Neonatal/Infant Resuscitation 4
Session: Neonatal/Infant Resuscitation 4
405 - Targeted Educational Intervention to Improve Knowledge, Skills, and Confidence in Laryngeal Mask Insertion among Nurse NRP Providers and Instructors
Monday, April 28, 2025
7:00am - 9:15am HST
Publication Number: 405.6731
Sura Lee, Childrens Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, United States; Lauren Heimall, Childrens Hospital of Philadelphia, Westmont, NJ, United States; Brielle Formanowski, Children's Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, United States; Paul Wildenhain, Childrens Hospital of Philadelphia, Wilmington, DE, United States; Jennifer Smolenski, CHOP, Phoenixville, PA, United States; Anne Ades, Childrens Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, United States; Kari Roberts, University of Minnesota, St Paul, MN, United States; Elizabeth Foglia, Childrens Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia, PA, United States
- SL
Sura Lee, MSN
Nurse Practitioner
Children's Hospital of Philadelphia
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Laryngeal Mask (LM) insertion is a critical skill for Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) providers. Little is known about nurse NRP providers’ knowledge, skills, and confidence (KSC) for LM insertion. We hypothesized that (1) nurse NRP instructors are not confident or skilled in LM placement, resulting in suboptimal training for the nurse NRP providers they are teaching during instructor-led NRP classes and (2) a targeted intervention directed at instructors would directly improve KSC for LM insertion for both groups.
Objective: 1. During the Pre-Intervention Phase (Pre-I), establish providers’ baseline KSC level for LM insertion. 2. During the Intervention Phase, measure impact of a targeted Educational Session (ES) for instructors. 3. During the Post-Intervention Phase (Post-I), assess new group of providers’ KSC levels after attending an instructor led class with an instructor after their ES.
Design/Methods: Pre/Post intervention study. In Pre-I, provider subjects’ cognitive and technical skills in LM insertion were measured using a 9-point “LM scale.” All 9 items were scored as yes/no; 2 items assessed cognitive skills, and 7 items assessed technical skills. Confidence was assessed using a 5-point Likert scale. Study intervention was a targeted ES delivered to instructors. Primary outcome was LM scale compared between Pre-I and Post-I providers using the Wilcoxon rank sum. Secondary outcome was confidence score for providers and instructors, compared between Pre-I and Post-I.
Results: “LM scale” were equal in Pre-I and Post-I among providers with median scores of 8. Among instructors, the median “LM scale” increased from 8 (IQR 7, 9) to 9 (IQR 9, 9) after the ES (p=0.02; Figure 1). Pre-I and Post-I provider’s confidence level for inserting a LM were “not confident” 80% vs 32% (p=0.003). Instructor’s Pre-I vs Post-I confidence levels for inserting a LM were “not confident” 70% vs 0% (p=0.002;Figure 2). Pre-I, 50% of instructors felt “not confident” in teaching didactic and hands-on skills of LM, however, after the ES, 80% became “very confident” (p=0.004;Figure 3).
Conclusion(s): High “LM scale” scores for both Pre-I and Post-I imply that providers and instructors have the knowledge and the skills in LM insertion. The low confidence level suggests it is a barrier in LM use in this population. Since the targeted ES training significantly improved one’s confidence level, focusing on enhancing instructors’ KSC could result in downstream improvement for provider’s overall competence and confidence.
