Genomics/Epigenomics 1
Session: Genomics/Epigenomics 1
384 - Recessive variants in WSB2 encoding a substrate receptor of E3 ubiquitin ligase underlie a neurodevelopmental syndrome
Friday, April 25, 2025
5:30pm - 7:45pm HST
Publication Number: 384.6211
Shiyu Luo, University of Miami Leonard M. Miller School of Medicine, Miami, FL, United States; Valérie Gailus-Durner, Helmholtz Munich, Neuherberg, Bayern, Germany; Bobbi McGivern, GeneDx, Gaithersburg, MD, United States; Qifei Li, University of Miami Miller School of Medicine and Holtz Children's Hospital, Miami, FL, United States; Jessica Kottmeier, University of Missouri, Columbia, MO, United States; Mai-Lan Ho, University of Missouri-Columbia School of Medicine, Columbia, MO, United States; Erfan Aref-Eshghi, GeneDx, Philadelphia, PA, United States; Amanda Brodeur, University of Missouri-Columbia School of Medicine, Columbia, MO, United States; Klaus Schmitz-Abe, University of Miami Leonard M. Miller School of Medicine, Miami, FL, United States; Casie A. Genetti, Boston Children's Hospital, Boston, MA, United States; Jonathan M. Picker, Boston Childrens Hospital, Boston, MA, United States; Reem Ibrahim Bux, Hamad Medical Corporation, Doha, Ad Dawhah, Qatar; Helmut Fuchs, Helmholtz Munich, Neuherberg, Bayern, Germany; Martin Hrabě de Angelis, Helmholtz Zentrum München GmbH, Neuherbreg, Bayern, Germany; Pankaj B.. Agrawal, University of Miami Leonard M. Miller School of Medicine, Miami, FL, United States
- SL
Shiyu Luo, PhD (she/her/hers)
Research assistant professor
University of Miami Leonard M. Miller School of Medicine
Miami, Florida, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Neurodevelopmental disorders (NDDs) represent a large group of disorders arising from alterations of tightly coordinated processes that regulate development and function of the brain, including intellectual disability, autism spectrum disorders, and epilepsy. With genomic advances, novel genes and related pathways are being identified at a rapid pace, but a significant gap continues to exist in our molecular understanding of NDDs.
Objective: To describe a novel disease-causing gene linked with a neurodevelopmental syndrome.
Design/Methods: Participants were identified through the Manton Center for Orphan Disease Research, GeneDx, and GeneMatcher. Informed consent has been obtained from all subjects or their legal guardians, and all clinical investigations adhered to the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Exome and genome sequencing were performed by GeneDx and data analyzed using a custom-developed pipeline. The Wsb2-knockout (KO) mice were derived from the International Knockout Mouse Consortium (Knockout Mouse Project (KOMP) Repository, IKMC project 22842), which is developed by the Monterotondo Mouse Clinic. From the age of 8-16 weeks, the Wsb2-KO mice were phenotyped systematically in the German Mouse Clinic (GMC) at Helmholtz Munich and in accordance with the standardized phenotyping pipeline of the IMPC.
Results: Here we report three unrelated individuals (Fig. 1) presenting with low birth weight, neurodevelopmental delay, hypotonia, eye/vision problems, and dysmorphic features, all of whom are homozygous for extremely rare and predicted loss-of-function (pLoF) variants in WSB2 inherited from consanguineous parents. Interestingly, Wsb2-KO mice exhibited several neurological findings that include hyperactivity, decreased exploration, and hyper alertness (Fig. 2). The Wsb2-KO mice weighed less, had a lower heart rate, and depicted an abnormal retinal blood vessel morphology and vasculature pattern along with decreased total thickness of the retina (Fig. 3). Both male and female Wsb2-KO mice were infertile and histological examination of testes revealed severe testicular tubular atrophy and Leydig cell hyperplasia.
Conclusion(s): In summary, our study provides evidence that recessive WSB2 variants result in a syndromic neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by global developmental delays, cognitive impairments, hypotonia, microcephaly and visual impairments with or without seizures.
Figure 1. Identification of WSB2 variants in three individuals featuring syndromic NDDs.
.jpg) (A) Representative schematic of WSB2 gene (NM_018639) containing seven WD-repeats and a suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) box in the C-terminus. The WSB2 variants are positioned in WD1, WD2, and SOCS box domain, respectively. (B) Common features of the three individuals carrying WSB2 homozygous variants, as indicated in grey.Key: GDD = global developmental delay; ID = intellectual disability (C) Representative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of individual 2 (I:2) with homozygous c.399del p.(Q134Rfs*14) at 12 months of age. (i) Sagittal T1-weighted MRI showing microcephaly, callosal hypogenesis (white arrow), tectal dysplasia (yellow arrow), and severe cerebellar hypoplasia/atrophy (dotted oval). (ii and iii) Axial T1- and T2-weighted MRI show undersulcation and white matter hypomyelination for age. (iv-vi) Coronal T2-weighted with fat suppression show small olfactory bulbs (black arrows), optic nerves (white arrows), and hippocampi (yellow arrows).
