Neonatal Fetal Nutrition & Metabolism 1
Session: Neonatal Fetal Nutrition & Metabolism 1
606 - Serum Zinc (Zn) and Vitamin D associations with the development of Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP) in very preterm (VPT, < 33 weeks gestational age, GA).
Saturday, April 26, 2025
2:30pm - 4:45pm HST
Publication Number: 606.6659
Dimitrios Angelis, University of Texas Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, TX, United States; Tina A. Seidu, University of Texas Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, TX, United States; Roy Heyne, University of Texas Southwestern Medical School, Southlake, TX, United States; L. Steven Brown, Parkland Health, Dallas, TX, United States; Theresa Jacob, Parkland Health, Dallas, TX, United States; Audrey Edwards, Parkland Health, Dallas, TX, United States; Cheryl S. Lair, Parkland Health & Hospital System, Arlington, TX, United States; Myra H. Wyckoff, UT Southwestern, Dallas, TX, United States; David B. Nelson, University of Texas Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, TX, United States; Luc (middle name P) P. Brion, University of Texas Southwestern Medical School, Dallas, TX, United States
- DA
Dimitrios Angelis, MD (he/him/his)
Neonatologist
University of Texas Southwestern Medical School
Dallas, Texas, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Zn concentration in the retina is the highest among other organs. Zn acts as a protective signal against excitotoxicity, by inhibiting glutamate in neurons, which in turn can induce vascular endothelial growth factor, a key molecule for development of ROP. Zn deficiency (serum level < 0.74 mcg/ml) is frequently encountered in up to 30-50% premature infants. Zn also regulates Vitamin D, which has been linked to ROP. Clinical studies investigating the role of Zn in ROP showed no clear role. As a result, the actual clinical link of Zn deficiency with ROP is not well established.
Objective: To describe possible associations between Zn (and Vitamin D) deficiency as well as possible role of Zn supplementation with the development of ROP in VPT
Design/Methods: In this intervention cohort study that included increased dosing and routine supplementation of Zn, in VPT we conducted retrospective data analysis in Epoch-1 (Zn provided only in growth failure) and Epoch-2 [post era, routine Zn, table 1]. Since severe ROP occur in infants < 29 weeks, a subgroup analysis of these infants was also conducted. In Epoch-2, serial Zn levels were obtained at birth, when the infant was at 140 ml/kg/day of feeds, and one month later. ROP was reported as none, mild/moderate and severe (requiring intervention). Vitamin D was also available in a subset of newborns (deficiency defined < 30 ng/ml).
Results: Baseline characteristics among EPOCHs are shown in table 1. In Epoch-2, ROP was associated with the lower minimum serum Zn level and with low serum Zn and vitamin D level. ROP was only observed among infants < 33 weeks GA. Among infants < 33 weeks GA, ROP was associated with low GA and BW, higher stage of BPD, and growth failure pattern [area under the receiver operating curve, AUROC = 0.867 (95% CI 0.842, 0.892)]. In Epoch-2 ROP was associated with low GA and BW, higher stage of BPD and lowest serum Zn concentration [AUROC= 0.928 and area under the precision-recall curve (AUPRC=0.827, Figure 1) and had better fitting than the first model when the latter was applied to Epoch-2] (Table 2.1 and 2.2). In the sub-analysis of 122 ELGANs in Epoch-2 (Table 2.3), severity of ROP was associated with low GA, low BW, low minimum Zn and both low Zn and low vitamin D. In multivariable analysis adjusted for GA, BW and stage of BPD, mild/moderate and severe ROP were associated with any low serum level of Zn or Vit D.
Conclusion(s): Infants with ROP tend to have lower Zn and Vitamin D levels. Inclusion of Zn level in a logistic model for development of ROP improved discrimination and fit. Further studies are needed to investigate this interaction.
