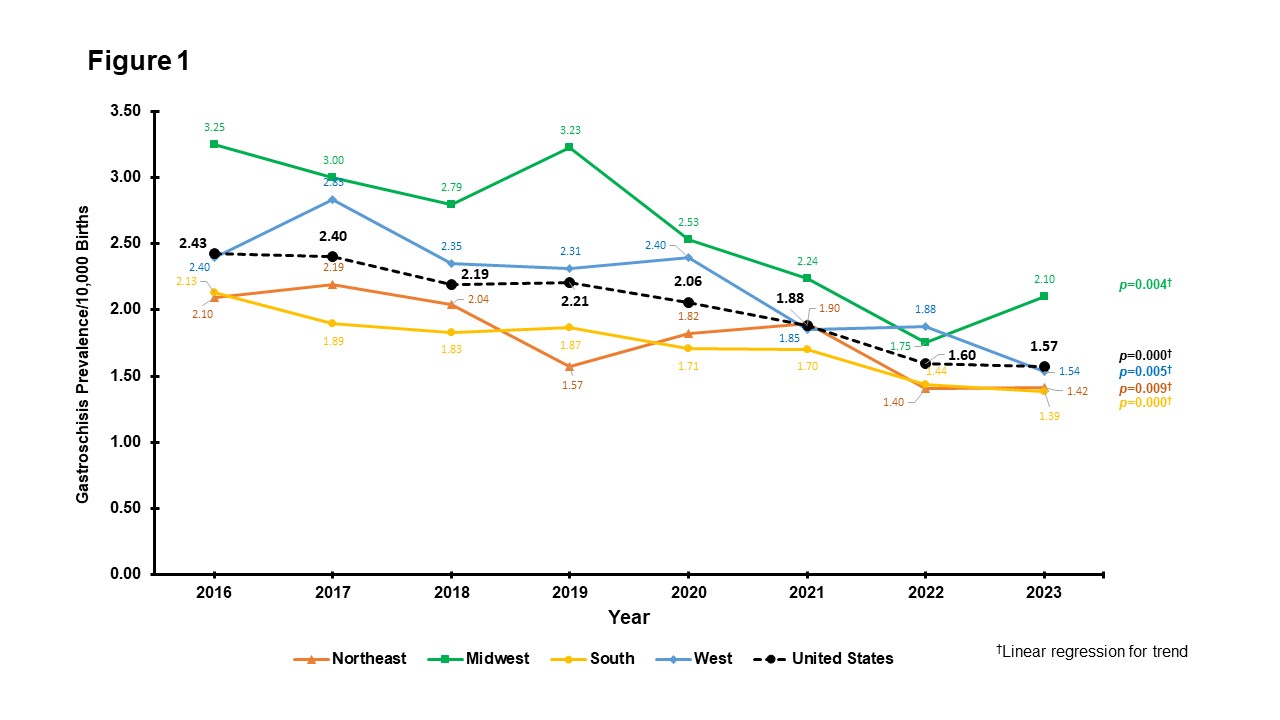 Linear regression coefficient (95% CI) for the decrease in gastroschisis prevalence: Northeast(NE), -1.1 (-1.17 - -0.04), p=0.009; Midwest(MW), -0.20 (-0.30 - -0.09), p=0.004; South(S), -0.10 (-0.12 - -0.07), p=0.000; West(W), -0.15 (0.23 - -0.06), p=0.005; and Nationwide(U.S.), -0.13 (-0.16 - -0.10), p=0.000.
