Genomics/Epigenomics 1
Session: Genomics/Epigenomics 1
377 - Enhancing pediatric rare disease diagnosis by long-read HiFi-genome sequencing
Friday, April 25, 2025
5:30pm - 7:45pm HST
Publication Number: 377.4999
Tomi Pastinen, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, MO, United States; Carol Saunders, Children's Mercy Kansas City, Kansas City, MO, United States; Isabelle Thiffault, Children's Mercy Hospitals and Clinics, Kansas City, MO, United States; Emily G. Farrow, Children's Mercy Hospital, Kansas City, MO, United States
- TP
Tomi Pastinen, MD PhD (he/him/his)
Director of Genomic Medicine Center
Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics
Kansas City, Missouri, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Current clinical genetic testing faces significant challenges due to reliance on multiple testing modalities to capture genomic variations, complicating clinical reporting and involving multiple reference laboratories. Building on our research experience, with over 2,100 long-read genomes (HiFi-GS) in a rare disease cohort included in the Genomic Answers for Kids (GA4K) program, we validated a clinical HiFi-GS test.
Objective: We hypothesize that a single HiFi-GS for newborns and children admitted to Children's Mercy Kansas City can improve and simplify molecular testing.
Design/Methods: Molecular testing among 200 consecutive inpatient test orders were filled by single-test HiFi-GS. The preceding clinical validation of the test had been completed on the Revio platform (Pacific Biosciences, Menlo Park, CA). Standard procedures and resources of the PacBio WGS WDL pipeline were employed for alignment, small variant calling, structural variant (SV) calling, and variant phasing. Additional analyses included tandem genotype repeat expansion testing (TRGT) for 52 pediatric loci, methylation detection via the 5-methyl-Cytosine (mCpG) kinetic algorithm, and Paraphase analysis of 11 complex pediatric loci. Tertiary analysis incorporated both commercial and custom software, while patient-specific assemblies facilitated interpretation of complex SVs..Comparison to previous testing at CMKC included inpatients from 2020 onwards with same test indications and similar age/sex distribution.
Results: To date 186 HiFi-GS orders have been completed. Referrals (97% inpatient) were predominantly from by genetics (69%), neurology (17%), and pulmonology (6%). The majority of patients were male and tested at 2-6 wks of life. Most common testing indicating was multiple congenital anomalies. The comparative analyses included age/sex matched controls (n=2-3 per case). The characteristics of cases and controls are shown in Table 1. HiFi-GS resulted in diagnostic rate of 42% significantly (P=0.014) higher than previous testing with 32% rate of pathogenic variation (Figure 1). The single HiFi-GS compared favorably to average 1.67 tests required by traditional testing scheme and the average time to positive report was 29 days by HiFi-GS vs. 68 days by traditional expedited testing Notably, nearly 10% of positive findings involved variants identified uniquely through long-read sequencing, such as complex structural variants, repeat expansions, and methylation changes.
Conclusion(s): Clinical HiFi-GS as a single comprehensive genomic test increases diagnostic yield and improves timely delivery of molecular diagnosis in children.
Table 1. Characteristics of patients sequenced by clinical HiFi-GS (Cases) or by traditional in-patient expedited molecular testing (Controls).
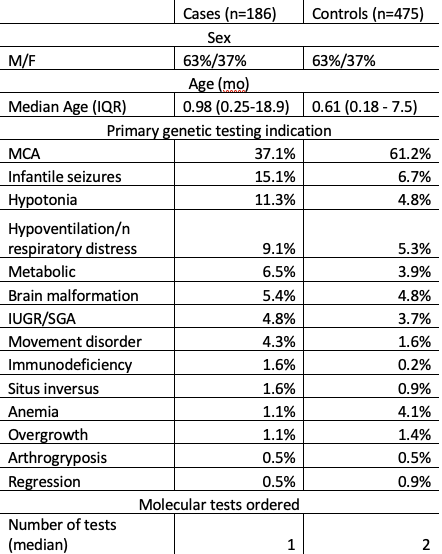
Figure 1. First 183 consecutive inpatient HiFi-GS tests (10/2023.- 9/2024) compared to matched (n=475) conventional expedited genetic testing at CMKC (2020-2024).
