Obesity 2
Session: Obesity 2
293 - The Role of 27-hydroxycholesterol in Adipose Tissue
Sunday, April 27, 2025
8:30am - 10:45am HST
Publication Number: 293.6578
Charles Herrin, University of Texas Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, TX, United States; Ken Chambliss, University of Texas Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, TX, United States; Philip Shaul, University of Texas Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, TX, United States; chieko mineo, Chieko Mineo, Professor of Department of Pediatrics & Cell Biology, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, TX, United States

Charles Herrin, MD
Physician
University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center
Dallas, Texas, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Adipose tissue functions to store energy in the form of triglycerides (TG), and it harbors 20% of total body cholesterol. We recently determined that adipose cholesterol is primarily derived from high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL) transported into adipocytes by scavenger receptor class B type 1 (SR-B1), and that mice lacking adipocyte SR-B1 are protected from diet-induced obesity. TG accumulation in adipose is regulated by liver X receptor beta (LXRβ), which is activated by 27-hydroxycholesterol (27HC), a cholesterol metabolite generated by sterol 27-hydroxylase (Cyp27a1). Mice deficient in adipocyte SR-B1 have decreased 27HC in adipose tissue.
Objective: Studies were designed to investigate the role of 27HC in adipose tissue. The hypothesis raised was that mice lacking Cyp27a1 in adipocytes are protected from diet-induced obesity.
Design/Methods: Cyp27a1 floxed mice (Cyp27a1fl/fl) were crossed with mice carrying tetO-cre and rtTA-adiponectin to produce Cyp27a1fl/fl;tetO-cre;adiponectin rtTA mice, which have doxycycline inducible loss of Cyp27A1 in adipocytes (iCyp27a1∆AD). Cyp27a1fl/fl controls and iCyp27a1∆AD mice were fed a high fat diet for 12 weeks postweaning. Fat mass was evaluated by NMR, gene expression was assessed by qPCR, and adipose 27HC content was measured by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry.
Results: iCyp27a1∆AD mice demonstrated 84% and 56% reductions in Cyp27a1 expression in inguinal and gonadal fat, respectively. Body weights and body fat composition were not altered in iCyp27a1∆AD mice, and there were no changes in LXRβ target gene expression in adipose. Surprisingly, adipose 27HC content was similar in iCyp27a1∆AD and Cyp27a1fl/fl controls.
Conclusion(s): Genetic loss-of-function of adipocyte Cyp27a1 in mice does not result in protection from diet-induced obesity, possibly because adipose 27HC content is unaffected. 27HC abundance in adipocytes is controlled by factors other than levels of Cyp27a1 expression, and the basis of obesity protection with SR-B1 deletion in adipocytes remains unknown.
