Neonatal GI Physiology & NEC 1
Session: Neonatal GI Physiology & NEC 1
713 - Effects of Inter-alpha Inhibitor Proteins Administration in a Mouse Model of Necrotizing Enterocolitis
Saturday, April 26, 2025
2:30pm - 4:45pm HST
Publication Number: 713.4948
Karni S. Moshal, University of Oklahoma College of Medicine, Oklahoma City, OK, United States; Jeffrey Eckert, University of Oklahoma College of Medicine, Oklahoma City, OK, United States; Adam Wilson, Oklahoma Childrens Hospital at OU Health, Oklahoma City, OK, United States; Kathryn Burge, University of Oklahoma College of Medicine, Oklahoma City, OK, United States; Addison Franca, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, OK, United States; Joseph Qiu, Prothera Biologics, Providence, RI, United States; James F. Padbury, UCSF, San francisco, CA, United States; Yow-Pin Lim, The Warren Alpert Medical School of Brown University, Providence, RI, United States; Hala Chaaban, Oklahoma University health sciences, Okl, OK, United States

Karni Singh Moshal, Ph. D. (he/him/his)
Staff Scientist
University of Oklahoma College of Medicine
Oklahoma City, Oklahoma, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) is a severe inflammatory disease primarily affecting preterm infants, characterized by significant intestinal damage and high mortality rates. Inter-alpha Inhibitor Proteins (IAIP), known for their anti-inflammatory properties, have shown efficacy in sepsis models. Our previous data using ELISA and bedside point-of-care tests showed that preterm infants with NEC have reduced IAIP levels, supporting its potential as a therapeutic target.
Objective: Evaluate the effects of IAIP administration at different time points relative to NEC induction, focusing on mortality, histological injury scores, and potential sex differences.
Design/Methods: Using a DK NEC model, P14 mouse pups were induced with NEC via intraperitoneal injection of dithizone (33 mg/kg), followed by oral Klebsiella pneumoniae (1 × 10^7 CFU/kg). IAIP (30 mg/kg) was administered at 3-time points: prophylactically (1 hour before NEC induction), early (30 minutes before bacterial gavage), and late (1-hour post-induction). Groups included NEC (n=20), NEC + IAIP (n=20), IAIP only (n=10), and sham (n=6). Pups were monitored for distress and mortality over 16 hours, after which tissues were collected for histological and cytokine analysis of the distal ileum. Mortality was analyzed using Kaplan-Meier survival curves, and histological injury was assessed by ANOVA, with scores ≥2 considered as NEC.
Results: Prophylactic IAIP administration did not reduce mortality or histological injury. Late IAIP administration did not improve survival but showed a trend toward reduced histological injury (p=0.07). Early IAIP treatment was associated with minor improved survival, though not statistically significant (Fig 1A-D). Histological analysis showed that the mean injury score in the NEC + IAIP group (1.5 ± 0.25) was significantly lower than in the NEC group (2.5 ± 0.25, p=0.0014). Sex-specific analysis indicated that IAIP treatment had a more pronounced effect on female survival (77.8% compared to males 61.5%); however, these trends were not statistically significant. No significant sex-based differences in histological injury scores were observed (Fig 2A &B).
Conclusion(s): Early IAIP treatment shows potential in reducing NEC-related intestinal injury. Although survival benefits were more pronounced in females, additional studies are warranted to validate these findings and refine IAIP administration strategies to optimize clinical outcomes, especially when guided by point-of-care IAIP level assessments.
Figure 1.Effect of Early IAIP Administration on Survival and Intestinal Injury in a Mouse Model of NEC.
