Neonatal Pulmonology - Clinical 5: Pulmonary Imaging and Lung Function Testing
Session: Neonatal Pulmonology - Clinical 5: Pulmonary Imaging and Lung Function Testing
364 - Dynamic lung stress in extremely preterm infants estimated with electrical activity of the diaphragm
Monday, April 28, 2025
7:00am - 9:15am HST
Publication Number: 364.4706
Daniele De Luca, APHP - Paris Saclay University, Paris, Ile-de-France, France; Sofia De La Rubia Ortega, APHP-Paris Saclay University, Paris, Ile-de-France, France; francesca Miselli, AdventHealth for Children, modena, Emilia-Romagna, Italy; Laura Vivalda, Antoine Beclere Medical Center, Paris, Ile-de-France, France; Barbara Loi, Antoine Beclere Medical Center - Paris Saclay University Hospitals, Paris, Ile-de-France, France; Guillaume Emeriaud, CHU Sainte Justine, Montreal, PQ, Canada; Massimo Antonelli, Catholic University, Rome, Lazio, Italy; Domenico Luca Grieco, Università Cattolica del Sacro Cuore, Rome, Lazio, Italy

Daniele De Luca, n/a (he/him/his)
Full Professor of Neonatology
APHP Paris Saclay University
Paris, Ile-de-France, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Transpulmonary pressure represents the “stress” to which the lung is subjected and is a main determinant of patient self-inflicted lung injury (PSILI). Nonetheless, this has not been studied in neonates, due to the difficulty to obtain reliable esophageal pressure measurements, particularly in preterm patients.
Objective: To describe dynamic lung stress (i.e., dynamic transpulmonary pressure (PL)) values in neonates with or without lung diseases estimated electrical activity of the diaphragm (EAdi) and to validate measurements with diaphragmatic ultrasound and oxygenation metrics.
Design/Methods: Five term neonates with no lung disease (NLD), 10 preterm neonates with RDS and 25 preterm infants with evolving BPD, all ventilated with non-invasive NAVA, were enrolled. EAdi was captured over 1’. Preductal SpO2, FiO2 and ventilator setting were simultaneously recorded. Esophageal pressure (Pes) swing was estimated from EAdi swing as previously described.(1) Diaphragmatic thickening fraction (TF) was assessed within 1h from the recording.
Results: Electromiographic and pressure data were summarised as mean of each breath in NLD (n=5; 216 breaths), RDS (n=10; 509 breaths) and evolving BPD (n=25; 1143 breaths) patients. EAdi, Pes, PL and TF are not different between groups (Tab.1). No patient failed non-invasive ventilation and needed intubation, however 6%, 17% and 27% of breaths have a PL >= 25 cmH2O in NLD, RDS and BPD group, respectively. In a subgroup of patients, there are significant correlations between EAdi and TF, TF and Pes, TF and SpO2/FiO2 as well as between SpO2/FiO2 and PL (Fig.1).
Conclusion(s): Dynamic lung stress estimated using EAdi is on average similar between non-invasively ventilated neonates with RDS, evolving BPD and controls. Sick neonates have however higher proportions of breaths with relevant lung stress (i.e., transpulmonary pressure swing >= 25 cmH2O). Estimations obtained with EAdi significantly correlate with diaphragmatic effort and oxygenation.
References: Essouri S et al. Pediatr Crit Care Med 2019 Jul;20(7):e319-e325. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000001981.
