Neonatal Neurology 7: Pre-Clinical 1
Session: Neonatal Neurology 7: Pre-Clinical 1
003 - Structural and functional effects of combination complement modulation and hypothermia therapies in a rat model of neonatal HIE
Monday, April 28, 2025
7:00am - 9:15am HST
Publication Number: 3.6611
Angela Saadat, Old Dominion University, NORFOLK, VA, United States; Sai Susmitha Ravi, Children's Hospital of The King's Daughters, Norfolk, VA, United States; Amy Gaines, Children's Hospital of The King's Daughters, Norfolk, VA, United States; Haree K. Pallera, Children's Hospital of The King's Daughters / Eastern Virginia Medical School, Norfolk, VA, United States; Stephanie Newman, Eastern Virginia Medical School, Virginia Beach, VA, United States; Asna Sulaiman, Children's Hospital of The King's Daughters, Norfolk, VA, United States; Carlos Rodrigo Castro Castaneda, Children's Hospital of The King's Daughters, Norfolk, VA, United States; Tushar A. Shah, Children's Hospital of The King's Daughters, Norfolk, VA, United States
- AS
Angela Saadat, PhD (she/her/hers)
Community Assistant Professor
Old Dominion University
NORFOLK, Virginia, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Complement is an innate immune defense with important roles in normal development. In neonatal HIE and other diseases of reperfusion injury, complement pathways are key contributors to excessive inflammation and tissue loss. Complement proteins C3a and C5a are central to all complement pathways. C3a plays a paradoxical role in neuroinflammation and can be anti-inflammatory in acute phases of injury. C5a facilitates inflammation by binding C5aR1, and PMX205 is a small molecule inhibitor of this interaction.
Objective: We aimed to determine if complement modulation following hypoxic-ischemic-injury in conjunction with therapeutic hypothermia (TH) improves structural and functional outcomes (Fig. 1).
Design/Methods: Neonatal HIE was induced in P10-P12 rat pups by Vannucci’s method. Subsets of rats received no treatment (NT, normothermia), complement therapy (CT, PMX205 + C3a peptides), TH, or combination therapy (CT+TH). Structural injury was assessed 3 days post-injury. Lesion area was measured from whole and coronal brain images with ImageJ software. Inflammatory and injury markers assessed by IHC and immunoblotting. Functional deficits were measured with open field exploration, food handling, accelerod, and novel object recognition. Behavioral tests were filmed for offline analysis and movement tracked with ANY-maze software. Data were analyzed with JMP V17, (Cary, NC).
Results: While brain lesion measurements in NT and TH were significantly larger than Sham, treatment with CT and CT+TH mitigated injury, with lesion sizes not significantly different from Sham values. CT reduced lesion area in male rats and demonstrated synergy with TH. In male rats, treatment with CT reduced cortical and hippocampal levels of astrocytes, and treatment with CT+TH reduced levels of activated microglia (Fig. 2).
Male rats treated with CT+TH showed improvement in ability to maintain locomotion on an accelerating rod. Where NT and TH-treated male rats showed recognition memory deficits relative to Sham rats, rats treated with CT and CT+TH demonstrated abilities not different from Sham rats. Topographical disorientation, seen as increased rotations during locomotion, were reduced by CT+TH treatment (Fig. 3).
Conclusion(s): Overall, TH demonstrated more improvement in female rats, CT demonstrated more improvement in male rats, and combining the two treatments CT+TH treatments showed additive improvement in both sexes. These results help us better understand the sex-specific differences in HIE pathology and response to treatment, and may translate to an adjuvant to TH.
Figure. 1. Illustrated hypothesis.
 We hypothesized temporarily attenuating complement following hypoxic-ischemic injury in may lead to less neurological injury and improve functional outcomes in HIE. Further, we tested complement modulation with and without the SOC, TH, to determine if the two therapies synergize.
We hypothesized temporarily attenuating complement following hypoxic-ischemic injury in may lead to less neurological injury and improve functional outcomes in HIE. Further, we tested complement modulation with and without the SOC, TH, to determine if the two therapies synergize. Figure 2. Effects of complement modulation on short-term brain injury and markers of inflammation.