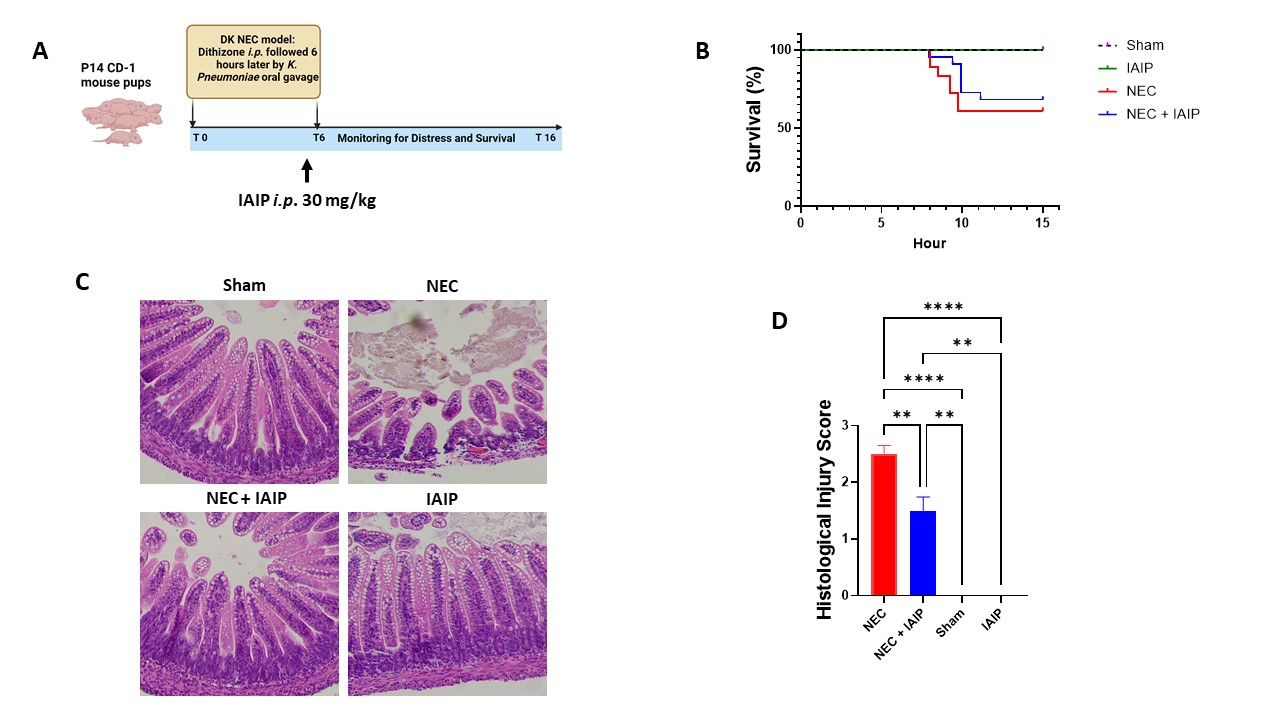 (A) Schematic representation of the experimental design using P14 CD-1 mouse pups. NEC was induced via i.p. injection of dithizone (33 mg/kg) at T0, followed by oral gavage with Klebsiella pneumoniae 6 hours later (T6). IAIP (30 mg/kg) was administered i.p. 30 minutes before bacterial gavage, and the pups were monitored for distress and survival until T16. (B) Kaplan-Meier survival curves depicting the survival rate of pups across different treatment groups: Sham, IAIP only, NEC, and NEC + IAIP. (C) Representative histological sections of the distal ileum from the Sham, NEC, NEC + IAIP, and IAIP groups stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). (D) Quantitative analysis of histological injury scores across groups. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, with significant differences indicated (**p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001).