Adipocyte Cyp27a1 RNA Expression after Inducible Deletion
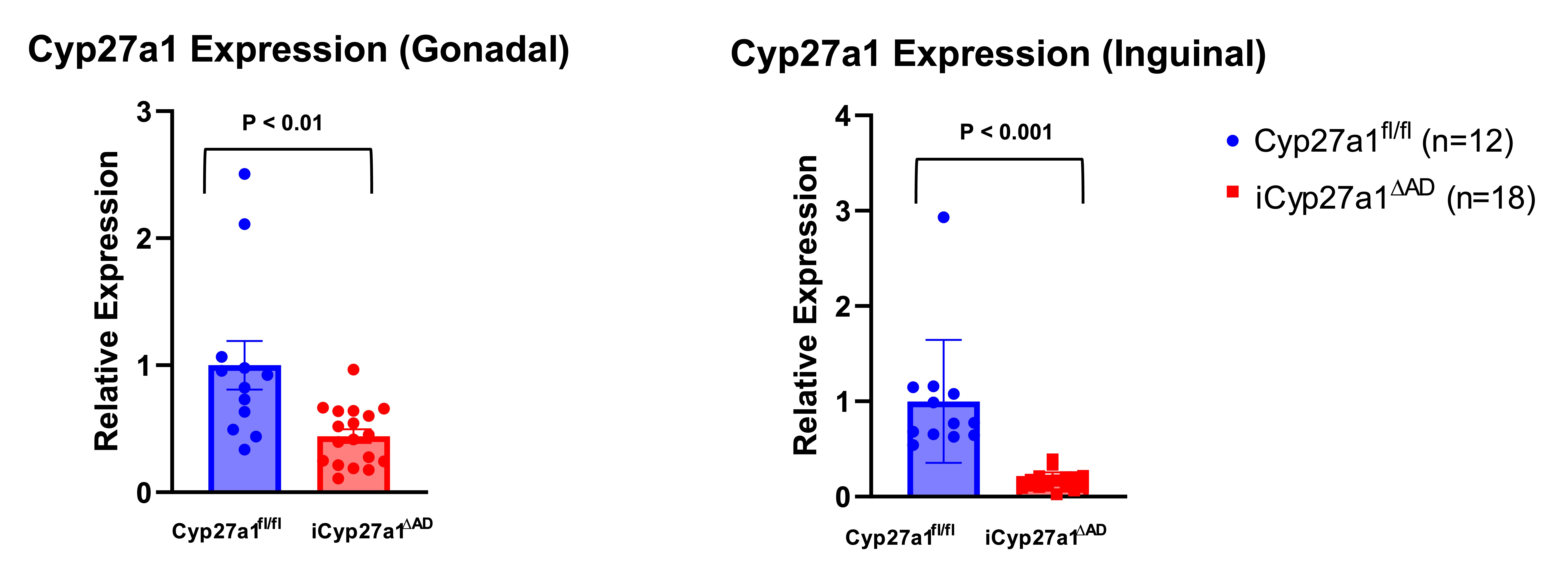 Changes in cellular Cyp27a1 expression in adipocytes. vWAT and sWAT adipocytes were analyzed by RT-qPCR. N=12,18 (p < 0.01 and p<0.001 respectively). Unpaired t-test.
Changes in cellular Cyp27a1 expression in adipocytes. vWAT and sWAT adipocytes were analyzed by RT-qPCR. N=12,18 (p < 0.01 and p<0.001 respectively). Unpaired t-test.Cyp27a1 Inducible Deletion Phenotype
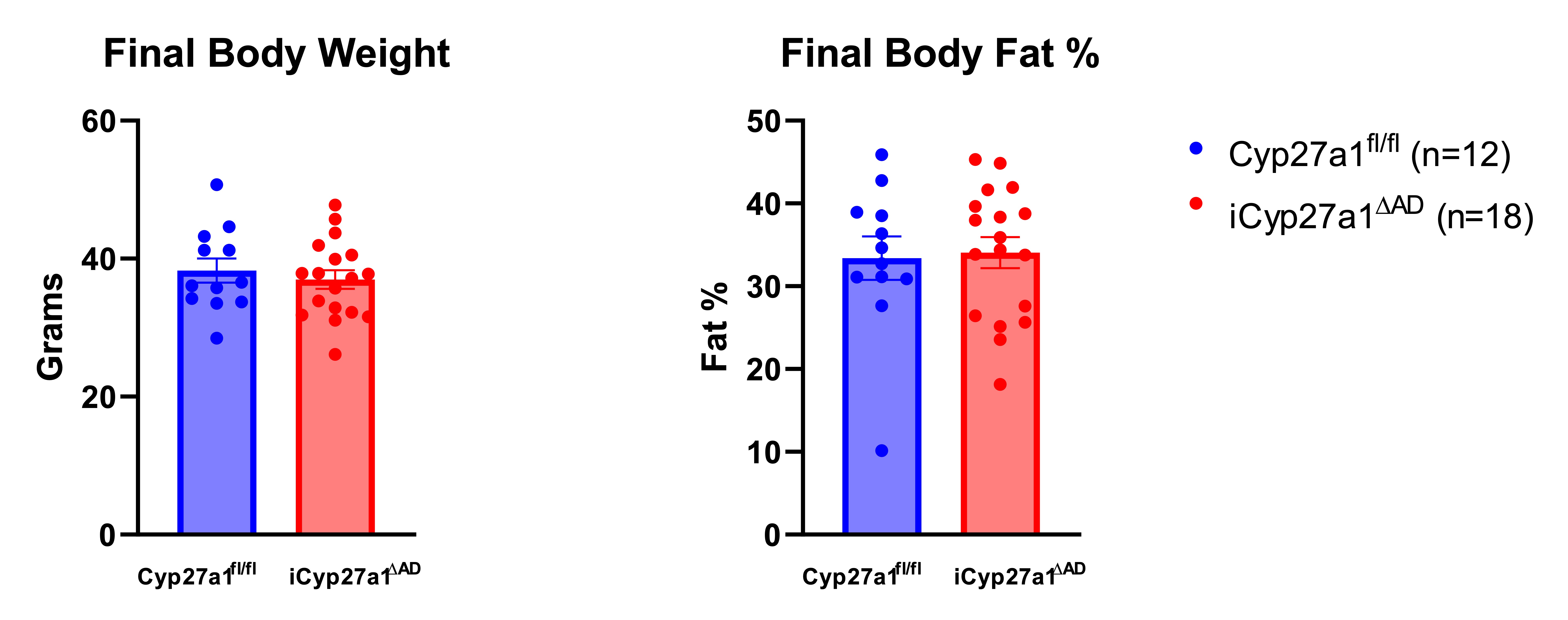 Body compositions of Cyp27a1fl/fl and iCyp27a1∆AD. Cyp27a1fl/fl and iCyp27a1∆AD were harvested after 12 weeks on HFD, final body weights were taken and final body fat was measured by NMR N=12,18 (p>0.99). Unpaired t-test.
Body compositions of Cyp27a1fl/fl and iCyp27a1∆AD. Cyp27a1fl/fl and iCyp27a1∆AD were harvested after 12 weeks on HFD, final body weights were taken and final body fat was measured by NMR N=12,18 (p>0.99). Unpaired t-test.Adipose 27HC Content
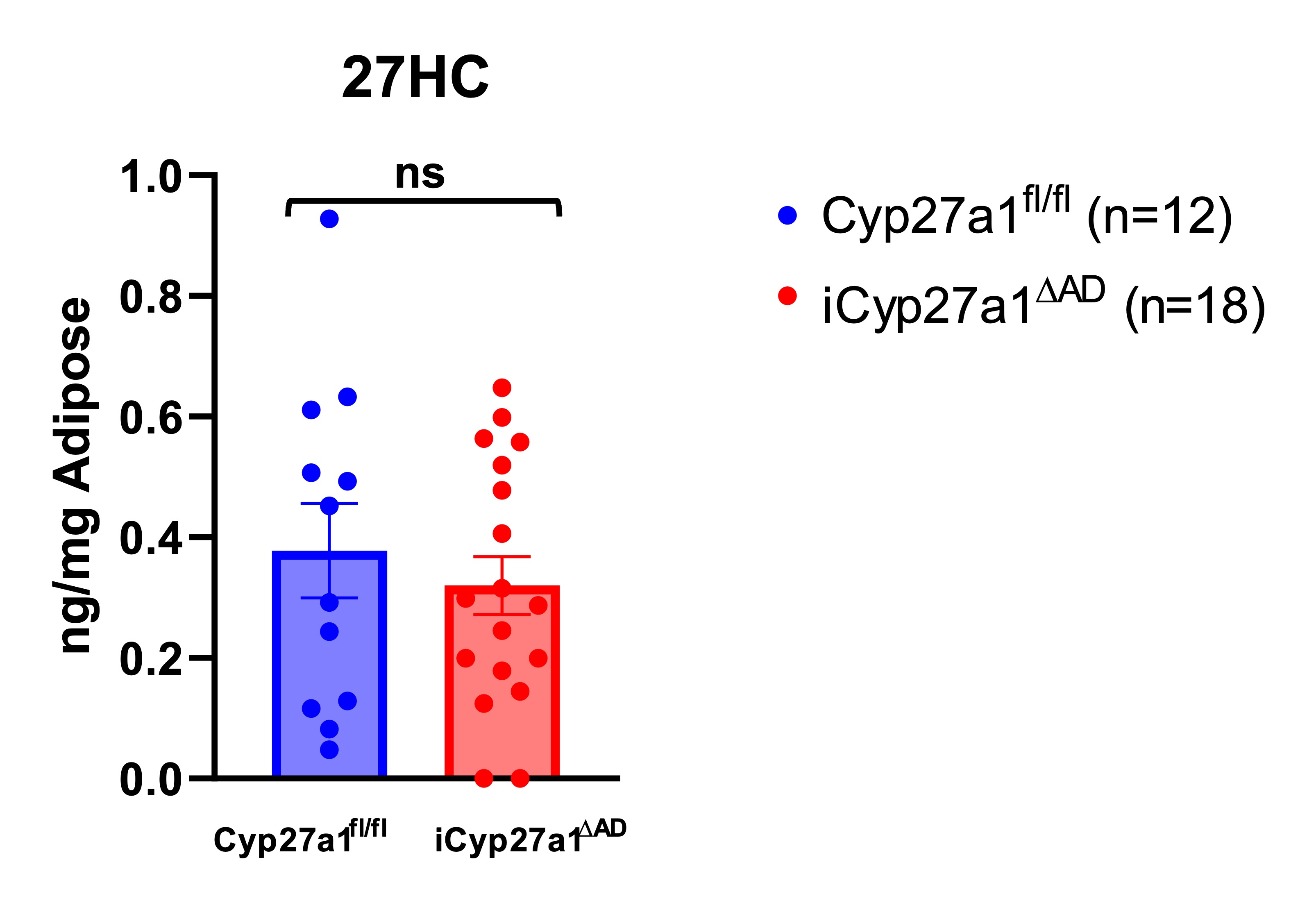 Cellular 27HC content in adipose tissue. Cyp27a1fl/fl and iCyp27a1∆AD were fed chow or HFD for 12 weeks, and vWAT were isolated for measurement of oxysterol concentrations using LC/MS. N=12,18. Unpaired t-test.