Tab.1.Spontaneous breathing effort and dynamic transpulmonary pressure
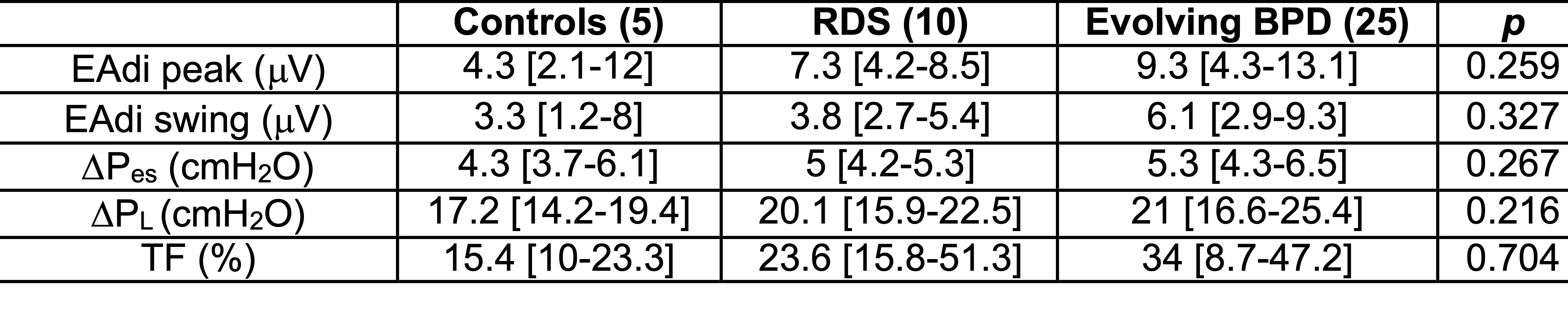 Data are expressed as median [25th – 75th percentile] and analyzed with Kruskal-Wallis test. Electromiographic and pressure data are based on the mean of each breath in patients with no lung disease (n=5; 216 breaths), with RDS (n=10; 509 breaths) and evolving BPD (n=25; 1143 breaths). Ultrasound diaphragmatic measurements were obtained in a subgroup of 23 patients (4 controls, 6 with RDS and 13 with evolving BPD). Abbreviations: BPD: bronchopulmonary dysplasia; EAdi: electrical activity of the diaphragm; Pes: esophageal pressure swing; PL: dynamic transpulmonary pressure; RDS: respiratory distress syndrome; TF: thickening fraction.
Data are expressed as median [25th – 75th percentile] and analyzed with Kruskal-Wallis test. Electromiographic and pressure data are based on the mean of each breath in patients with no lung disease (n=5; 216 breaths), with RDS (n=10; 509 breaths) and evolving BPD (n=25; 1143 breaths). Ultrasound diaphragmatic measurements were obtained in a subgroup of 23 patients (4 controls, 6 with RDS and 13 with evolving BPD). Abbreviations: BPD: bronchopulmonary dysplasia; EAdi: electrical activity of the diaphragm; Pes: esophageal pressure swing; PL: dynamic transpulmonary pressure; RDS: respiratory distress syndrome; TF: thickening fraction. Fig.1. Correlations between diaphragmatic function, spontaneous breathing effort, dynamic transpulmonary pressure and oxygenation.
