Breastfeeding/Human Milk 1
Session: Breastfeeding/Human Milk 1
645 - Exclusive Parents-Own Milk at NICU Discharge: Associations with Prenatal and Postnatal Factors and NICU Fluid and Feeding Management
Saturday, April 26, 2025
2:30pm - 4:45pm HST
Publication Number: 645.4891
Krystle M.. Perez, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, United States; Olivia C. Brandon, University of Washington: Magnuson Health Sciences Center – RR 544A, Seattle, WA, United States; Gabriel H. Byram, University of Washington, Tacoma, WA, United States; Cayla M. Canney, University of Washington Medicine, Port Orchard, WA, United States; Sandy L. Huang, University of Washington, Sammamish, WA, United States; John F. Haddock, University of Washington Tacoma, Edgewood, WA, United States; Natalie Chapkis, Seattle Children's Hospital and University of Washington, Seattle, WA, United States; Ineeya Senthilnathan Kayal, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, United States; Sarah E. Rodriguez, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, United States; Elizabeth L. Riffel, University of Washington Tacoma, Tacoma, WA, United States; D. Taylor Hendrixson, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA, United States; Sarah E. Kolnik, University of Washington - Seattle Children's Hospital, Seattle, WA, United States; Rebecca Hoban, Seattle Children's, Seattle, WA, United States; Jill Irvine, university of washington medical center, Seattle, WA, United States; Katie M. Strobel, University of Washington School of Medicine, Seattle, WA, United States; Gregory C.. Valentine, University of Washington School of Medicine, Tacoma, WA, United States

Olivia C. Brandon, BS (she/her/hers)
Research Scientist
University of Washington: Magnuson Health Sciences Center – RR 544A
Seattle, Washington, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Exclusive human milk (EHM) diets have significant short- and long-term health benefits. However, many preterm infants do not achieve exclusive-parents-own milk (EPM) diets by NICU discharge. Understanding factors, including early NICU nutritional practices, associated with EPM at NICU discharge is essential to promote evidence-based long-term EHM diets for preterm infants.
Objective: To identify maternal-infant factors and first-week nutritional practices association with EPM at NICU discharge for preterm infants in 2 level III/IV NICUs.
Design/Methods: We performed a retrospective review of preterm infants born < 34 weeks’ gestation and birthweight < 2000 grams discharged from 2 level III/IV NICUs. We defined EPM at discharge as exclusive direct breastfeeding or unfortified EPM feeds with < 3 supplemental formula bottles/day in lieu of fortification and/or (b) EPM with added fortification via bottle. We performed forward stepwise AIC regression models to determine variables most associated with EPM at discharge, including first-week average total fluid intake (TFI), enteral and parenteral intakes, and day achieving >140 ml/kg/day of enteral feeds. Given the co-linearity of TFI with parenteral and enteral fluids, we performed 2 separate AIC models (the first including TFI and the second including enteral and parenteral fluids).
Results: 85 preterm infants were included; 54 (63%) achieved EPM at NICU discharge (Table 1). Within both AIC models, 3 variables (gestational age, 5-minute Apgar, and day enteral feeds ≥140 mL/kg/day achieved) were positively associated with EPM at discharge, whereas self-identifying as Hispanic was negatively associated with EPM at discharge (Figures 1, 2). Within the first model including TFI, increasing first-week average TFI and higher birthweight were positively associated with EPM at discharge (Figure 1). However, neither birthweight nor average first-week enteral or parenteral intake were selected as significant variables associated with EPM at discharge within the second AIC model (Figure 2).
Conclusion(s): Hispanic ethnicity was associated with >83% reduced odds of discharge on EPM, with further assessment needed on drivers and solutions for this disparity. While increasing average first-week TFI was associated with EPM at discharge, the association disappeared when evaluating first-week enteral and parenteral intake separately. Larger studies accounting for severity of illness and additional societal-social factors are needed to better assess how early NICU nutritional practices influence EPM exposure at discharge.
Table 1. Maternal and Infant Characteristics by exclusive parent’s own milk (EPM) at Discharge versus no EPM at NICU discharge.
