Neonatal Pulmonology - Clinical 5: Pulmonary Imaging and Lung Function Testing
Session: Neonatal Pulmonology - Clinical 5: Pulmonary Imaging and Lung Function Testing
367 - Evaluating CPAP to HFNC Transitions in Preterm Infants using Electrical Impedance Tomography: a prospective, observational study
Monday, April 28, 2025
7:00am - 9:15am HST
Publication Number: 367.4889
David M. Rub, CHOP, Voorhees, NJ, United States; Natalie Napolitano, Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, United States; Francis W. Simmons, The Children's hospital of Philadelphia, Cherry HIll, NJ, United States; Rachel Mackenzie, Childrens Hospital of Philadelphia, Swedesboro, NJ, United States; Kelle J. Matthews, CHOP, Huntingdon Valley, PA, United States; Elizabeth Foglia, Childrens Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, United States; Howard B.. Panitch, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, PHILADELPHIA, PA, United States

David M. Rub, MD
Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine Fellow
CHOP
Voorhees, New Jersey, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: High flow nasal cannula (HFNC) therapy is increasingly used to wean preterm infants from nasal continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP). The timing and levels of support during transition are variable, partly due to the inability to equate CPAP (cmH₂O) with HFNC (L/min).
Objective: We hypothesized that transitions from CPAP to HFNC result in inconsistent changes in lung aeration, and that substantial decreases in lung volume at transition are associated with subsequent transition failure. We used Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT) to assess lung aeration changes during transitions from CPAP to HFNC in preterm infants.
Design/Methods: Prospective observational study of infants born < 32 weeks gestational age (GA) undergoing a clinically indicated transition from CPAP to HFNC following ≥2 weeks of respiratory support. EIT data were recorded 30-60 minutes before and after transition. The primary outcome was change in end-expiratory lung impedance (ΔEELI). Secondary outcomes included changes in end-inspiratory lung impedance (ΔEILI), tidal volume impedance (TVI), and ventilation heterogeneity. The association between ΔEELI and weight gain over 7 days was assessed. Wilcoxon signed-rank tests, linear and logistic regression were used for analysis.
Results: From 15 subjects, a total of 4,257 breaths were analyzed. No significant difference in ∆EELI was found between HFNC and CPAP (Median ∆: –1.0%; IQR –3.6% to 6.0%; p=0.78). Similarly, no significant differences were observed in secondary outcomes (Table 1). Individually, 4 subjects had >5% increase in EELI after transition, while 2 had >5% decrease (Fig. 1A). The largest ∆EELI decrease (-9.8%) occurred in subject 1, who failed transition. This subject exhibited frequent large TVI peaks, indicative of recruitment breaths (Fig. 1B). A significant inverse relationship was found between ∆EELI and the likelihood of recruitment breaths (p < 0.001) (Fig. 2). Across all patients, we found a significant association between ∆EELI and average daily weight gain over 7 days when adjusting for GA and postnatal age (β = 1.15, P = 0.03, 95% CI [.117, 2.09], adj R2 = 0.42).
Conclusion(s): Transitioning from CPAP to HFNC did not consistently decrease lung aeration in preterm infants. Notably, we identified a distinct respiratory pattern using EIT—characterized by a decrease in EELI coupled with frequent recruitment breaths—that may serve as an early predictor of transition failure. These findings suggest better methods are needed to individualize and titrate respiratory support at the bedside for preterm infants. EIT may serve as a valuable tool to help guide these transitions.
