Neonatal Fetal Nutrition & Metabolism 2
Session: Neonatal Fetal Nutrition & Metabolism 2
622 - Percent Maximal Weight Loss, First Week Average Total Fluid Administration and 2-Year Neurodevelopmental Outcomes among US-Born Extremely Preterm Newborns
Saturday, April 26, 2025
2:30pm - 4:45pm HST
Publication Number: 622.6191
Gregory C.. Valentine, University of Washington School of Medicine, Tacoma, WA, United States; Olivia C. Brandon, University of Washington: Magnuson Health Sciences Center – RR 544A, Seattle, WA, United States; Krystle M.. Perez, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, United States; Dennis E. Mayock, UWMC, Lake Forest Park, WA, United States; Katie M. Strobel, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA, United States; Patrick Heagerty, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, United States; Thomas R. Wood, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA, United States; Sandra E. Juul, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, United States

Gregory C. Valentine, MD, MED, FAAP (he/him/his)
Associate Professor of Pediatrics, Division of Neonatology
University of Washington
Seattle, Washington, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Extremely premature (EP) neonates, born < 28 weeks’ gestation, are at risk for excessive weight loss. Maximal weight loss (MWL) percentage and average first-week total fluid administration (TFA) in the first week after birth is associated with adverse in-hospital outcomes, but it is unclear whether the percent MWL from birthweight and/or the average first-week TFA has any relationship with neurodevelopmental outcomes.
Objective: To explore the association between first week MWL and average TFA and neurodevelopmental outcomes at 2-years corrected gestational age (CGA) among US-born EP infants.
Design/Methods: We conducted a retrospective secondary analysis of the Preterm Erythropoietin Neuroprotection Trial (PENUT). Outcome analyses were performed evaluating lowest, middle two, and highest quartiles of MWL and average TFA over the first week after birth with 2-year CGA neurodevelopmental outcomes assessed by the Bayley Scales of Infant and Toddler Development 3rd Edition (Bayley-3). Generalized estimating equations, logistic, or linear regression univariate and multivariate models were used. Infants who survived for the first 7 days were included in the primary analysis. In a sensitivity analysis, infants who died in the first 7 days were included and assigned a Bayley-3 score 1 point below the lowest survivor’s score.
Results: Among n=895 EP neonates (Table 1), percent MWL was not associated with significant differences in Bayley-3 domains at 2 years CGA within either the primary (survivor-only) or sensitivity (including mortality cases) analyses (Figure 1). Compared to infants with an average TFA of < 120 mL/kg birthweight/day, an average TFA of 120 to < 150 mL/kg birthweight/day was associated with higher cognitive scores in both primary (+3.4 points, 95% CI: 0.8-6.0 points; Figure 2) and sensitivity (+3.2 points, 95% CI: 0.4-6.1 points) analyses. In unadjusted analyses, TFA ≥150 mL/kg birthweight/day was associated with lower Bayley-3 scores across all 3 domains, but lost significance after adjustment for severity of illness covariates (Figure 2) and in adjusted sensitivity analyses.
Conclusion(s): Among US-born EP neonates, there were no significant associations between percent MWL and 2-year neurodevelopmental outcomes. Average first week TFA of 120 to < 150 mL/kg birthweight/day was associated with modestly improved 2-year neurodevelopmental outcomes, with outcomes in the highest TFA quartile likely driven by associated illness-related factors. Further studies are needed to explore this relationship including separation of enteral and parenteral fluid contributions.
