Neonatal Hematology & Bilirubin Metabolism 1
Session: Neonatal Hematology & Bilirubin Metabolism 1
655 - Diagnostic accuracy of handheld point-of-care device (Bilistick) versus laboratory-based quantification for assessing neonatal bilirubin
Monday, April 28, 2025
7:00am - 9:15am HST
Publication Number: 655.4510
Lauren EH. Westenberg, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, Zuid-Holland, Netherlands; Christian V. Hulzebos, Beatrix Children's Hospital, Unversity Medical Center Groningen, Groningen, Groningen, Netherlands; Jasper V. Been, Erasmus MC Sophia Children's Hospital, Rotterdam, Zuid-Holland, Netherlands

Lauren EH Westenberg, MD (she/her/hers)
PhD-Candidate
Erasmus MC
Rotterdam, Zuid-Holland, Netherlands
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Quantification of bilirubin in blood is essential for early diagnosis and treatment of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Handheld point-of-care (POC) devices may be a faster alternative and require less blood volume than conventional laboratory-based bilirubin (LBB), but their diagnostic accuracy is unclear.
Objective: We evaluated the diagnostic accuracy of Bilistick as compared to LBB for quantification of bilirubin in neonates.
Design/Methods: We conducted a prospective multicenter cohort study in nine Dutch midwifery practices, enrolling neonates born after 35 weeks' gestation who were at home within the first week of life. When LBB was deemed necessary based on visual inspection and/or an elevated transcutaneous bilirubin reading, Bilistick was used in parallel by the midwife.
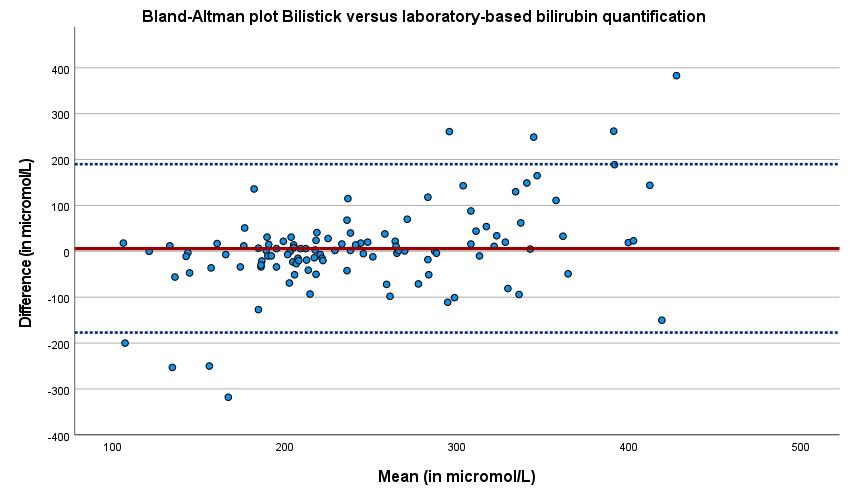
Results: We enrolled 2314 neonates at home (median gestational age 39 weeks; birth weight 3505 grams). A total of 13 hospital-laboratories participated using whole blood on blood gas analyzers or plasma bilirubin on chemistry analyzers. Of the 401 laboratory-based bilirubin quantifications, 115 paired Bilistick assessments were available. Reasons for no Bilistick value being available were: in 101 (25%) Bilistick did not provide a reading and in 185 cases (46%) the midwife either did not use the Bilistick or experienced trouble using the Bilistick equipment. In 28 (24%) of the 115 Bilistick readings an alert of hemolysis was displayed. The Bland-Altman plot of the 115 paired measurements showed a pooled mean difference of 6 µmol/L, with a 95% confidence interval ranging from -177 to 190 μmol/L (Figure 1).
Conclusion(s): Bilistick readings commonly failed and demonstrated substantial imprecision in comparison to LBB readings in otherwise well (near)term newborns managed at home. These aspects need to be improved before routine use of Bilistick in neonatal jaundice management can be recommended in high-income settings.
Figure 1: Bland Altman plot between Bilistick and laboratory-based bilirubin for quantification in neonates.