Cognitive and Technical Skills Measured using 9-Point LM Scale among NRP-Providers and NRP-Instructors during Pre-Intervention and Post-Intervention Phase
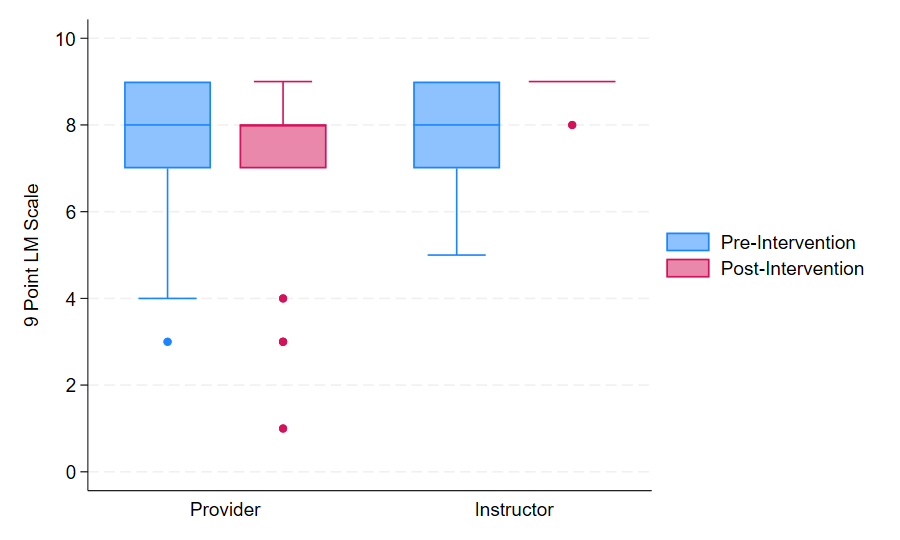 Instructor's "LM Scale" p=0.02
Instructor's "LM Scale" p=0.02Confidence Levels among NRP-Providers and NRP-Instructors in Inserting the LM
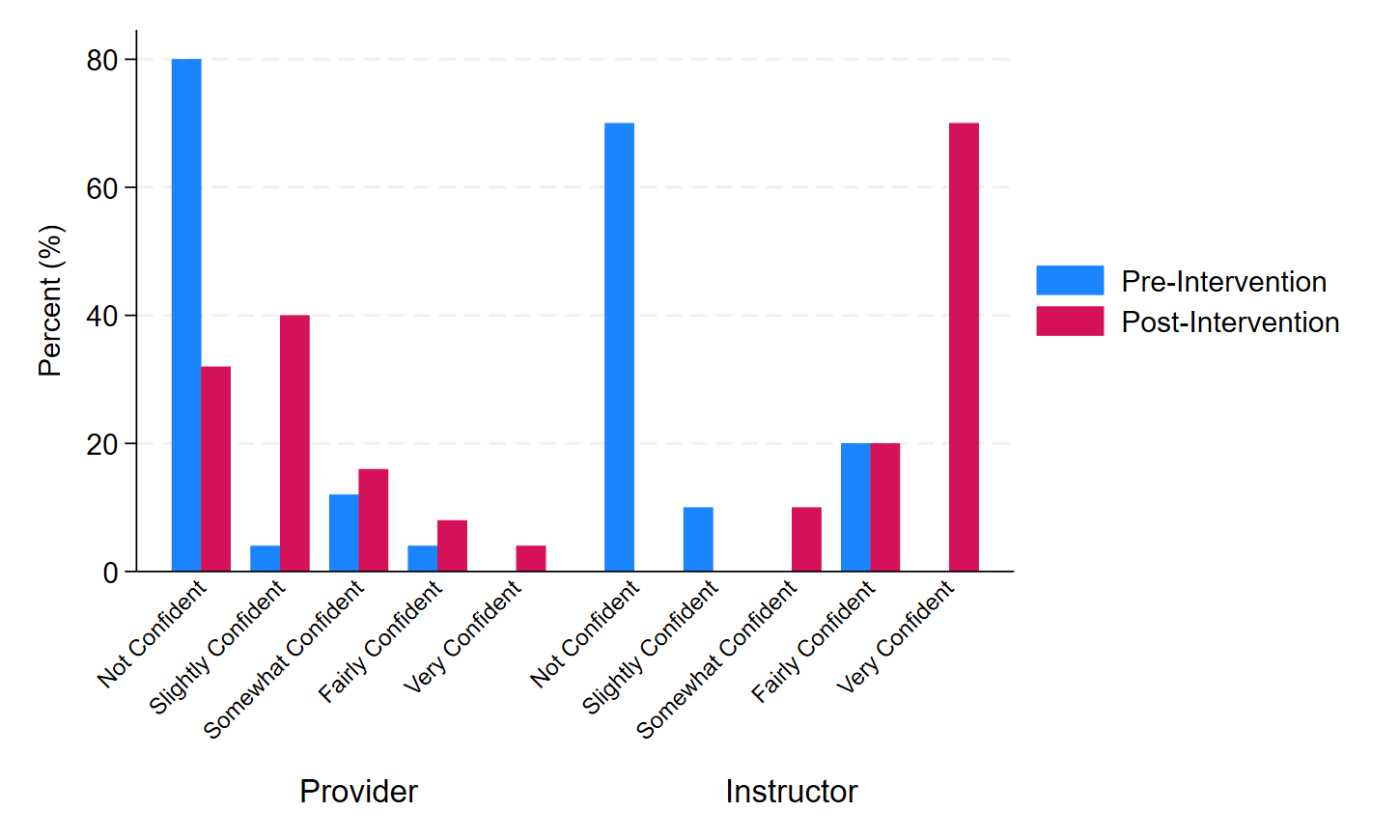 Provider's Pre-I and Post-I Confidence Level for inserting a LM "not confident" (p=0.003)