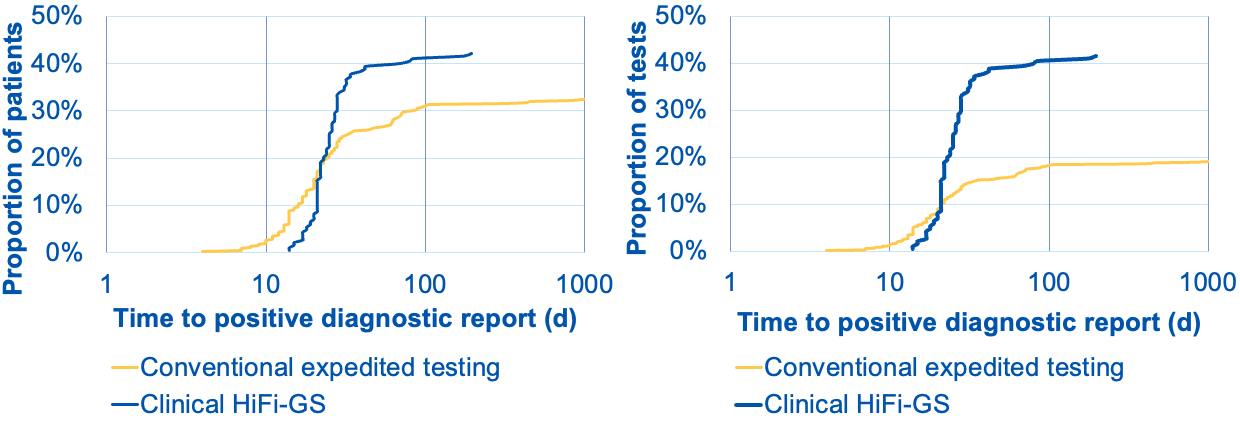 Left graph shows cumulative distribution of positive diagnoses (pathogenic variants returned in EMR) as fraction of patients tested (Y-axis) over turnaround time from order to diagnostic report (X-axis). The blue curve shows the clinical HiFi-GS test, whereas the the yellow curve represents traditional testing consisting of various combinations of clinical microarray (CMA), clinical exome, cytogenetic (FISH) and panel (gene panels and specific tests for complex genes, repeat expansions or methylation). HiFi-GS yields higher diagnostic rate (42 vs. 32%) and on average the overall testing process is shorter: conventional testing can continue by reflex follow-up tests for months. The right graph shows the rate of diagnosis as a fraction of independent molecular tests ordered, where the conventional testing required nearly twice as many tests (e.g. panel + CMA or exome +FISH, etc.) number of tests to reach lower diagnostic ceiling translating to less than 1/2 of overall diagnostic yield per test as compared to clinical HiFi-GS.
Left graph shows cumulative distribution of positive diagnoses (pathogenic variants returned in EMR) as fraction of patients tested (Y-axis) over turnaround time from order to diagnostic report (X-axis). The blue curve shows the clinical HiFi-GS test, whereas the the yellow curve represents traditional testing consisting of various combinations of clinical microarray (CMA), clinical exome, cytogenetic (FISH) and panel (gene panels and specific tests for complex genes, repeat expansions or methylation). HiFi-GS yields higher diagnostic rate (42 vs. 32%) and on average the overall testing process is shorter: conventional testing can continue by reflex follow-up tests for months. The right graph shows the rate of diagnosis as a fraction of independent molecular tests ordered, where the conventional testing required nearly twice as many tests (e.g. panel + CMA or exome +FISH, etc.) number of tests to reach lower diagnostic ceiling translating to less than 1/2 of overall diagnostic yield per test as compared to clinical HiFi-GS.