Table 1: Baseline maternal and neonatal characteristics of overall cohort
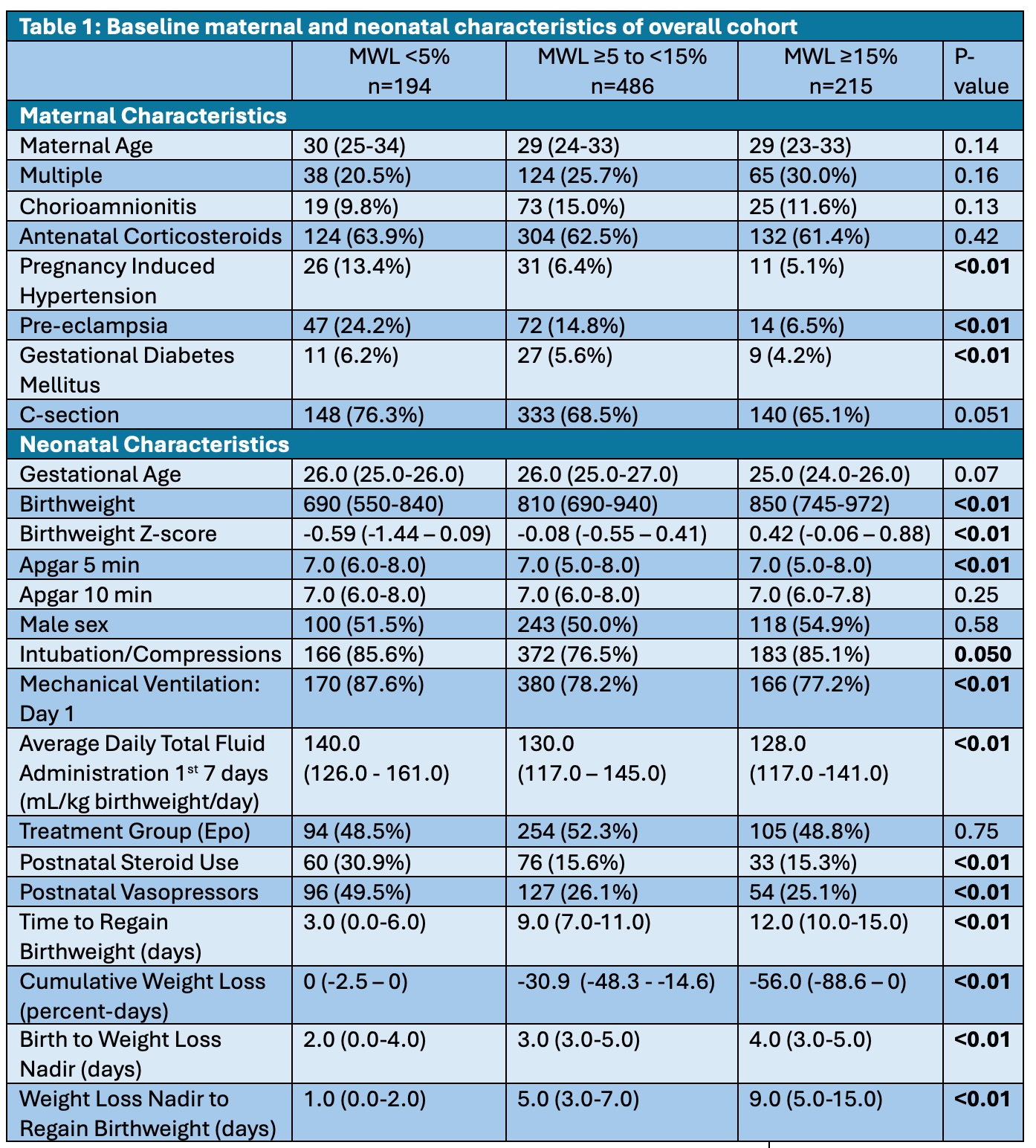 Data is reported as median (interquartile range). P-values obtained via ANOVA.
Data is reported as median (interquartile range). P-values obtained via ANOVA. Percent maximal weight loss (MWL) and 2-Year Bayley-3 Neurodevelopmental Outcomes.