Comparison of baseline maternal and neonatal characteristics in the growth cohort in both epochs
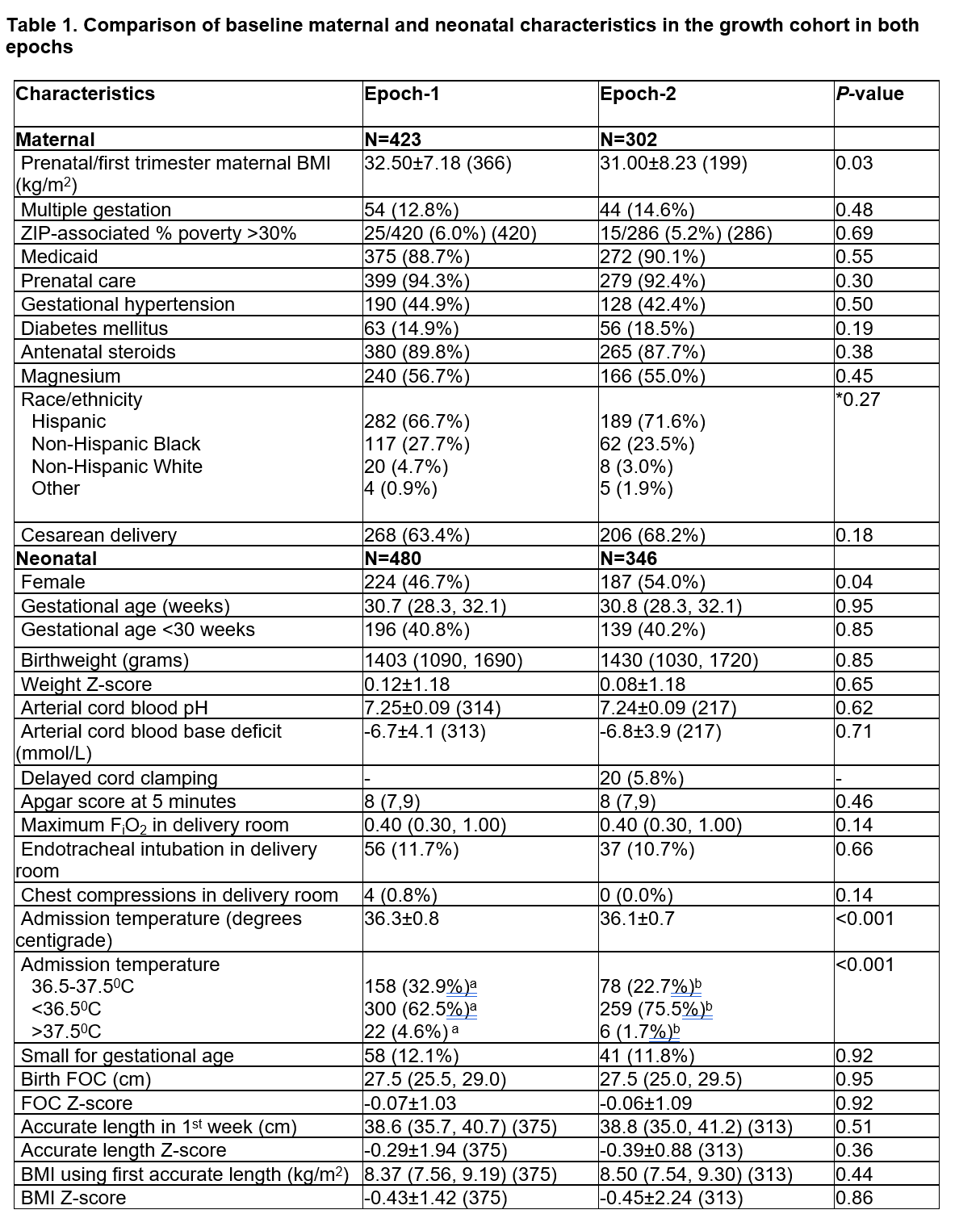 In Epoch-1, Zn supplementation in total parenteral nutrition (TPN) was 450 mcg/kg/day and enteral supplementation was provided only to those with documented Zn deficiency. In Epoch-2, Zn was provided with 500 mcg/kg/day in TPN and routine enteral supplementation, to achieve a total of 2.5 and later 2.7-3 mg/kg/day until 36 weeks postmenstrual age (PMA) or discharge. The discrepancy between the number of maternal and neonatal characteristics corresponds to multiple pregnancies.
In Epoch-1, Zn supplementation in total parenteral nutrition (TPN) was 450 mcg/kg/day and enteral supplementation was provided only to those with documented Zn deficiency. In Epoch-2, Zn was provided with 500 mcg/kg/day in TPN and routine enteral supplementation, to achieve a total of 2.5 and later 2.7-3 mg/kg/day until 36 weeks postmenstrual age (PMA) or discharge. The discrepancy between the number of maternal and neonatal characteristics corresponds to multiple pregnancies.Values are mean ± SD (n if less than N in top row), median (IQR) (n if number < N in upper row) or number (%). Student t-test, Mann-Whitney test, χ2 analysis or *Fisher’s exact test
Different alphabetic superscripts across columns indicate significant pair-wise differences.
Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; FiO2, fractional inspiration level of oxygen; FOC, fronto-occipital circumference
Multivariate analaysis of ROP in VPT and ELGAN newborns in both epoch (2.1) and in epoch-2 (2.2, 2.3).
