Emergency Medicine 10
Session: Emergency Medicine 10
512 - Do Children with Community-Acquired Sepsis and Septic Shock meet the Phoenix Criteria while in the Emergency Department?
Monday, April 28, 2025
7:00am - 9:15am HST
Publication Number: 512.4258
Nathan Georgette, Boston Children's Hospital, Brookline, MA, United States; Matthew Eisenberg, Boston Children's Hospital, Boston, MA, United States
- NG
Nathan Georgette, MD (he/him/his)
Instructor in Pediatrics
Boston Children's Hospital
Brookline, Massachusetts, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: The Phoenix criteria for sepsis and septic shock use four organ dysfunction scores and define sepsis as a total score of ≥ 2. Septic shock is defined as sepsis with cardiovascular dysfunction (score ≥ 1). Due to the high threshold for organ dysfunction set out in the Phoenix criteria, many patients with community-acquired sepsis or septic shock may not meet these criteria during their stay in the emergency department (ED).
Objective: First, to determine the frequency of Phoenix criteria sepsis and septic shock among children with suspected infection presenting to a pediatric emergency department (ED). Second, to determine when these patients first met Phoenix criteria. We hypothesized that most patients will meet the Phoenix criteria after disposition from the ED. Because findings in the ED can determine early intervention and disposition, the ED stay was chosen as the timeframe of interest.