.png) 3 days post-injury. a. Representative brain images and b. lesion area measurements demonstrate treatment with CT and TH each yielded smaller brain lesions compared to untreated rats, and combining the treatments further reduced lesion sizes. When the data were stratified by sex, females benefited from TH and not CT therapies, where males benefitted from CT but not TH, but both benefited from combination therapy. Total lesion area was calculated from hemispheric loss and white infarct area measurements. Floating bars represent median values, shaded bars represent absolute deviation. c. & d. Immunofluorescence demonstrates levels of inflammatory markers in coronal brain sections. Red bars indicate median (c) or mean (d) fluorescence with absolute deviation or standard error bars. * Signifies p-values <0.05>0.005, **p-value <0.005 by Steel-Dwass, Dunnett’s or Wilcoxan methods.
3 days post-injury. a. Representative brain images and b. lesion area measurements demonstrate treatment with CT and TH each yielded smaller brain lesions compared to untreated rats, and combining the treatments further reduced lesion sizes. When the data were stratified by sex, females benefited from TH and not CT therapies, where males benefitted from CT but not TH, but both benefited from combination therapy. Total lesion area was calculated from hemispheric loss and white infarct area measurements. Floating bars represent median values, shaded bars represent absolute deviation. c. & d. Immunofluorescence demonstrates levels of inflammatory markers in coronal brain sections. Red bars indicate median (c) or mean (d) fluorescence with absolute deviation or standard error bars. * Signifies p-values <0.05>0.005, **p-value <0.005 by Steel-Dwass, Dunnett’s or Wilcoxan methods.Figure 3. Functional effects of complement modulation in HIE.
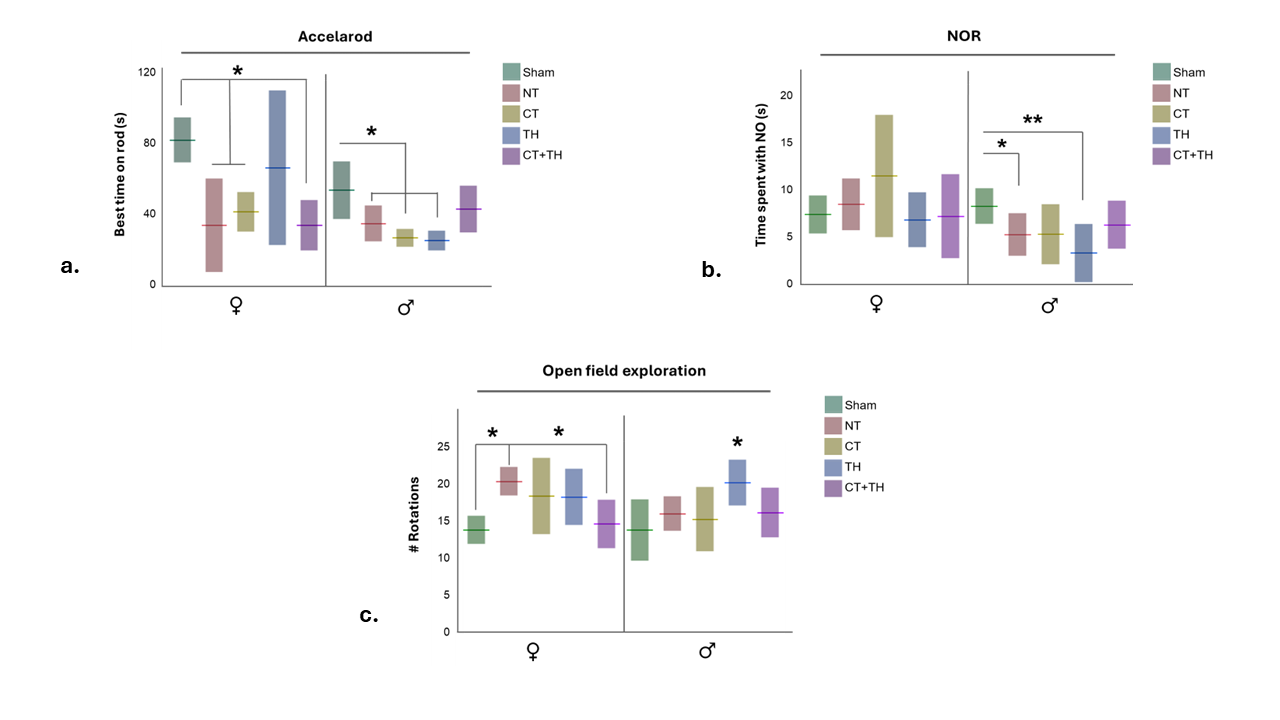 a. Rats were challenged to maintain locomotion on a rotating rod that accelerated in speed over 60s. b. Memory was tested in rats with the novel object recognition was test. c. General movement and exploration was assessed in the open field test. Floating bars indicate median (a) or mean (b & c), and shaded bars absolute deviation or standard deviation. * Signifies p-values <0.05>0.005, **p-value <0.005 by Wilcoxan or Tukey’s method.