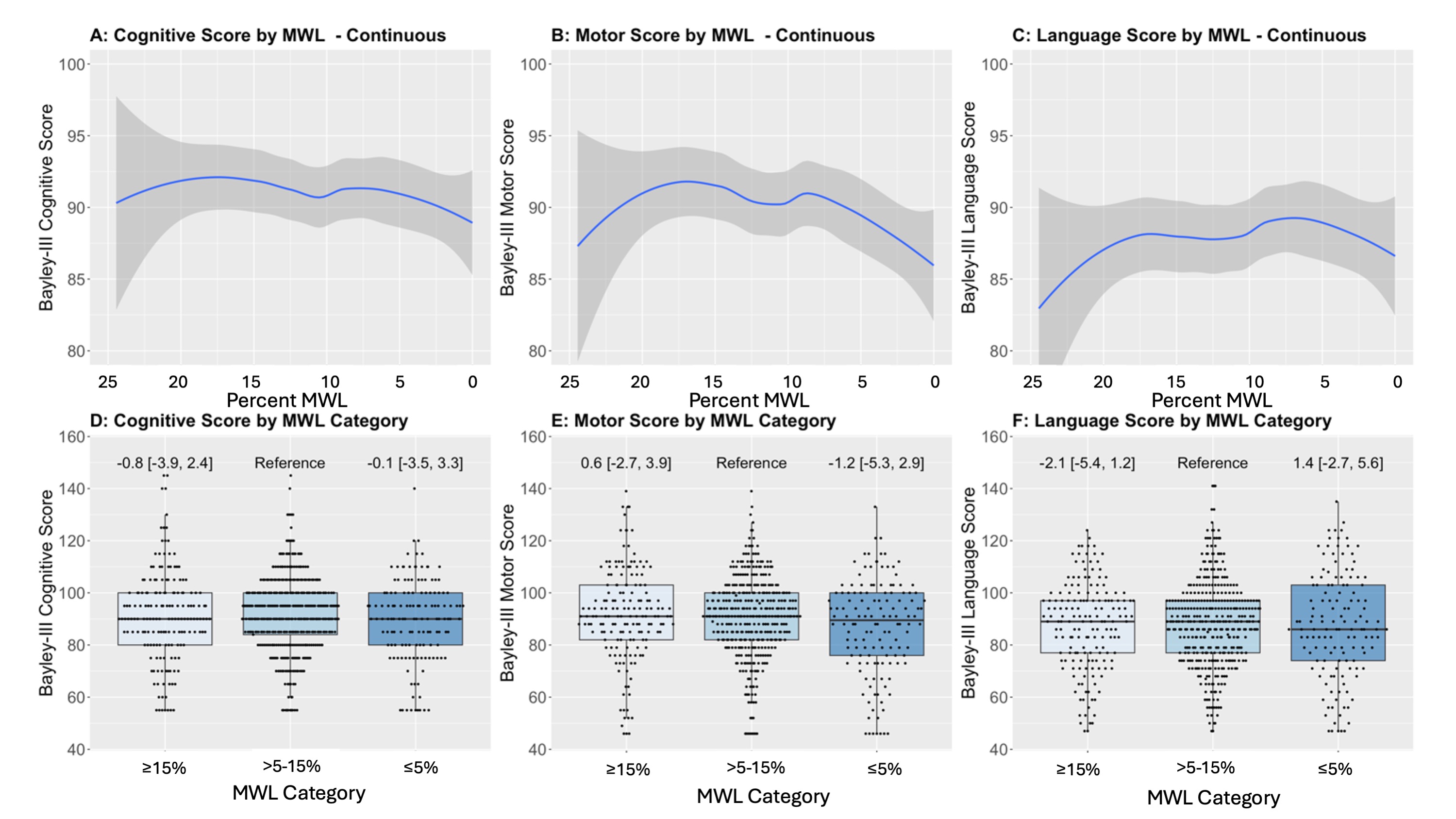 Panels A-C: Unadjusted visual depictions via loess smooth plots of percent MWL (on a continuous scale) within the first week after birth and Bayley-3 cognitive (A), motor (B), and language (C) domain scores. Panels D-E: Box plots depicting the percent MWL category and Bayley-3 cognitive (D), motor (E), and language (F) domain scores with the point estimate and 95% confidence intervals from the adjusted models. There are no significant associations with percent MWL and 2-year corrected gestational age Bayley-3 cognitive, motor, or language domains. Covariates included in the adjustments included: Gestational age at birth, birthweight Z-score, intubation/chest compressions, mechanical ventilation need on day 1, average TFA category, treatment group within PENUT Trial, postnatal steroid use, postnatal vasopressor use, cumulative weight loss, time from nadir of weight loss to regain of birthweight (nadir-to-regain), and highest level of maternal education. Sensitivity analyses including those that died not shown.