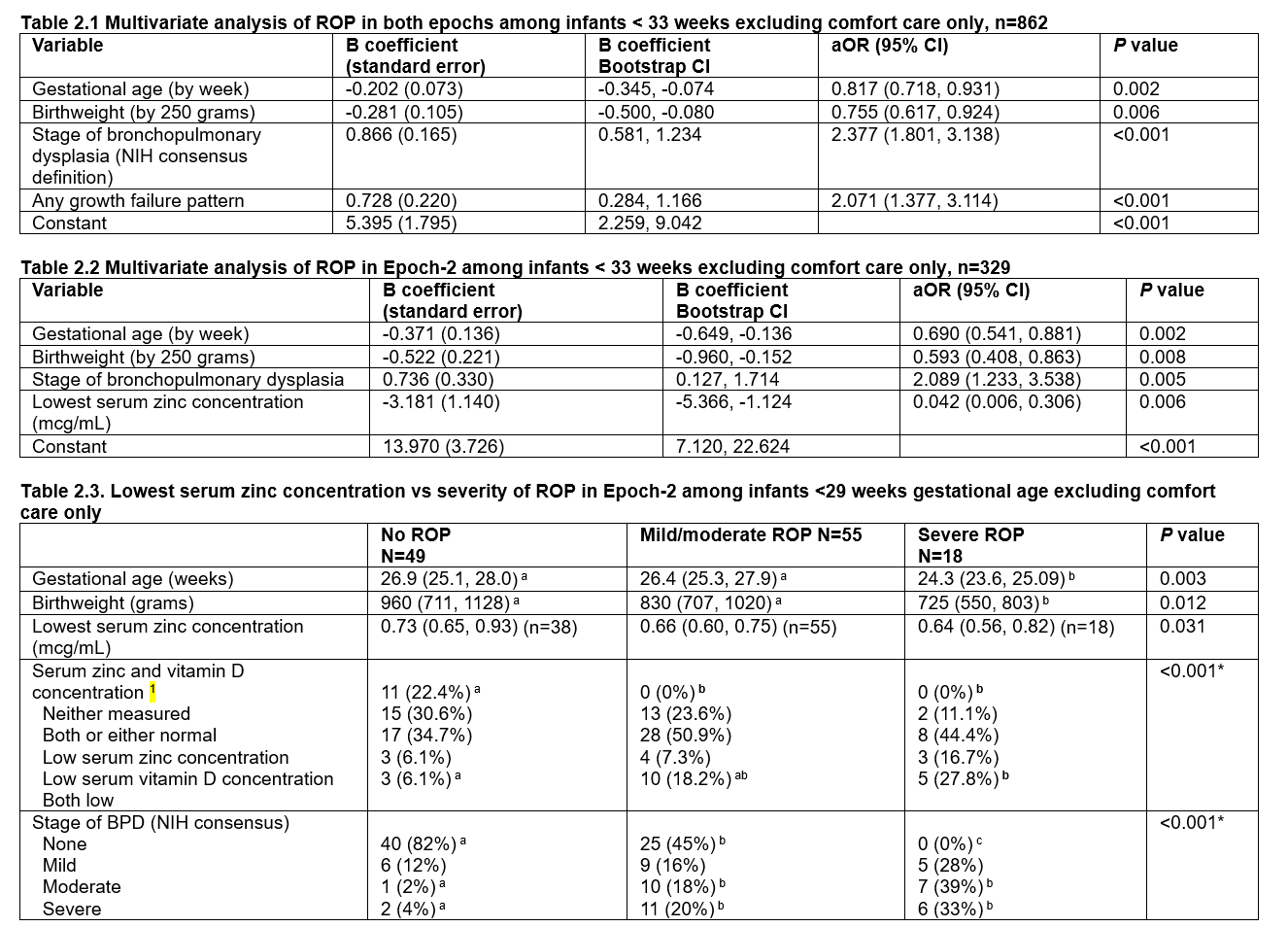 Table 2.1. Stepwise logistic regression analysis with bias-corrected accelerated 95% confidence intervals of the B coefficients was performed using 1000 bootstrap samples with SPSS: n=216 cases with ROP among 862 infants; Nagelkerke R2=0.472; Hosmer and Lemeshow test <0.001; AUROC=0.878 (95% CI 0.854, 0.902); Youden’s index 0.693 (predicted probability 0.140, sensitivity 0.907; specificity 0.686)
Table 2.1. Stepwise logistic regression analysis with bias-corrected accelerated 95% confidence intervals of the B coefficients was performed using 1000 bootstrap samples with SPSS: n=216 cases with ROP among 862 infants; Nagelkerke R2=0.472; Hosmer and Lemeshow test <0.001; AUROC=0.878 (95% CI 0.854, 0.902); Youden’s index 0.693 (predicted probability 0.140, sensitivity 0.907; specificity 0.686)Not significant: small for gestational age, sex, race/ethnicity, epoch, any zinc concentration <0.74 mcg/mL, maximum respiratory support, surfactant, severe BPD, RDS, documented sepsis; rate of weight gain was excluded because it was missing in 34 infants.