Linear regression coefficient (95% CI) for the decrease in gastroschisis prevalence: Northeast(NE), -1.1 (-1.17 - -0.04), p=0.009; Midwest(MW), -0.20 (-0.30 - -0.09), p=0.004; South(S), -0.10 (-0.12 - -0.07), p=0.000; West(W), -0.15 (0.23 - -0.06), p=0.005; and Nationwide(U.S.), -0.13 (-0.16 - -0.10), p=0.000.Table 1A&B: Trends in Maternal Age and Race/Ethnicity by US Census Regions Among Mothers of Infants with Gastroschisis, 2016 to 2023 (Expressed as Per 10,000 births)
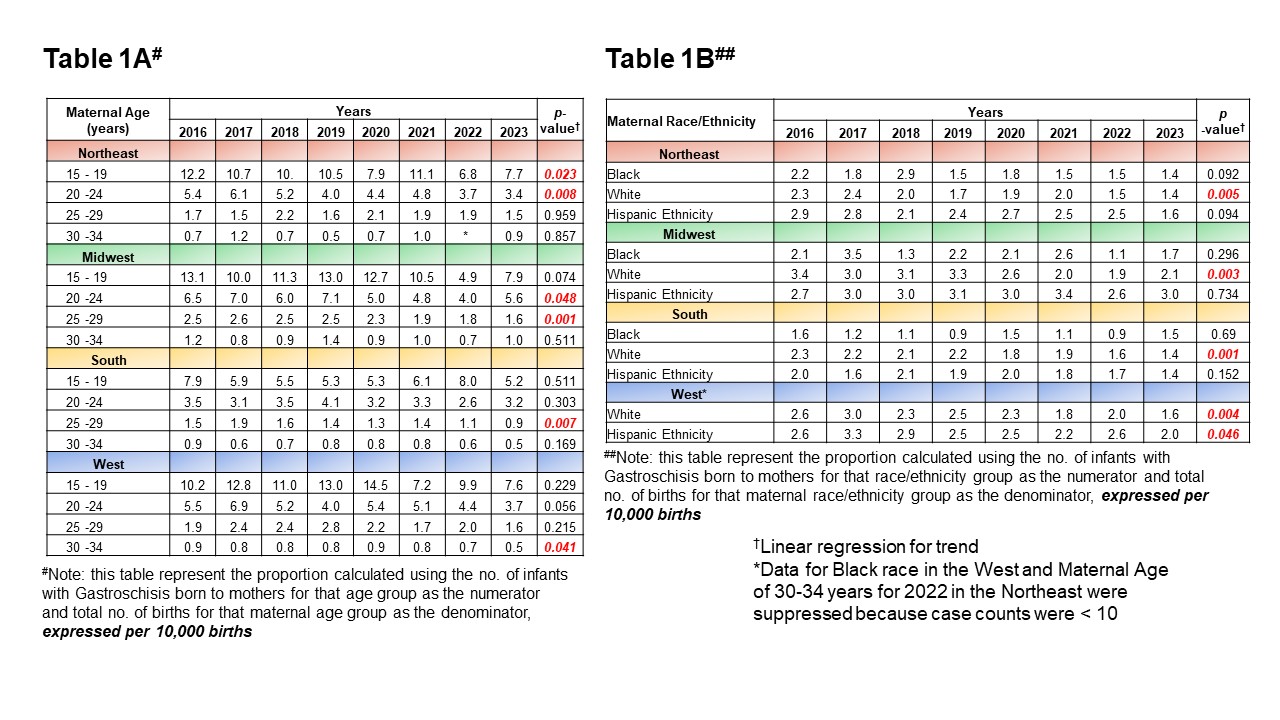 Table 1A. In the eight-year analysis, the Northeast(NE) showed a significant decrease in the proportion of gastroschisis infants among mothers aged 15-19 (p=0.023) and 20-24 (p=0.008), the Midwest(MW) among mothers aged 20-24 (p=0.048) and 25-29 (p=0.001), the South(S) among mothers aged 25-29 (p=0.007), and West(W) among mothers aged 30-34 (p=0.041). Table 1B. In the eight-year analysis, all four census regions demonstrated a significant decrease in the proportion of gastroschisis infants among the White maternal population [Northeast(NE), p=0.005; Midwest(MW), p=0.003); South(S), p=0.001, and West(W), p=0.004]. Additionally, a significant decrease was observed in the proportion of gastroschisis infants born to the Hispanic maternal population in the West(W, p=0.046).
Table 1A. In the eight-year analysis, the Northeast(NE) showed a significant decrease in the proportion of gastroschisis infants among mothers aged 15-19 (p=0.023) and 20-24 (p=0.008), the Midwest(MW) among mothers aged 20-24 (p=0.048) and 25-29 (p=0.001), the South(S) among mothers aged 25-29 (p=0.007), and West(W) among mothers aged 30-34 (p=0.041). Table 1B. In the eight-year analysis, all four census regions demonstrated a significant decrease in the proportion of gastroschisis infants among the White maternal population [Northeast(NE), p=0.005; Midwest(MW), p=0.003); South(S), p=0.001, and West(W), p=0.004]. Additionally, a significant decrease was observed in the proportion of gastroschisis infants born to the Hispanic maternal population in the West(W, p=0.046).Figures 2A-2D: Proportion of Maternal Tobacco Use During Pregnancy Among Gastroschisis Infants and All Births by US Census Regions [NE, Fig.2A; MW, Fig.2; S, Fig.2C; and West(W), Fig.2D], 2016 to 2023, Expressed as Percentages. Table 2: Trends in Population Attributable Risk (PAR) of Tobacco Use in the Context of Gastroschisis by US Census Regions, 2016 to 2023, Expressed as Percentages.