Panels A-C: Unadjusted visual depictions via loess smooth plots of percent MWL (on a continuous scale) within the first week after birth and Bayley-3 cognitive (A), motor (B), and language (C) domain scores. Panels D-E: Box plots depicting the percent MWL category and Bayley-3 cognitive (D), motor (E), and language (F) domain scores with the point estimate and 95% confidence intervals from the adjusted models. There are no significant associations with percent MWL and 2-year corrected gestational age Bayley-3 cognitive, motor, or language domains. Covariates included in the adjustments included: Gestational age at birth, birthweight Z-score, intubation/chest compressions, mechanical ventilation need on day 1, average TFA category, treatment group within PENUT Trial, postnatal steroid use, postnatal vasopressor use, cumulative weight loss, time from nadir of weight loss to regain of birthweight (nadir-to-regain), and highest level of maternal education. Sensitivity analyses including those that died not shown. First-Week Average TFA and 2-Year Bayley-3 Neurodevelopmental Outcomes.
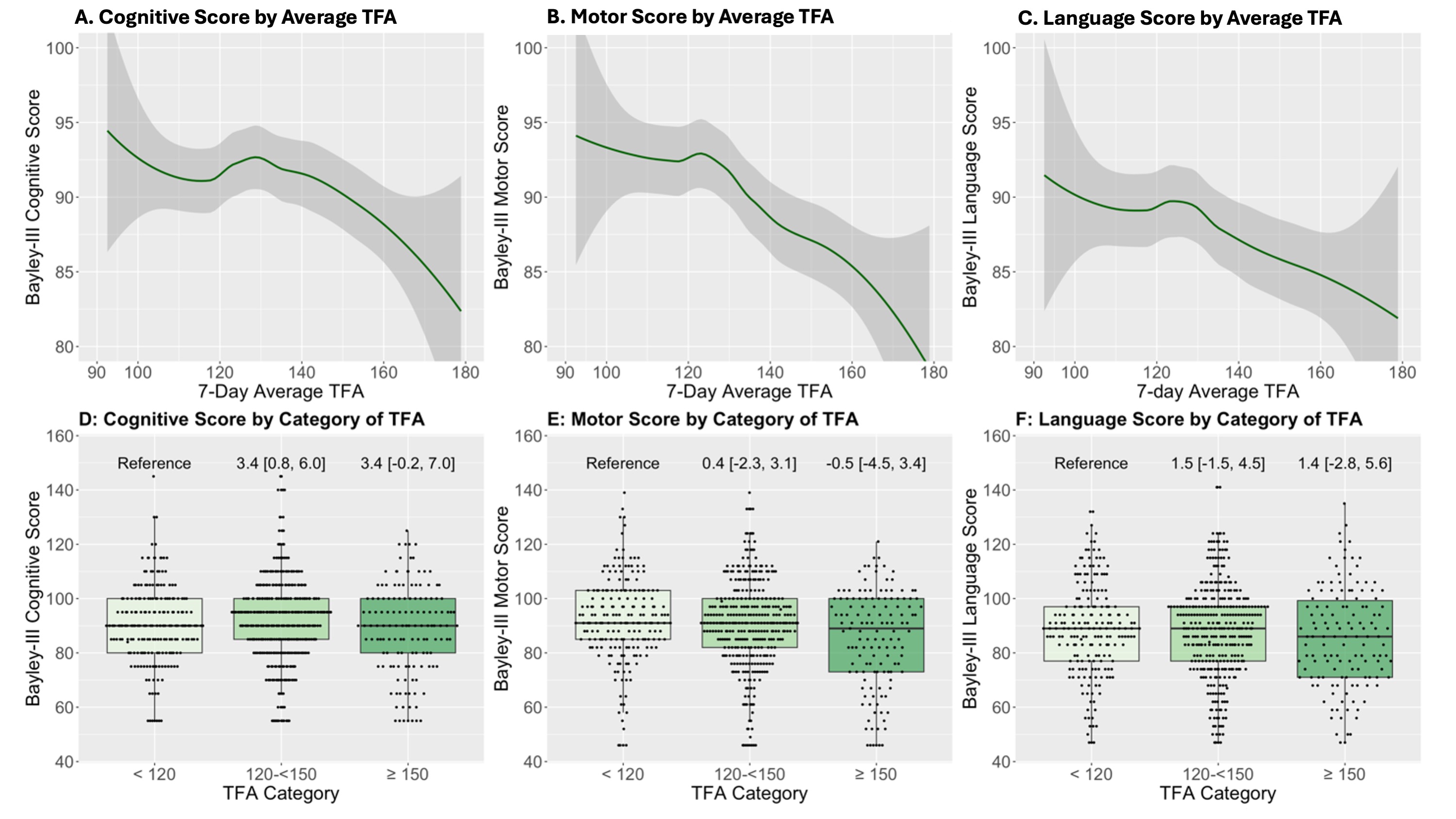 Panels A-C: Unadjusted visual depictions via Loess smooth plots of average TFA within the first week after birth (on a continuous scale) and Bayley-3 cognitive (A), motor (B), and language (C) domain scores. Panels D-E: Box plots depicting the average TFA category and Bayley-3 cognitive (D), motor (E), and language (F) domain scores with the point estimate and 95% confidence intervals from the adjusted models written above each respective box plot. While the unadjusted analyses demonstrate a linear association between increasing average TFA and 2-year corrected gestational age Bayley-3 neurodevelopmental outcomes, the only significant findings after adjustment for confounders was a 3.4 point higher score in the 120- <150 mL/kg birthweight/day TFA group as compared to <120 mL/kg birthweight/day suggesting the clear linear trend in the unadjusted analyses is likely predominantly due to confounders related to severity