(A) Representative schematic of WSB2 gene (NM_018639) containing seven WD-repeats and a suppressor of cytokine signaling (SOCS) box in the C-terminus. The WSB2 variants are positioned in WD1, WD2, and SOCS box domain, respectively. (B) Common features of the three individuals carrying WSB2 homozygous variants, as indicated in grey.Key: GDD = global developmental delay; ID = intellectual disability (C) Representative magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of individual 2 (I:2) with homozygous c.399del p.(Q134Rfs*14) at 12 months of age. (i) Sagittal T1-weighted MRI showing microcephaly, callosal hypogenesis (white arrow), tectal dysplasia (yellow arrow), and severe cerebellar hypoplasia/atrophy (dotted oval). (ii and iii) Axial T1- and T2-weighted MRI show undersulcation and white matter hypomyelination for age. (iv-vi) Coronal T2-weighted with fat suppression show small olfactory bulbs (black arrows), optic nerves (white arrows), and hippocampi (yellow arrows).Figure 2. Behavioral testing revealed decreased exploratory behavior in response to a novel environment and blunted acoustic reactivity in Wsb2-KO mice.
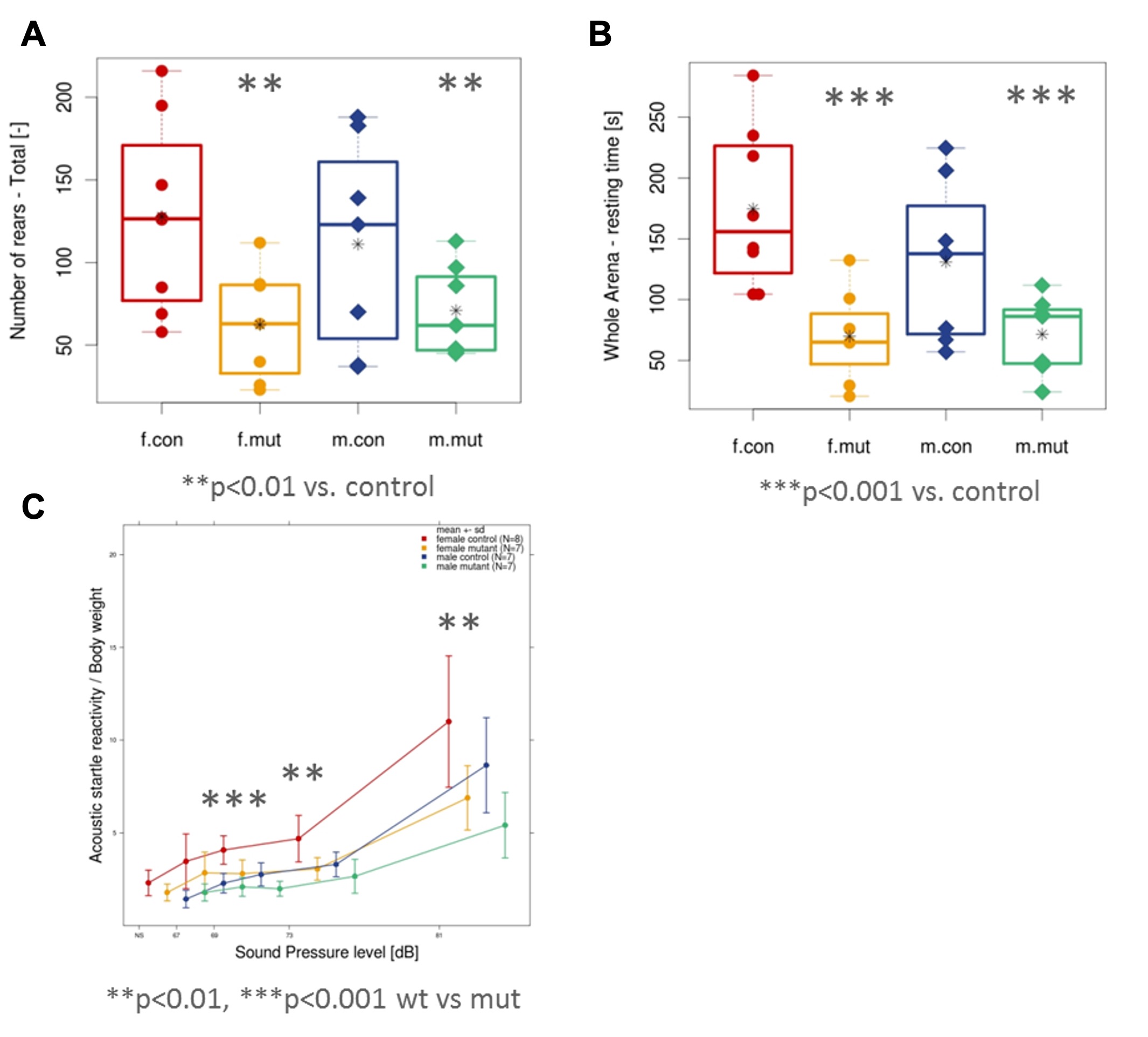 In the novel open field test, the mutant mice showed decreased rearing activity (A) and decreased resting time (B) when compared to control mice. (C) Prepulse Inhibition (PPI)/Acoustic Startle Response (ASR) testing showed decreased acoustic reactivity in the mutant mice at lower sound pressure levels.