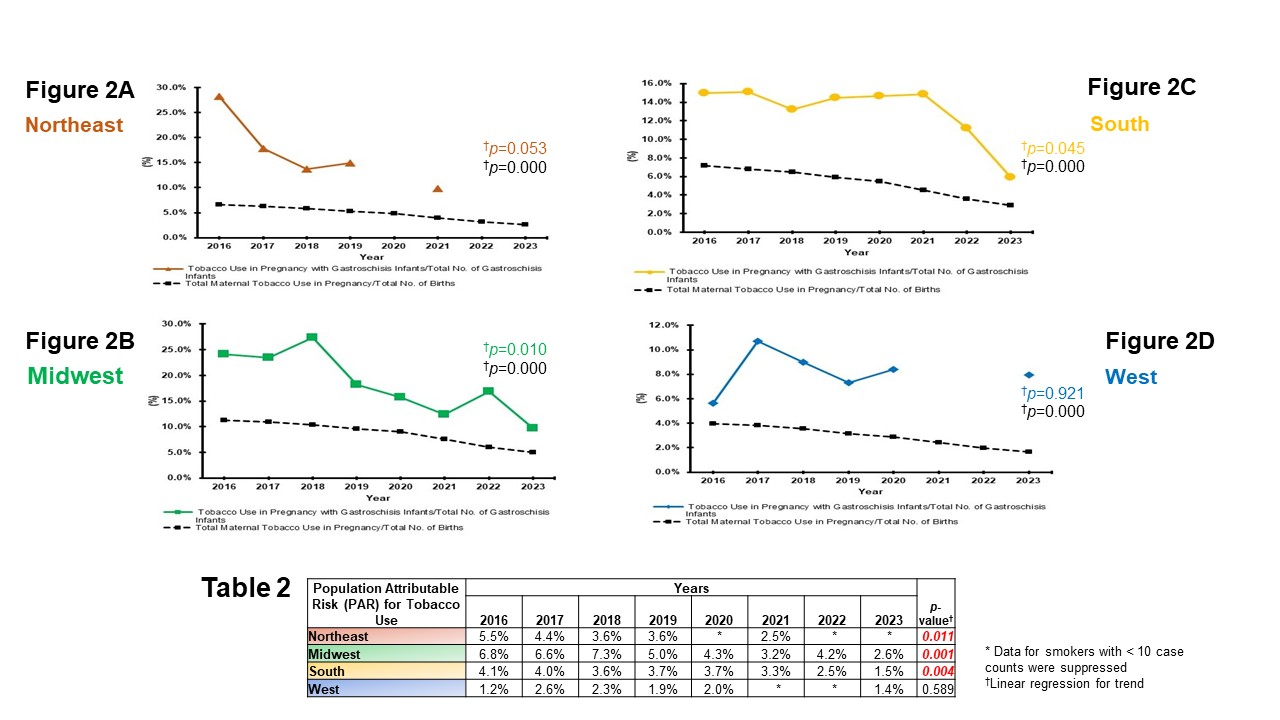 Figures 2A-2D: Each figure depicts trends in the proportion of maternal tobacco use during pregnancy in the context of Gastroschisis (proportion of tobacco use during pregnancy with gastroschisis infants/total number of gastroschisis infants) and the overall maternal tobacco use in pregnancy (proportion of total maternal tobacco use in pregnancy/total number of births) across the four U.S. Census regions. The proportion of overall maternal tobacco use showed a decreasing trend in all four regions, while the proportion specific to gastroschisis infants decreased only in the Midwest(MW), p=0.010 and South(S), p=0.045. Table 2: This table shows the eight-year trends in the Population Attributable Risk (PAR) of maternal tobacco use during pregnancy in relation to Gastroschisis across the four US census regions. The PAR showed a decreasing trend in the Northeast(NE, p=0.011), Midwest(MW, p=0.001), and South(S, p=0.004), while no significant decrease seen in the West(W).
Figures 2A-2D: Each figure depicts trends in the proportion of maternal tobacco use during pregnancy in the context of Gastroschisis (proportion of tobacco use during pregnancy with gastroschisis infants/total number of gastroschisis infants) and the overall maternal tobacco use in pregnancy (proportion of total maternal tobacco use in pregnancy/total number of births) across the four U.S. Census regions. The proportion of overall maternal tobacco use showed a decreasing trend in all four regions, while the proportion specific to gastroschisis infants decreased only in the Midwest(MW), p=0.010 and South(S), p=0.045. Table 2: This table shows the eight-year trends in the Population Attributable Risk (PAR) of maternal tobacco use during pregnancy in relation to Gastroschisis across the four US census regions. The PAR showed a decreasing trend in the Northeast(NE, p=0.011), Midwest(MW, p=0.001), and South(S, p=0.004), while no significant decrease seen in the West(W).