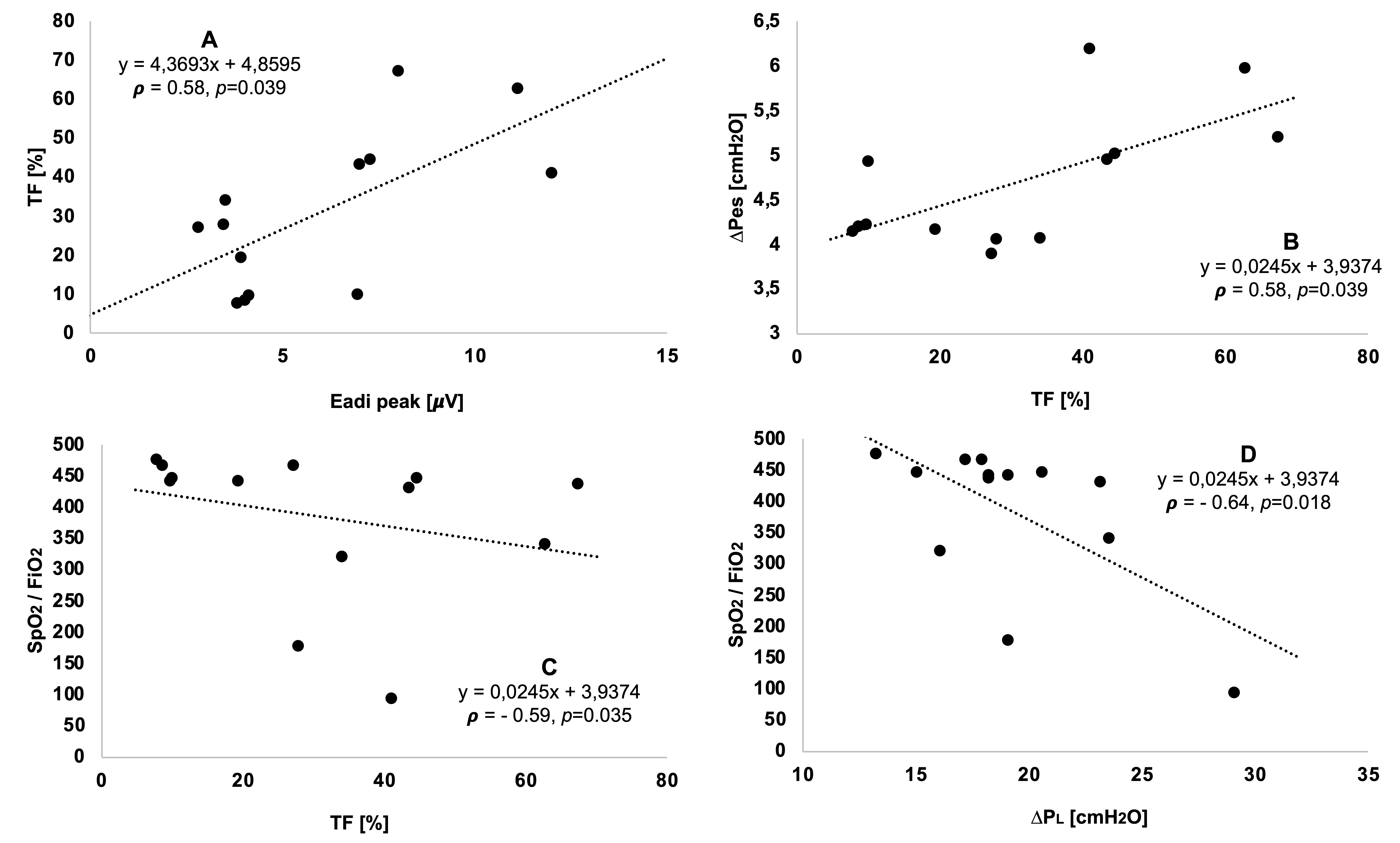 Analyses performed on a subgroup of extremely preterm infants for whom data were available (n=13, 9 with evolving BPD and 4 with RDS). Graphs show the correlation line, its equation and Spearman correlation coefficient. Panel A shows the relationship between peak electrical activity of the diaphragm and its thickening fraction. Panel B shows the relationship between the thickening fraction of the diaphragm and the esophageal pressure swing. Panel C shows the relationship between the thickening fraction of the diaphragm and the SpO2/FiO2 ratio. Panel D shows the relationship between dynamic transpulmonary pressure and the SpO2/FiO2 ratio. Abbreviations: BPD: bronchopulmonary dysplasia; EAdi: electrical activity of the diaphragm; Pes: esophageal pressure swing; PL: dynamic transpulmonary pressure; RDS: respiratory distress syndrome; SpO2/FiO2: pre-ductal peripheral hemoglobin saturation / inspired oxygen fraction ratio; TF: thickening fraction of the diaphragm.
Analyses performed on a subgroup of extremely preterm infants for whom data were available (n=13, 9 with evolving BPD and 4 with RDS). Graphs show the correlation line, its equation and Spearman correlation coefficient. Panel A shows the relationship between peak electrical activity of the diaphragm and its thickening fraction. Panel B shows the relationship between the thickening fraction of the diaphragm and the esophageal pressure swing. Panel C shows the relationship between the thickening fraction of the diaphragm and the SpO2/FiO2 ratio. Panel D shows the relationship between dynamic transpulmonary pressure and the SpO2/FiO2 ratio. Abbreviations: BPD: bronchopulmonary dysplasia; EAdi: electrical activity of the diaphragm; Pes: esophageal pressure swing; PL: dynamic transpulmonary pressure; RDS: respiratory distress syndrome; SpO2/FiO2: pre-ductal peripheral hemoglobin saturation / inspired oxygen fraction ratio; TF: thickening fraction of the diaphragm.