In the novel open field test, the mutant mice showed decreased rearing activity (A) and decreased resting time (B) when compared to control mice. (C) Prepulse Inhibition (PPI)/Acoustic Startle Response (ASR) testing showed decreased acoustic reactivity in the mutant mice at lower sound pressure levels. Figure 3. Retinal abnormalities in Wsb2-KO mice
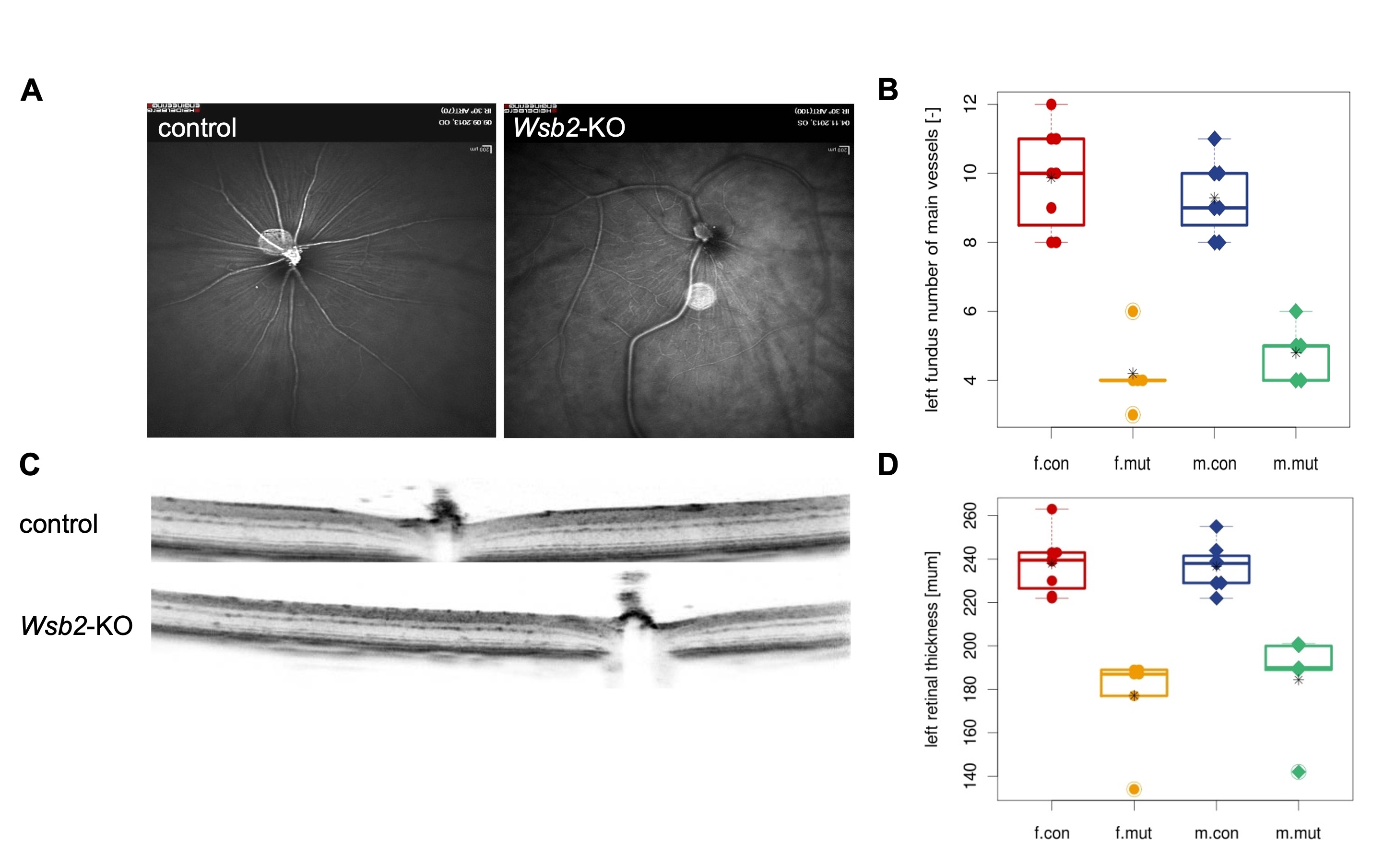 including irregular retinal blood vessel morphology (A, B) and reduced total retinal thickness (C, D) in the left eye. Controls n=15 (8 females/7 males) vs mutants n=11 (6 females/5 males). The right eye shows a similar phenotype.
including irregular retinal blood vessel morphology (A, B) and reduced total retinal thickness (C, D) in the left eye. Controls n=15 (8 females/7 males) vs mutants n=11 (6 females/5 males). The right eye shows a similar phenotype.
