Asthma 2
Session: Asthma 2
480 - Exploring the Relationship between ADHD, Autism, and Asthma Symptoms in a Pediatric Asthma Trial
Sunday, April 27, 2025
8:30am - 10:45am HST
Publication Number: 480.4769
Sonia Radu, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Uxbridge, MA, United States; Christine Frisard, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, United States; Sybil Crawford, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, United States; Melissa Goulding, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, United States; Grace W. Ryan, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA, United States; Michelle Spano, UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, MA, United States; Jeneva A. Smith, UMass Memorial Children's Medical Center, Shrewsbury, MA, United States; Milagros C.. Rosal, UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, MA, United States; Stephenie C. Lemon, UMass Chan Medical School, Worcester, MA, United States; Nancy Byatt, UMass Chan Medical School/UMass Memorial Health, Shrewsbury, MA, United States; Wanda Phipatanakul, Boston Children's Hospital, Hopkinton, MA, United States; Lynn B. Gerald, University of Illinois at Chicago, Chicago, IL, United States; sarabeth broder-fingert, UMASS Medical School, Worcester, MA, United States; Lori Pbert, University of Massachusetts Medical School, Harvard, MA, United States; Michelle Trivedi, UMass Chan, Worcester, MA, United States
- SR
Sonia Radu (she/her/hers)
Medical Student
UMass Chan Medical School, Massachusetts, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Asthma Link is an intervention of school-supervised inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) administration, wherein pediatric providers identify children with persistent/poorly controlled asthma and engage school nurses to initiate daily supervised administration of ICS. Pilot studies of Asthma Link versus enhanced usual care (receipt of asthma educational workbook) have demonstrated potential to improve ICS adherence and asthma symptoms. Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and autism spectrum disorder (ASD), the most common neurodevelopmental conditions, can influence daily ICS adherence and asthma outcomes due to sensory, behavioral, and executive function challenges. We hypothesized that children with ADHD/ASD in a pilot trial of Asthma Link may have different asthma control test (ACT) scores compared with children without these conditions.
Objective: To investigate whether baseline asthma symptoms differ among children with ADHD and/or ASD; and whether ACT scores are different over time for children with ADHD and/or ASD.
Design/Methods: We conducted a secondary analysis of data from a pilot trial of AL (n=66; 9 ADHD, 2 ASD, 2 both ADHD&ASD), including children aged 5-14 with persistent/poorly controlled asthma. (Table 1) ADHD and ASD diagnoses were obtained from medical record problem lists. Asthma symptoms were assessed using the ACT completed on parent/child surveys at baseline, 3, 6, and 12 months. Given few children with ADHD/ASD in each study condition, we combined conditions and performed linear regression analysis, accounting for repeated measurements by the same subject and including interaction terms of time and ADHD/ASD as well as study condition and time.
Results: Children with poorly controlled asthma who also had ADHD/ASD had higher baseline ACT scores than counterparts without these conditions. (Table 2, Figure 1) This trend did not persist at 3, 6, and 12-month timepoints. (Table 2) While our sample size was insufficient to detect a significant interaction, both groups showed improved ACT scores over time, indicating participation in both Asthma Link and EUC improved asthma control for both groups.
Conclusion(s): Asthma, ADHD and ASD are three of the most common chronic pediatric conditions, yet few studies examine the relationship between them. Higher baseline ACT scores for children with ADHD/ASD may be due to more frequent health visits for their neurodevelopmental conditions and warrants further study. These findings will inform future research and could support targeted asthma management for children with ADHD and ASD, who may otherwise struggle with poorly controlled asthma.
Table 1. Characteristics of the Asthma Link Pilot Trial Study Population
.png)
Table 2. ACT Scores Between Children With & Without ADHD/ASD At Each Study Timepoint
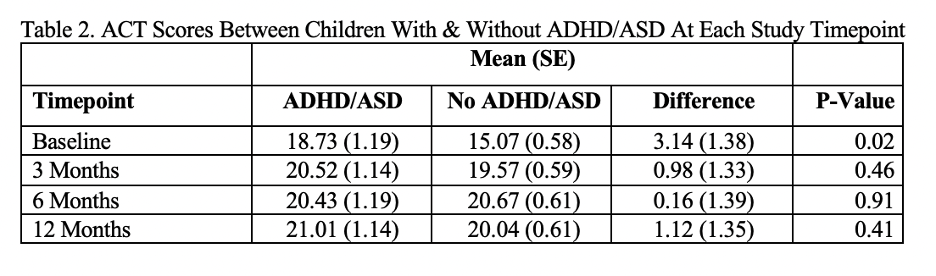
Figure 1. ACT Scores Over Time by ADHD/ASD Diagnosis
.png)