(A) Schematic representation of the experimental design using P14 CD-1 mouse pups. NEC was induced via i.p. injection of dithizone (33 mg/kg) at T0, followed by oral gavage with Klebsiella pneumoniae 6 hours later (T6). IAIP (30 mg/kg) was administered i.p. 30 minutes before bacterial gavage, and the pups were monitored for distress and survival until T16. (B) Kaplan-Meier survival curves depicting the survival rate of pups across different treatment groups: Sham, IAIP only, NEC, and NEC + IAIP. (C) Representative histological sections of the distal ileum from the Sham, NEC, NEC + IAIP, and IAIP groups stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). (D) Quantitative analysis of histological injury scores across groups. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, with significant differences indicated (**p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001).Figure 2. Sex-Specific Analysis of Early IAIP Administration on Intestinal Injury and Survival in a Mouse Model of NEC
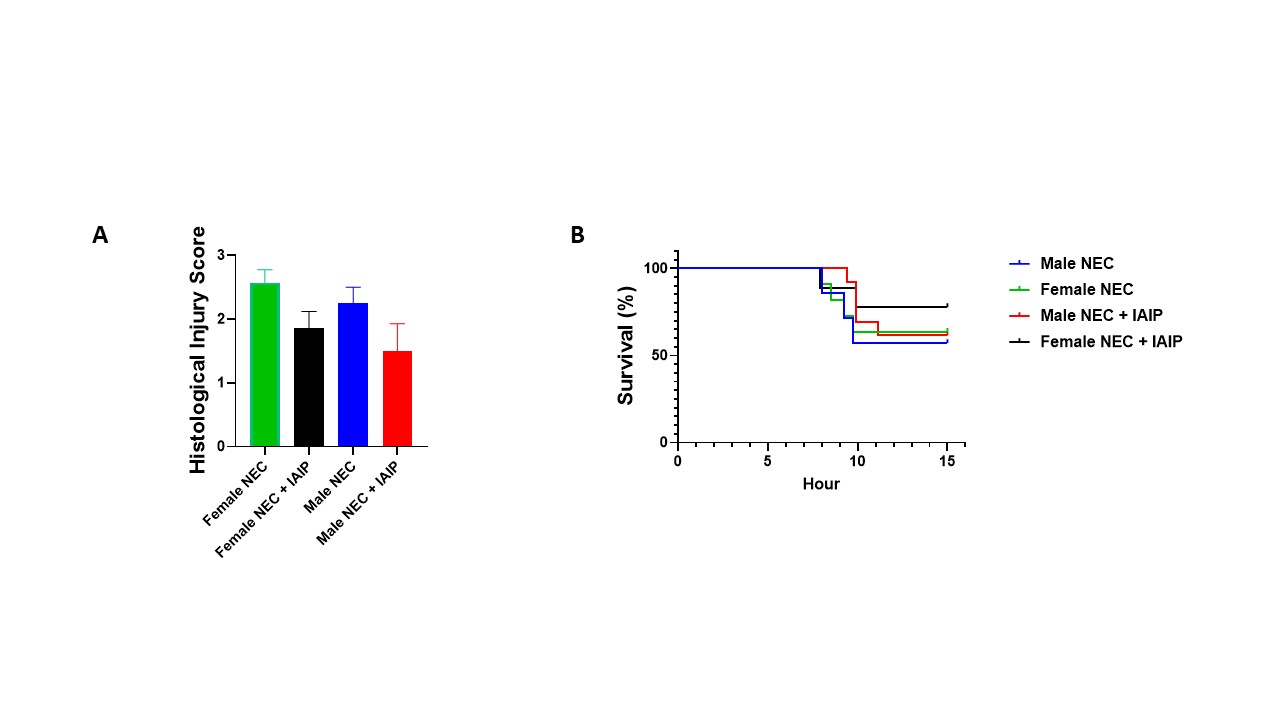 (A) Histological injury scores in male and female mouse pups with NEC and NEC + IAIP treatment. Group sizes were as follows: Female NEC (n=7), Female NEC + IAIP (n=7), Male NEC (n=4), Male NEC + IAIP (n=6). (B) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for male and female mouse pups in the NEC and NEC + IAIP treatment groups. IAIP administration was associated with a more pronounced effect observed in females, although statistical significance was not reached due to sample size limitations.
(A) Histological injury scores in male and female mouse pups with NEC and NEC + IAIP treatment. Group sizes were as follows: Female NEC (n=7), Female NEC + IAIP (n=7), Male NEC (n=4), Male NEC + IAIP (n=6). (B) Kaplan-Meier survival curves for male and female mouse pups in the NEC and NEC + IAIP treatment groups. IAIP administration was associated with a more pronounced effect observed in females, although statistical significance was not reached due to sample size limitations.