Design/Methods: We conducted a secondary analysis of a retrospective cohort of children (age 1 month to 18 years) with suspected infection presenting to a pediatric ED from 2012 through 2021. We excluded patients transferred in from another hospital. The primary outcome was sepsis within 24 hours of ED arrival by Phoenix criteria; the secondary outcome was septic shock within 24 hours of ED arrival by Phoenix criteria. We analyzed time from ED arrival to the outcomes being met.
Results: The cohort N = 141,510, with prevalence of sepsis within 24 hours of ED arrival of 2349 (1.7%) and septic shock within 24 hours of ED arrival of 895 (0.6%) (Table 1). For sepsis, the median time to first meeting Phoenix criteria was 4.5 hrs (IQR 1.6 - 10.3) (Figure 1); 1074/2349 cases (45.7%) met Phoenix criteria for sepsis during the ED stay. The median time to first meet Phoenix septic shock criteria was 5.1 hrs (1.9 – 10.5); 397/895 (44.3%) met Phoenix criteria for septic shock during the ED stay.
Conclusion(s): More than half of all cases of community-acquired sepsis and septic shock do not meet the Phoenix criteria during the ED stay. Caution should be applied if using the Phoenix criteria to determine care in and disposition from the emergency department.
Table 1
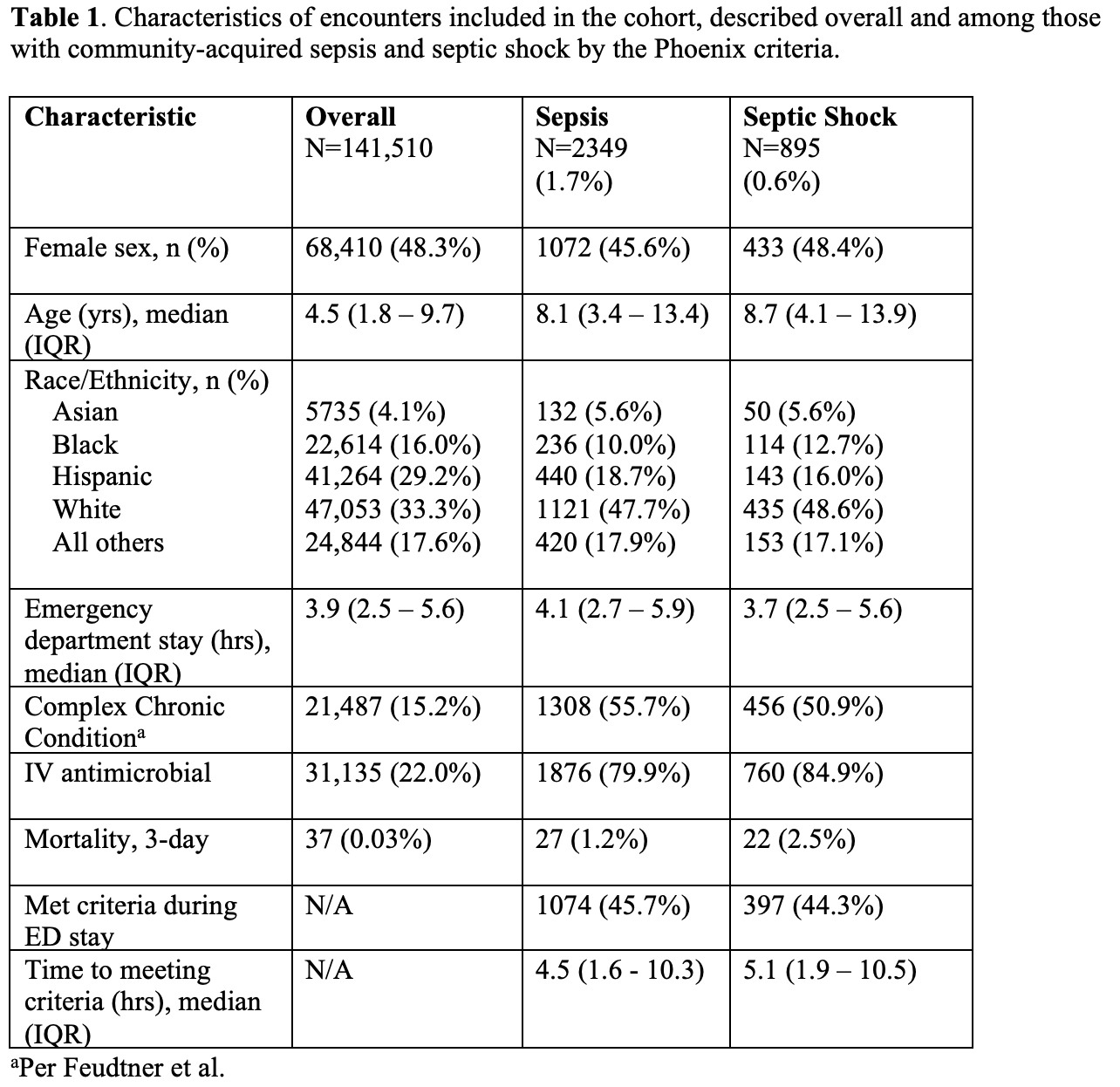 Characteristics of the cohort
Characteristics of the cohortFigure 1
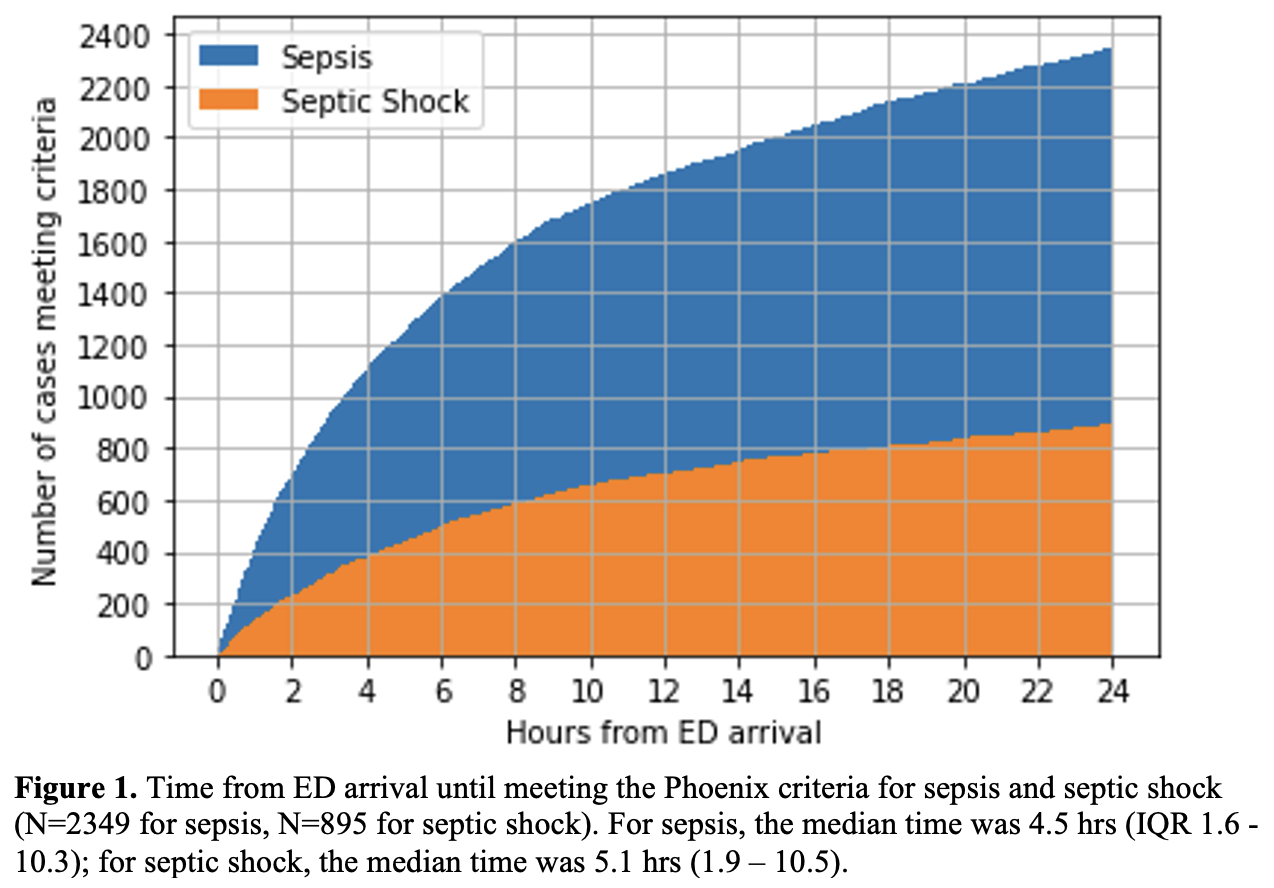 Time to meeting Phoenix criteria
Time to meeting Phoenix criteria
