Nephrology 3
Session: Nephrology 3
592 - Natural language processing (NLP) to structuralize free text data for quantifying childhood steroid sensitive nephrotic syndrome (SSNS) disease course variability
Sunday, April 27, 2025
8:30am - 10:45am HST
Publication Number: 592.5657
Arthur M. Lee, Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, United States; Rachel Sanderlin, Childrens Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, United States; Spandana Makeneni, Childrens Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, United States; Madhuri M. Vihani, Childrens Hospital of Philadelphia, Wilmington, DE, United States; Maryam Daniali, Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, Berkeley Heights, NJ, United States; Rebecca Scobell, Childrens Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, United States; Michelle Denburg, Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, United States

Arthur M. Lee, MD (he/him/his)
Nephrology Fellow, PGY-6
Children's Hospital of Philadelphia
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: : SSNS can have an unpredictable relapsing-remitting course over the first two decades of life. This longitudinal variability is challenging to capture in clinical research. We hypothesized that “acute relapse” and “entering remission” events are associated with communications patterns captured as electronic health record (EHR) unstructured free text data. NLP can convert unstructured free text data into structured data.
Objective: 1) Describe EHR communication patterns in childhood SSNS, 2) show the feasibility of and 3) develop an NLP pipeline to enable large-scale time-mapping of SSNS relapse-remission events to generate structured, real-world, clinical, disease course variability data.
Design/Methods: We created an NLP pipeline that included cohort identification, EHR free text extraction, training and validation dataset creation, clinician annotation, and a rule-based smart text search NLP algorithm (Figure 1).
Patients with SSNS at a single large children’s hospital were identified using queries from the Glomerular Learning Network (GLEAN) registry. Nephrology free text entries and clinical data from January 2022 – May 2024 were extracted from the EHR.
To show vocabulary associated with urinalysis results, LASSO penalized logistic regression was fit on a subset of participant-days with same-day urinalyses and text entries to assess if unique words associated with “3+” or “negative” urine protein.
Results: There were 217 participants with SSNS who had Nephrology EHR free text entries during the study period. 24 (11%) of participants were incident cases. Cohort demographic and disease history are shown in Table 1.
There were 494 patient-days with same-day urinalysis results. LASSO models were fit on 1796 text entries to identify “3+” urine protein (cross-validated [cv] λ=0.12, 201 words with non-zero coefficients, 160 unique to 3+ urine protein) and negative urine protein (cv λ=0.13, 128 words with non-zero coefficients, 87 unique to negative urine protein). Fit LASSO curves are shown in Figure 1.
Care utilization and communication characteristics are shown in Table 2.
Conclusion(s): We built an NLP pipeline to structuralize EHR unstructured free text data to generate structured SSNS disease course variability. We showed that communication patterns associated with same-day urinalysis results, demonstrating the feasibility of NLP for identifying relapse-remission events associated with communication patterns over time. This project’s next steps will be completing training and evaluation of the rules-based smart text search NLP model.
NLP pipeline
.jpg) Fit LASSO curves are shown as part of the NLP pipeline, showing the feasibility that NLP can detect relapse-remission events based on communication patterns.