Changes in EIT measures before and after transition to HFNC
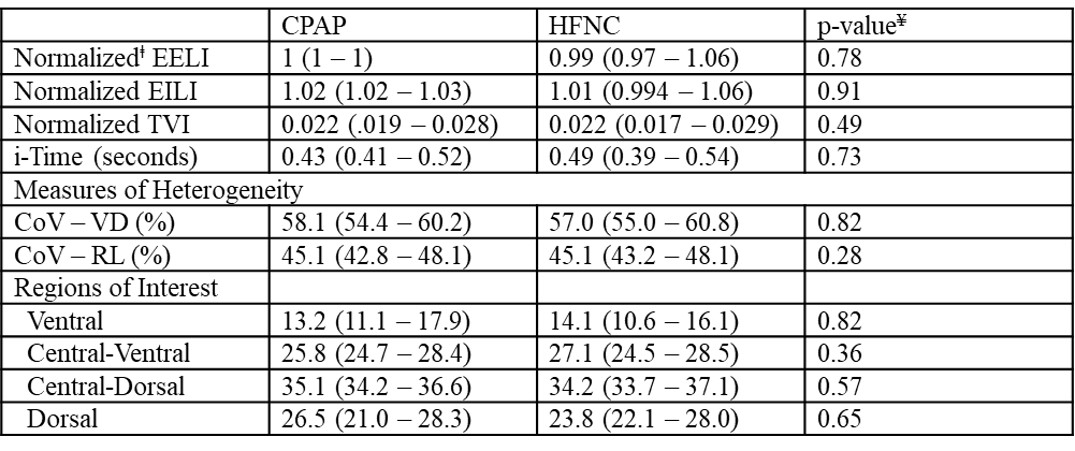 *End-Expiratory Lung Impedance (EELI); End-Inspiratory Lung Impedance (EILI); Tidal Volume Impedance (TVI); Inspiratory Time (i-Time); Center of Ventilation (CoV); Ventral-Dorsal (VD); Right-Left (RL); all values reported as median (IQR) unless otherwise specified.
*End-Expiratory Lung Impedance (EELI); End-Inspiratory Lung Impedance (EILI); Tidal Volume Impedance (TVI); Inspiratory Time (i-Time); Center of Ventilation (CoV); Ventral-Dorsal (VD); Right-Left (RL); all values reported as median (IQR) unless otherwise specified. ¥ Wilcoxon signed-rank test used for comparison before and after transition from CPAP to HFNC
ⱡEELI, EILI, TVI all normalized using baseline mean EELI on CPAP as reference.
Changes in EELI and TVI Before and After Transition from CPAP to HFNC
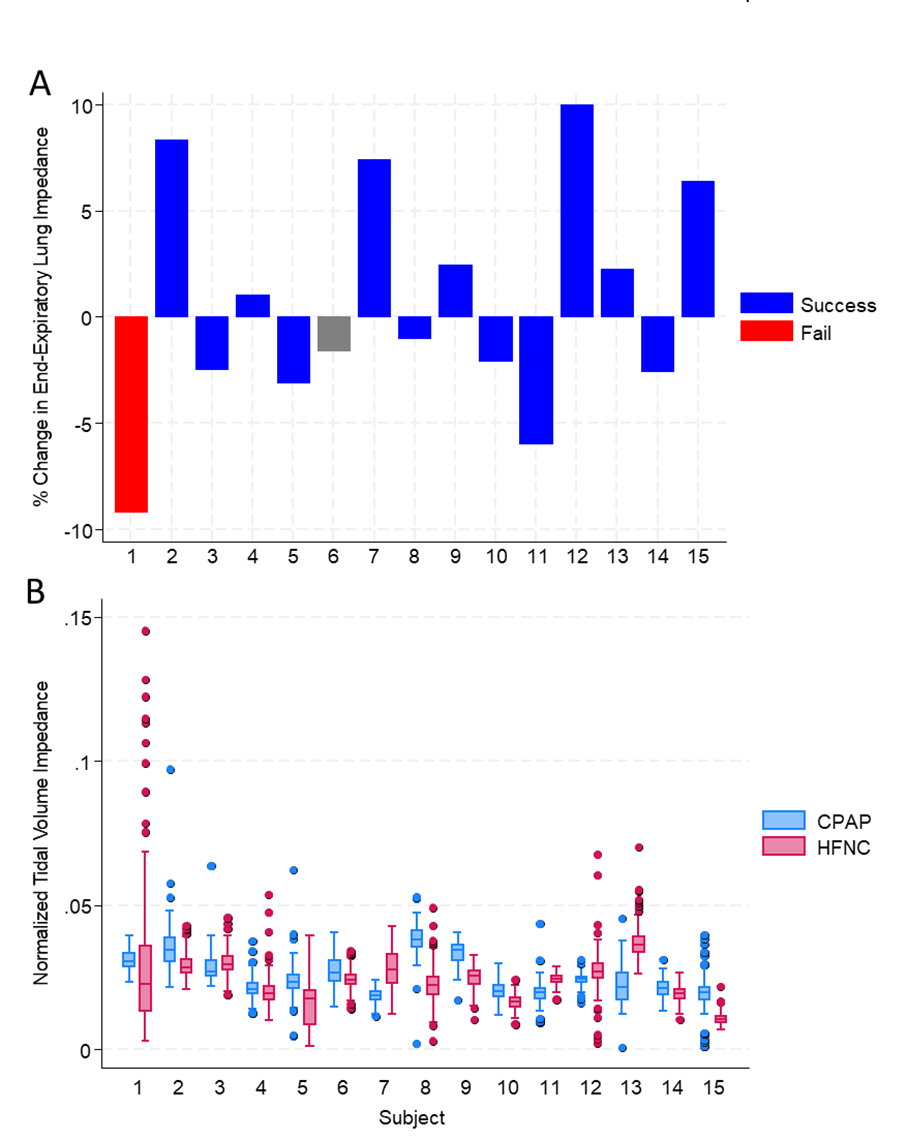 Figure 1A: Percentage change in end-expiratory lung impedance (∆EELI) for each subject following the transition from CPAP to HFNC. Each bar represents an individual subject; blue bars indicate a successful transition, while red bars denote a transition failure. Transition failure defined as reversion to CPAP, nasal intermittent mandatory ventilation (NIMV) or invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) within 7 days of transition. Subject 1 was the only subject meeting the criteria for transition failure. There was incomplete follow-up data for Subject 6.
Figure 1A: Percentage change in end-expiratory lung impedance (∆EELI) for each subject following the transition from CPAP to HFNC. Each bar represents an individual subject; blue bars indicate a successful transition, while red bars denote a transition failure. Transition failure defined as reversion to CPAP, nasal intermittent mandatory ventilation (NIMV) or invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV) within 7 days of transition. Subject 1 was the only subject meeting the criteria for transition failure. There was incomplete follow-up data for Subject 6.Figure 1B: Distribution of normalized tidal volume impedance (TVI) for each subject during CPAP (blue) and HFNC (red). Box plots display the median, interquartile range, and outliers, with individual points representing breaths. Subject 1 exhibited elevated TVI variability and presence of frequent, recruitment breaths (TVI > 99th percentile) on HFNC.