of illness. Covariates included in the adjustments included: Gestational age at birth, birthweight Z-score, intubation/chest compressions, mechanical ventilation need on day 1, average percent MWL category, treatment group within PENUT Trial, postnatal steroid use, postnatal vasopressor use, cumulative weight loss, time from nadir of weight loss to regain of birthweight (nadir-to-regain), and highest level of maternal education. TFA category is based on average first week TFA in mL/kg birthweight/day. Sensitivity analyses including those that died not shown.
Panels A-C: Unadjusted visual depictions via Loess smooth plots of average TFA within the first week after birth (on a continuous scale) and Bayley-3 cognitive (A), motor (B), and language (C) domain scores. Panels D-E: Box plots depicting the average TFA category and Bayley-3 cognitive (D), motor (E), and language (F) domain scores with the point estimate and 95% confidence intervals from the adjusted models written above each respective box plot. While the unadjusted analyses demonstrate a linear association between increasing average TFA and 2-year corrected gestational age Bayley-3 neurodevelopmental outcomes, the only significant findings after adjustment for confounders was a 3.4 point higher score in the 120- <150 mL/kg birthweight/day TFA group as compared to <120 mL/kg birthweight/day suggesting the clear linear trend in the unadjusted analyses is likely predominantly due to confounders related to severity of illness. Covariates included in the adjustments included: Gestational age at birth, birthweight Z-score, intubation/chest compressions, mechanical ventilation need on day 1, average percent MWL category, treatment group within PENUT Trial, postnatal steroid use, postnatal vasopressor use, cumulative weight loss, time from nadir of weight loss to regain of birthweight (nadir-to-regain), and highest level of maternal education. TFA category is based on average first week TFA in mL/kg birthweight/day. Sensitivity analyses including those that died not shown.