Cellular 27HC content in adipose tissue. Cyp27a1fl/fl and iCyp27a1∆AD were fed chow or HFD for 12 weeks, and vWAT were isolated for measurement of oxysterol concentrations using LC/MS. N=12,18. Unpaired t-test.Adipocyte Cyp27a1 RNA Expression after Inducible Deletion
 Changes in cellular Cyp27a1 expression in adipocytes. vWAT and sWAT adipocytes were analyzed by RT-qPCR. N=12,18 (p < 0.01 and p<0.001 respectively). Unpaired t-test.
Changes in cellular Cyp27a1 expression in adipocytes. vWAT and sWAT adipocytes were analyzed by RT-qPCR. N=12,18 (p < 0.01 and p<0.001 respectively). Unpaired t-test.Cyp27a1 Inducible Deletion Phenotype
 Body compositions of Cyp27a1fl/fl and iCyp27a1∆AD. Cyp27a1fl/fl and iCyp27a1∆AD were harvested after 12 weeks on HFD, final body weights were taken and final body fat was measured by NMR N=12,18 (p>0.99). Unpaired t-test.
Body compositions of Cyp27a1fl/fl and iCyp27a1∆AD. Cyp27a1fl/fl and iCyp27a1∆AD were harvested after 12 weeks on HFD, final body weights were taken and final body fat was measured by NMR N=12,18 (p>0.99). Unpaired t-test.Adipose 27HC Content
 Cellular 27HC content in adipose tissue. Cyp27a1fl/fl and iCyp27a1∆AD were fed chow or HFD for 12 weeks, and vWAT were isolated for measurement of oxysterol concentrations using LC/MS. N=12,18. Unpaired t-test.
Cellular 27HC content in adipose tissue. Cyp27a1fl/fl and iCyp27a1∆AD were fed chow or HFD for 12 weeks, and vWAT were isolated for measurement of oxysterol concentrations using LC/MS. N=12,18. Unpaired t-test.