Relationship Between Tidal Volume Impedance and End-Expiratory Lung Impedance Following Transition from CPAP to HFNC
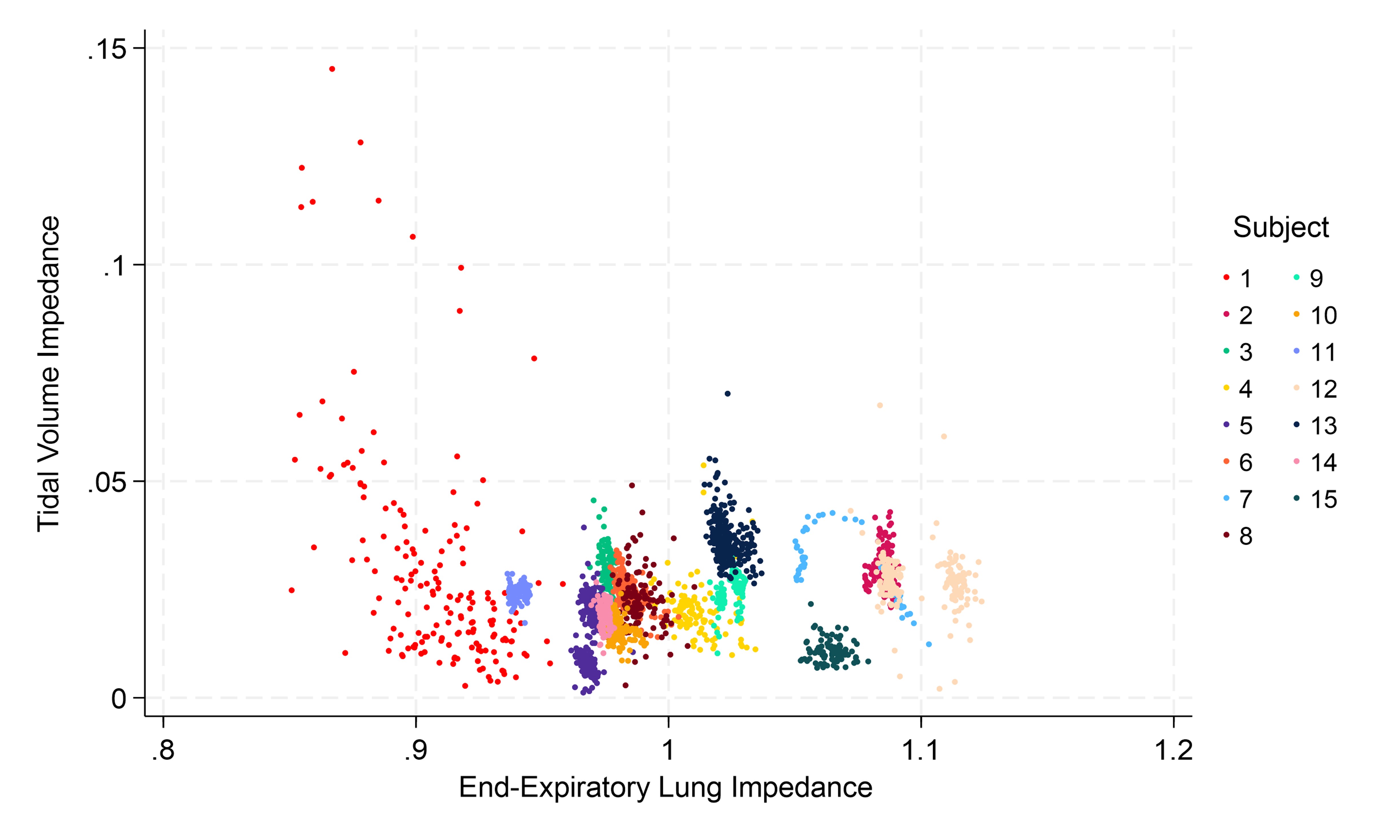 Scatter plot illustrating the relationship between tidal volume impedance (TVI) and end-expiratory lung impedance (EELI) across individual breaths for each subject following the transition from CPAP to HFNC. Each color represents a different subject, as indicated in the legend. Higher TVI values (>99th percentile), particularly observed in Subject 1 (red), indicate frequent recruitment breaths associated with lower EELI (β = -36.02, p < 0.001, 95% CI [-49.03, -23.02], Psuedo R2 = 0.32).
Scatter plot illustrating the relationship between tidal volume impedance (TVI) and end-expiratory lung impedance (EELI) across individual breaths for each subject following the transition from CPAP to HFNC. Each color represents a different subject, as indicated in the legend. Higher TVI values (>99th percentile), particularly observed in Subject 1 (red), indicate frequent recruitment breaths associated with lower EELI (β = -36.02, p < 0.001, 95% CI [-49.03, -23.02], Psuedo R2 = 0.32). 