Provider's Pre-I and Post-I Confidence Level for inserting a LM "not confident" (p=0.003)Confidence Levels among NRP-Instructors Teaching Didactic and Hands-On Skills of LM
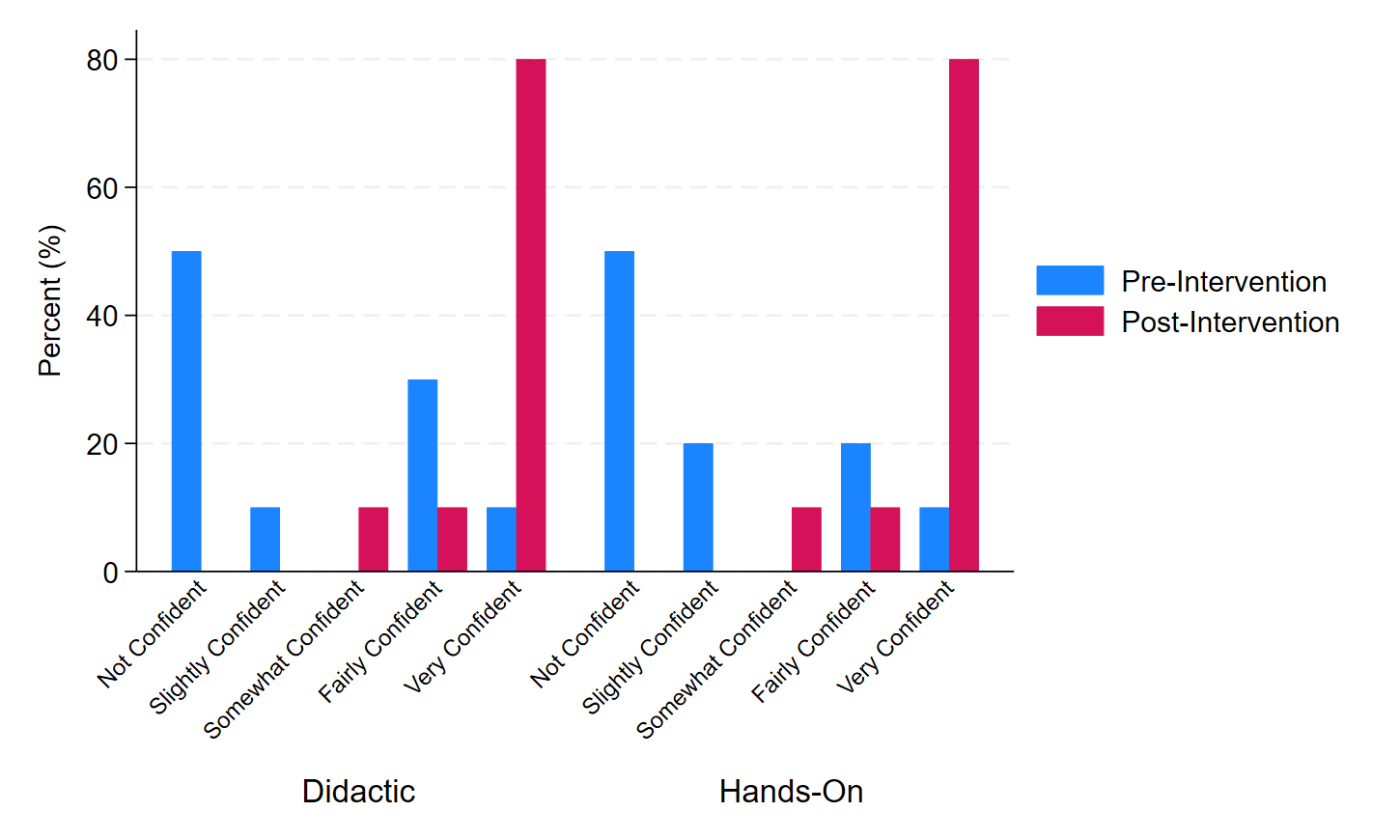 Instructor’s Pre-I vs Post-I Confidence Level for inserting a LM “not confident” (p=0.002)
Instructor’s Pre-I vs Post-I Confidence Level for inserting a LM “not confident” (p=0.002)After the ES, 80%of the instructors became “very confident” in teaching Didactic and Hands-On Skills of LM (p=0.004)