Fit LASSO curves are shown as part of the NLP pipeline, showing the feasibility that NLP can detect relapse-remission events based on communication patterns.Participant characteristics
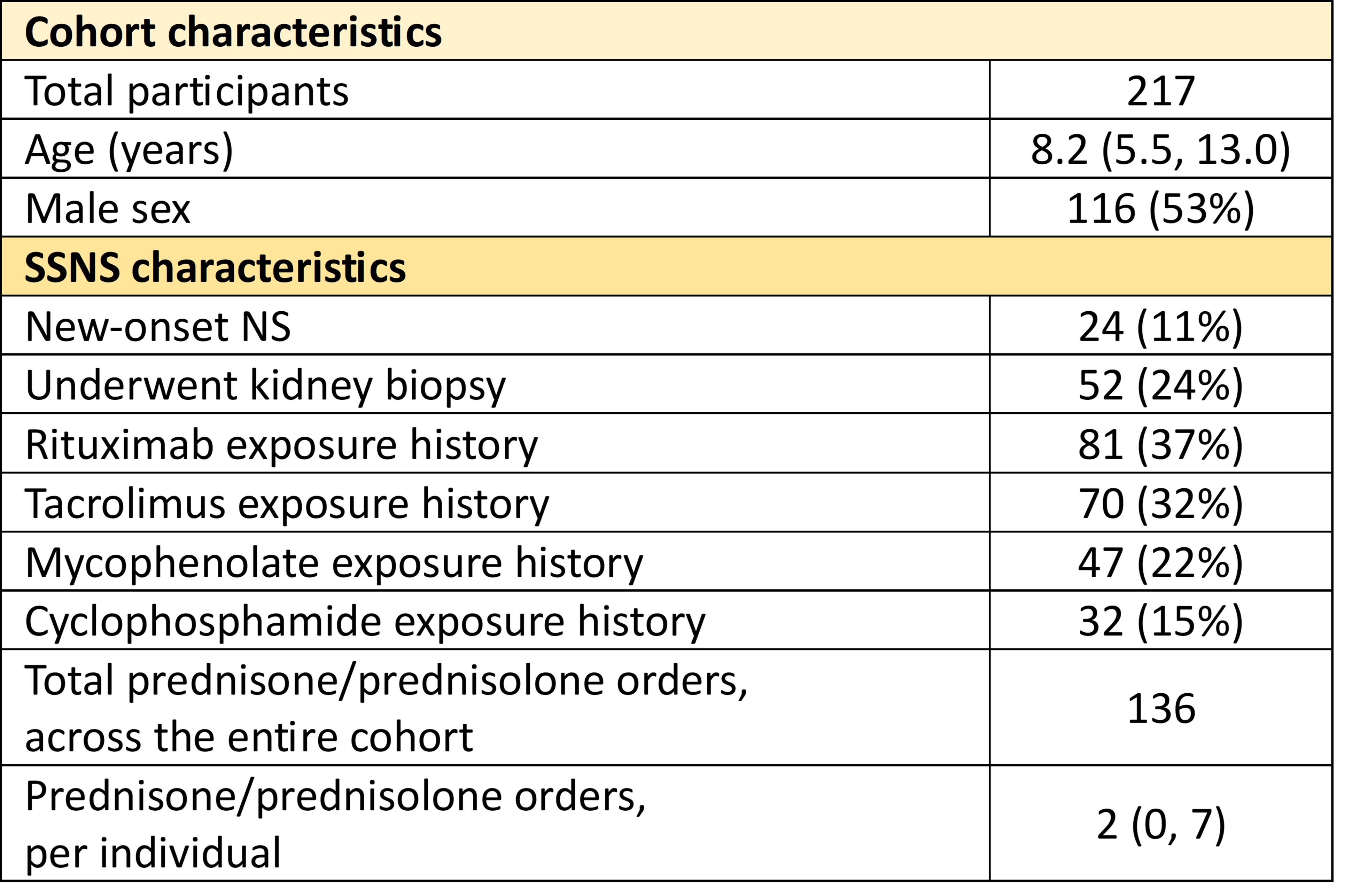 Continuous values are reported as median (interquartile range). Discrete values are reported as n (% of cohort).
Continuous values are reported as median (interquartile range). Discrete values are reported as n (% of cohort).EHR encounter and communication characteristics.