a. Rats were challenged to maintain locomotion on a rotating rod that accelerated in speed over 60s. b. Memory was tested in rats with the novel object recognition was test. c. General movement and exploration was assessed in the open field test. Floating bars indicate median (a) or mean (b & c), and shaded bars absolute deviation or standard deviation. * Signifies p-values <0.05>0.005, **p-value <0.005 by Wilcoxan or Tukey’s method.Figure. 1. Illustrated hypothesis.
 We hypothesized temporarily attenuating complement following hypoxic-ischemic injury in may lead to less neurological injury and improve functional outcomes in HIE. Further, we tested complement modulation with and without the SOC, TH, to determine if the two therapies synergize.
We hypothesized temporarily attenuating complement following hypoxic-ischemic injury in may lead to less neurological injury and improve functional outcomes in HIE. Further, we tested complement modulation with and without the SOC, TH, to determine if the two therapies synergize. Figure 2. Effects of complement modulation on short-term brain injury and markers of inflammation.
.png) 3 days post-injury. a. Representative brain images and b. lesion area measurements demonstrate treatment with CT and TH each yielded smaller brain lesions compared to untreated rats, and combining the treatments further reduced lesion sizes. When the data were stratified by sex, females benefited from TH and not CT therapies, where males benefitted from CT but not TH, but both benefited from combination therapy. Total lesion area was calculated from hemispheric loss and white infarct area measurements. Floating bars represent median values, shaded bars represent absolute deviation. c. & d. Immunofluorescence demonstrates levels of inflammatory markers in coronal brain sections. Red bars indicate median (c) or mean (d) fluorescence with absolute deviation or standard error bars. * Signifies p-values <0.05>0.005, **p-value <0.005 by Steel-Dwass, Dunnett’s or Wilcoxan methods.
3 days post-injury. a. Representative brain images and b. lesion area measurements demonstrate treatment with CT and TH each yielded smaller brain lesions compared to untreated rats, and combining the treatments further reduced lesion sizes. When the data were stratified by sex, females benefited from TH and not CT therapies, where males benefitted from CT but not TH, but both benefited from combination therapy. Total lesion area was calculated from hemispheric loss and white infarct area measurements. Floating bars represent median values, shaded bars represent absolute deviation. c. & d. Immunofluorescence demonstrates levels of inflammatory markers in coronal brain sections. Red bars indicate median (c) or mean (d) fluorescence with absolute deviation or standard error bars. * Signifies p-values <0.05>0.005, **p-value <0.005 by Steel-Dwass, Dunnett’s or Wilcoxan methods.Figure 3. Functional effects of complement modulation in HIE.
 a. Rats were challenged to maintain locomotion on a rotating rod that accelerated in speed over 60s. b. Memory was tested in rats with the novel object recognition was test. c. General movement and exploration was assessed in the open field test. Floating bars indicate median (a) or mean (b & c), and shaded bars absolute deviation or standard deviation. * Signifies p-values <0.05>0.005, **p-value <0.005 by Wilcoxan or Tukey’s method.
a. Rats were challenged to maintain locomotion on a rotating rod that accelerated in speed over 60s. b. Memory was tested in rats with the novel object recognition was test. c. General movement and exploration was assessed in the open field test. Floating bars indicate median (a) or mean (b & c), and shaded bars absolute deviation or standard deviation. * Signifies p-values <0.05>0.005, **p-value <0.005 by Wilcoxan or Tukey’s method.