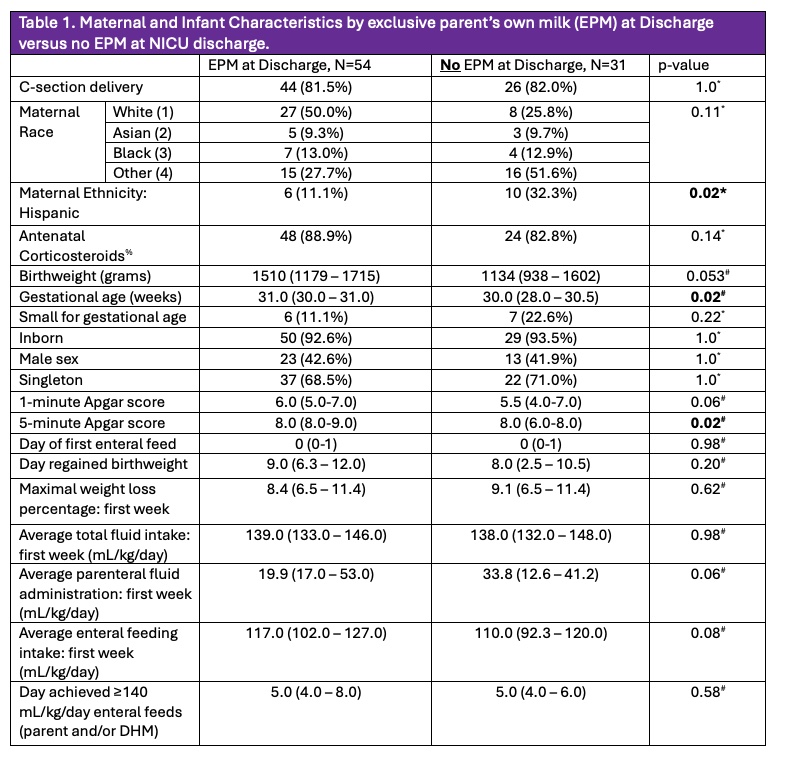 *p-value obtained via Fisher’s Exact Test, #p-value obtained via Kruskal-Walllis Rank Sum Test. All data presented in n(%) for categorical variables or median(interquartile range) for continuous variables. % 2 participants with unknown antenatal corticosteroid exposure within the “No EPM at discharge” group.
*p-value obtained via Fisher’s Exact Test, #p-value obtained via Kruskal-Walllis Rank Sum Test. All data presented in n(%) for categorical variables or median(interquartile range) for continuous variables. % 2 participants with unknown antenatal corticosteroid exposure within the “No EPM at discharge” group.Figure 1: Summary of Final Variable Selection of the 1st AIC Forward Step Regression Model (including total first-week average total fluid intake) with adjusted odds ratios of attainment of exclusive parent’s own milk (EPM) at discharge.
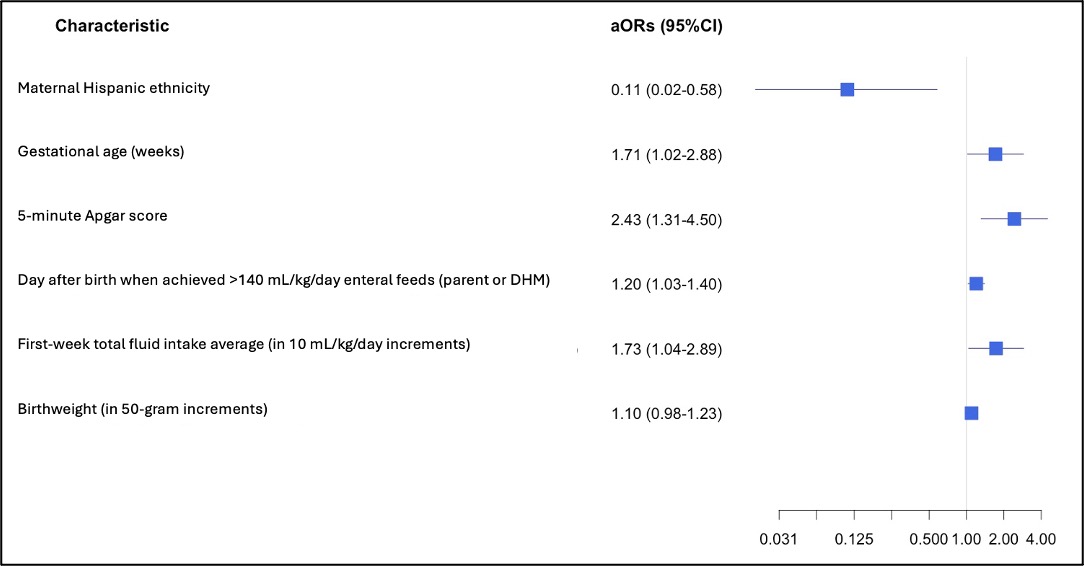 While all variables in Table 1 were initially included in the full model except average enteral and parenteral first-week intake, only 6 variables were found to be most associated with EPM at discharge in the first AIC forward step regression model. These 6 variables are presented in the Forest plot with their associated adjusted odds ratios (aOR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) visually depicted on the x-axis. aOR <1 suggest reduced odds of EPM at discharge whereas aOR >1 suggest increased odds of EPM at discharge.