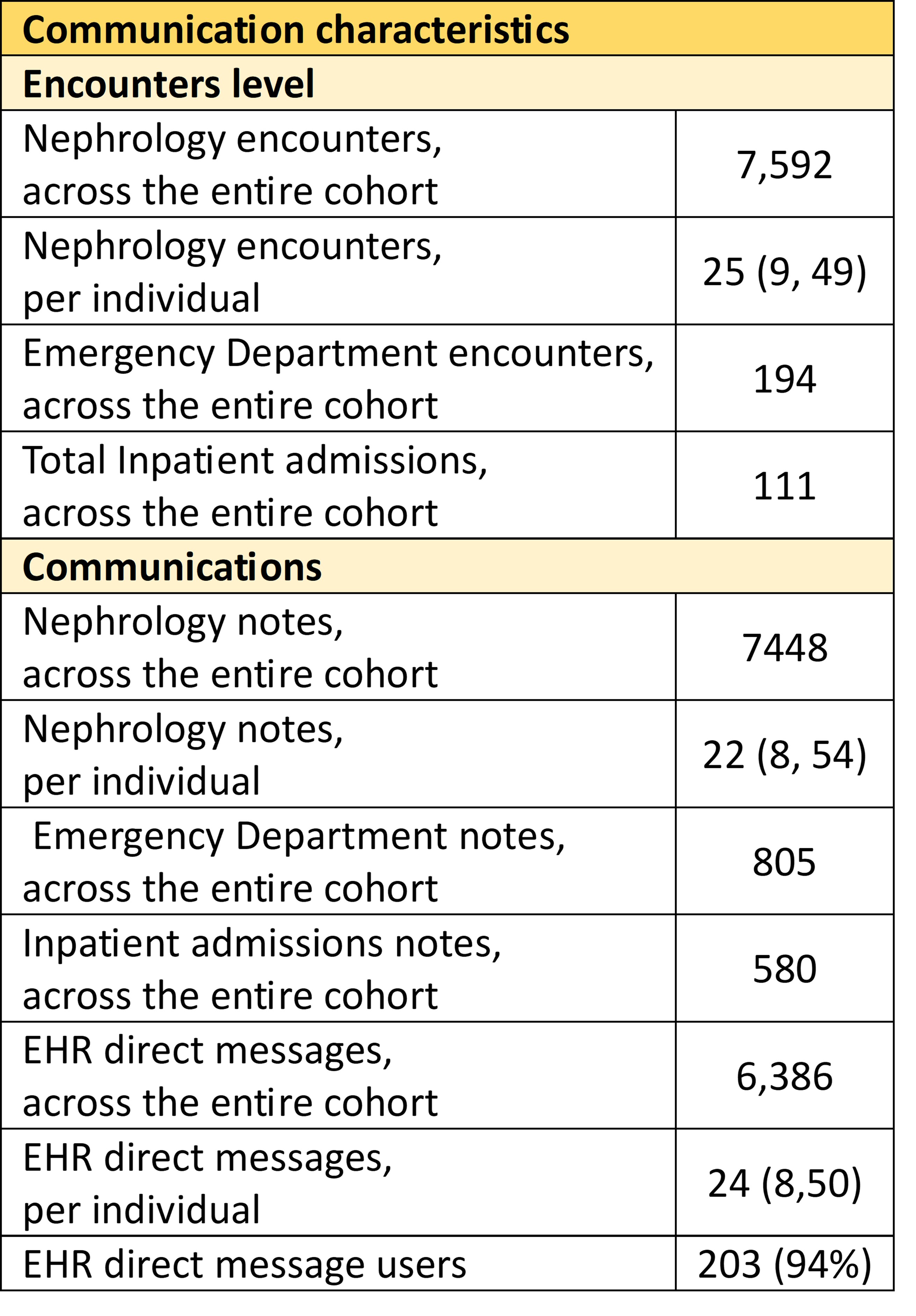 Median (interquartile range) are reported for “per individual” metrics. Nephrology encounters include office visits, emergency department presentations, inpatient admissions, telephone calls, and order entries. There are >13,000 EHR free text entries for these 217 participants over the 2.5 year study period. This is a large data source from which relapse-remission events can be identified and time-indexed.
Median (interquartile range) are reported for “per individual” metrics. Nephrology encounters include office visits, emergency department presentations, inpatient admissions, telephone calls, and order entries. There are >13,000 EHR free text entries for these 217 participants over the 2.5 year study period. This is a large data source from which relapse-remission events can be identified and time-indexed.NLP pipeline
.jpg) Fit LASSO curves are shown as part of the NLP pipeline, showing the feasibility that NLP can detect relapse-remission events based on communication patterns.
Fit LASSO curves are shown as part of the NLP pipeline, showing the feasibility that NLP can detect relapse-remission events based on communication patterns.Participant characteristics
 Continuous values are reported as median (interquartile range). Discrete values are reported as n (% of cohort).
Continuous values are reported as median (interquartile range). Discrete values are reported as n (% of cohort).EHR encounter and communication characteristics.
 Median (interquartile range) are reported for “per individual” metrics. Nephrology encounters include office visits, emergency department presentations, inpatient admissions, telephone calls, and order entries. There are >13,000 EHR free text entries for these 217 participants over the 2.5 year study period. This is a large data source from which relapse-remission events can be identified and time-indexed.
Median (interquartile range) are reported for “per individual” metrics. Nephrology encounters include office visits, emergency department presentations, inpatient admissions, telephone calls, and order entries. There are >13,000 EHR free text entries for these 217 participants over the 2.5 year study period. This is a large data source from which relapse-remission events can be identified and time-indexed.