Abbreviations: aOR, adjusted odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; ROP, retinopathy of prematurity; AUROC, area under the receiver operating characteristic curve
Table 2.2. Stepwise logistic regression analysis with bias-corrected accelerated 95% confidence intervals of the B coefficients was performed using 1000 bootstrap samples with SPSS: n=86 cases with ROP among 329 infants; Nagelkerke R2=0.621; Hosmer and Lemeshow test P=0.334; AUROC=0.928 (95% CI 0.899, 0.957); Youden’s index 0.716 (predicted probability 0.153, sensitivity 0.942, specificity 0.774).
Not significant: small for gestational age, sex, race/ethnicity, any growth failure pattern, any zinc concentration <0.74 mcg/mL, low serum zinc or vitamin D concentration, respiratory distress syndrome, surfactant, maximum respiratory support; rate of weight gain was excluded (missing in some infants).
bronchopulmonary dysplasia, duration of continuous positive airway pressure, duration of ventilation, maximum respiratory support, documented sepsis
Abbreviations: aOR, adjusted odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; ROP, retinopathy of prematurity; AUROC, area under the curve
Table 2.3 Values are mean±SD (n) or number (%).
1 Low serum zinc concentration: <0.74 mcg/mL; low serum 25 OH vitamin D concentration: <30 mcg/mL
Kruskal-Wallis test or *Fisher’s exact test followed by pair-wise comparisons with Bonferroni correction.
Different alphabetic superscripts across columns indicate significant pair-wise differences.
Abbreviations: ROP, retinopathy of prematurity; BPD, bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
Note: all infants with severe ROP had a GA <29 weeks
Figure 1. Receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) and Precision-recall curve (PRC) for ROP model in EPOCH -2
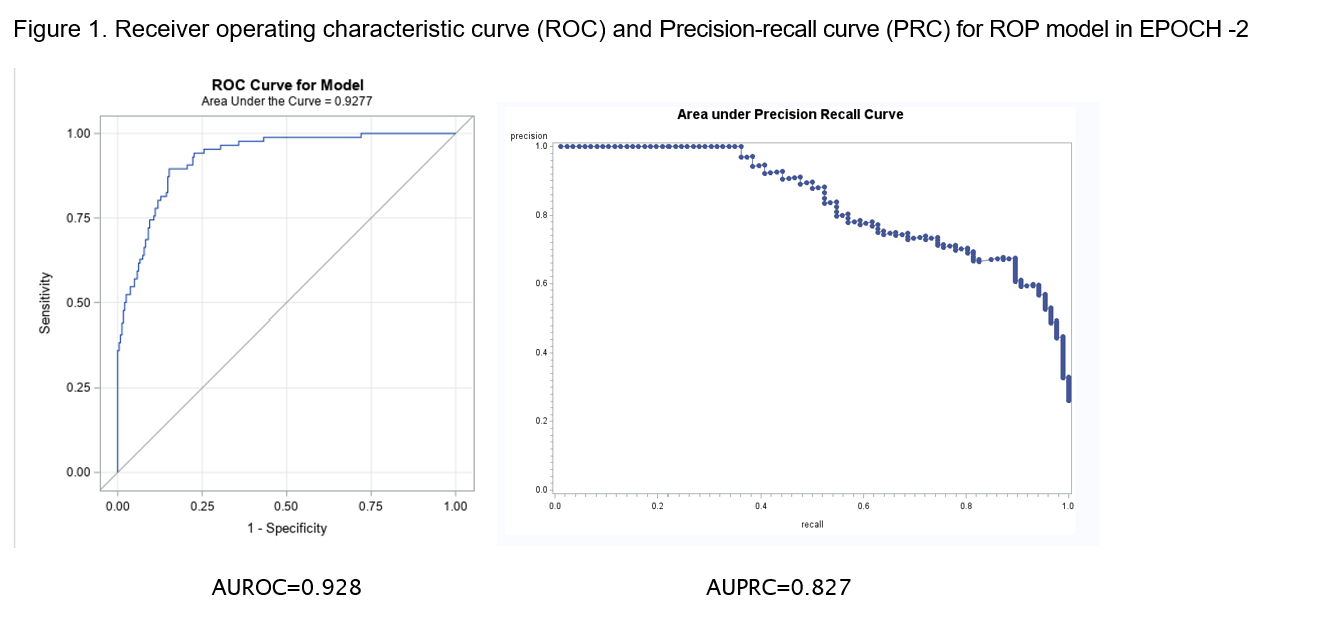 Abbreviations: AU: area under the curve; ROC Receiver operating characteristic curve; PRC: Precision-recall curve
Abbreviations: AU: area under the curve; ROC Receiver operating characteristic curve; PRC: Precision-recall curve 