While all variables in Table 1 were initially included in the full model except average enteral and parenteral first-week intake, only 6 variables were found to be most associated with EPM at discharge in the first AIC forward step regression model. These 6 variables are presented in the Forest plot with their associated adjusted odds ratios (aOR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) visually depicted on the x-axis. aOR <1 suggest reduced odds of EPM at discharge whereas aOR >1 suggest increased odds of EPM at discharge.Figure 2: Summary of Final Variable Selection of 2nd AIC Forward Step Regression Model (including total first-week average parenteral and enteral intake) with adjusted odds ratios of attainment of EPM at discharge.
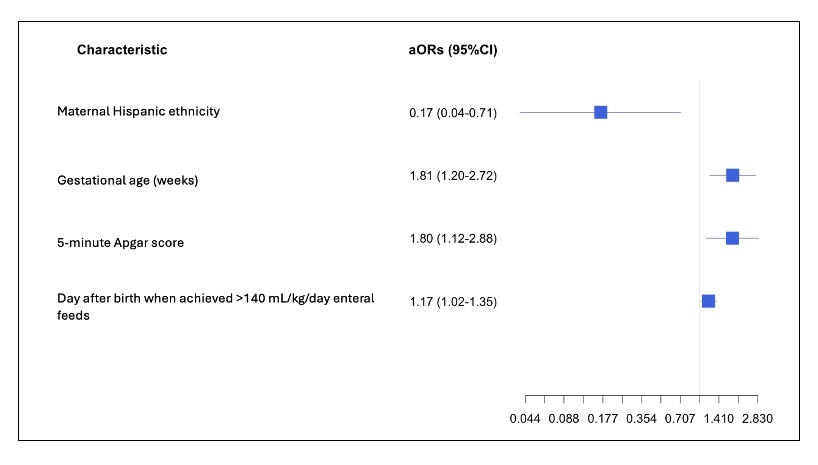 While all variables in Table 1 were initially included in the full model except average first-week total fluid intake (TFI) due to TFI co-linearity of parenteral and enteral intakes, only 4 variables were found to be most associated with EPM at discharge in the second AIC forward step regression model. These 4 variables are presented in the Forest plot with their associated adjusted odds ratios (aOR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) visually depicted on the x-axis. aOR <1 suggest reduced odds of EPM at discharge whereas aOR >1 suggest increased odds of EPM at discharge.
While all variables in Table 1 were initially included in the full model except average first-week total fluid intake (TFI) due to TFI co-linearity of parenteral and enteral intakes, only 4 variables were found to be most associated with EPM at discharge in the second AIC forward step regression model. These 4 variables are presented in the Forest plot with their associated adjusted odds ratios (aOR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) visually depicted on the x-axis. aOR <1 suggest reduced odds of EPM at discharge whereas aOR >1 suggest increased odds of EPM at discharge.
