Neonatal Pulmonology - Basic/Translational Science 2
Session: Neonatal Pulmonology - Basic/Translational Science 2
225 - Hyperoxia induced apoptosis in alveolar lung epithelial cells is attenuated by both small (sEVs) and Large extracellular vesicles (LEVs) derived from umbilical cord blood plasma (CBP)
Friday, April 25, 2025
5:30pm - 7:45pm HST
Publication Number: 225.5519
Ranga Prasanth Thiruvenkataramani, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine, Lansing, MI, United States; Amal Abdul-Hafez, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, United States; Tulasi Kesaraju, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine, Okemos, MI, United States; Burra V. Madhukar, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine, E. Lansing, MI, United States; Said Omar, Department of Pediatrics and Human Development, College of Human Medicine, Michigan State University. Regional Neonatal Intensive Care Unit, University of Michigan Health-Sparrow, East Lansing, MI, United States; Sherif Abd El Fattah. Ibrahim, University of Eastern Finland, KUOPIO, Pohjois-Savo, Finland; Hady Omar, Michigan State University College of Human Medicine, East Lansing, MI, United States

Ranga prasanth thiruvenkataramani, MD (he/him/his)
Assistant professor
Michigan State University
Lansing, Michigan, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: The incidence of chronic lung disease (CLD) in neonates has remained stable or increasing in the past decade. In preterm infants, CLD is a major cause of morbidity and mortality. Inflammation due to mechanical ventilation, hyperoxia, chorioamnionitis, and infection play a key role in the pathogenesis of CLD. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived Extracellular vesicles (EVs) play a critical role in immune system modulation and tissue regeneration. EVs are categorized based on their biogenesis and size as large EV (diameter 100-1000nm) and small EV (diameter 30-150 nm). Cord blood plasma (CBP) is a rich source of EV. EVs contain a cargo of mRNA, miRNA and protein. Previous work from our lab has shown that CBP sEVs and LEVs prevent apoptosis and necrosis in normoxic conditions and anti-inflammatory and regenerative capabilities in septic conditions.
Objective: To determine the effect of LEVs compared with sEVs from CBP on A549 lung alveolar epithelial cells under hyperoxia vs normoxia for 12 hours. Our hypothesis is that LEVs and sEVs are protective against apoptosis and increase cell viability.
Design/Methods: After obtaining maternal consent, CBP was collected from healthy full-term pregnancies. LEVs were collected by filtration and sEVs by ultrafiltration from CBP. sEVs were characterized based on Nanoparticle tracking analysis (NTA), Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and western blotting techniques. The cultured A549 cells were preincubated for 2 hrs +/- 400 ug/ ml protein concentration of LEVs or sEVs and exposed for 12 hours in hyperoxia and normoxia with 5% CO2 condition. Nuclear fragmentation as a measure of apoptosis and total cell count were determined by PI staining and data was analyzed using ANOVA.
Results: The characteristics of the isolated CBP LEVs and sEVs from NTA, western blotting and TEM are shown in Fig-1. Fig-2 shows the results of apoptosis assay. Apoptosis of A549 cells were significantly higher in hyperoxic when compared to normoxic conditions. Apoptosis of A549 was significantly reduced in cells treated with either sEVs or LEVs in comparison with untreated A549 cells (p < 0.01).
Conclusion(s): Our data shows that LEVs prevent apoptosis in A549 cells similar to sEVs in hyperoxic conditions. LEVs have similar protective effect compared with sEVs and have a potential therapeutic application to prevent hyperoxia induced lung injury and prevention of CLD in neonates.
Figure-1:
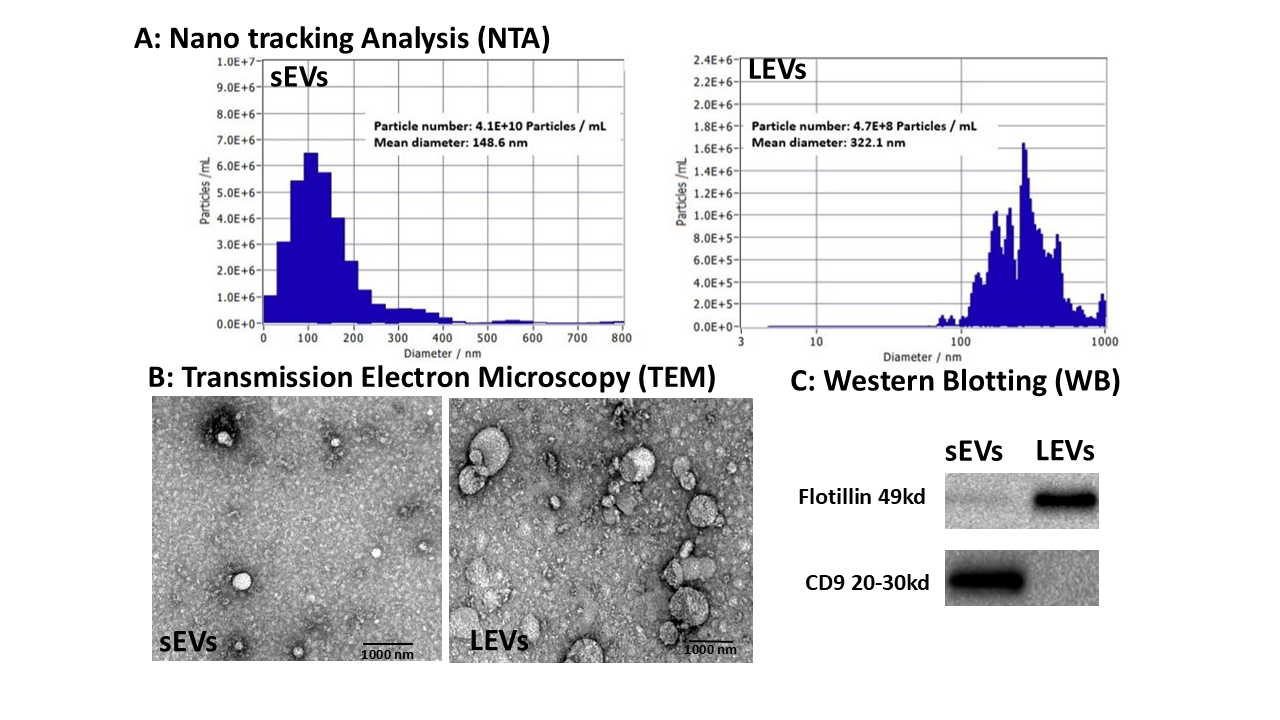 Characteristics for isolated CBP LEVS and sEVs via A Nanotracking analysis showed sEVS were between 50- 200 nm with median size around 100-120 nm and LEVS were between 100 -100 nm with median in around 500 nm; B Transmission electron microscopy shows the morphology of sEVs and LEVs; C Western blotting surface markers CD 9 and Flotillin for sEVS and LEVs.
Characteristics for isolated CBP LEVS and sEVs via A Nanotracking analysis showed sEVS were between 50- 200 nm with median size around 100-120 nm and LEVS were between 100 -100 nm with median in around 500 nm; B Transmission electron microscopy shows the morphology of sEVs and LEVs; C Western blotting surface markers CD 9 and Flotillin for sEVS and LEVs.Figure-2:
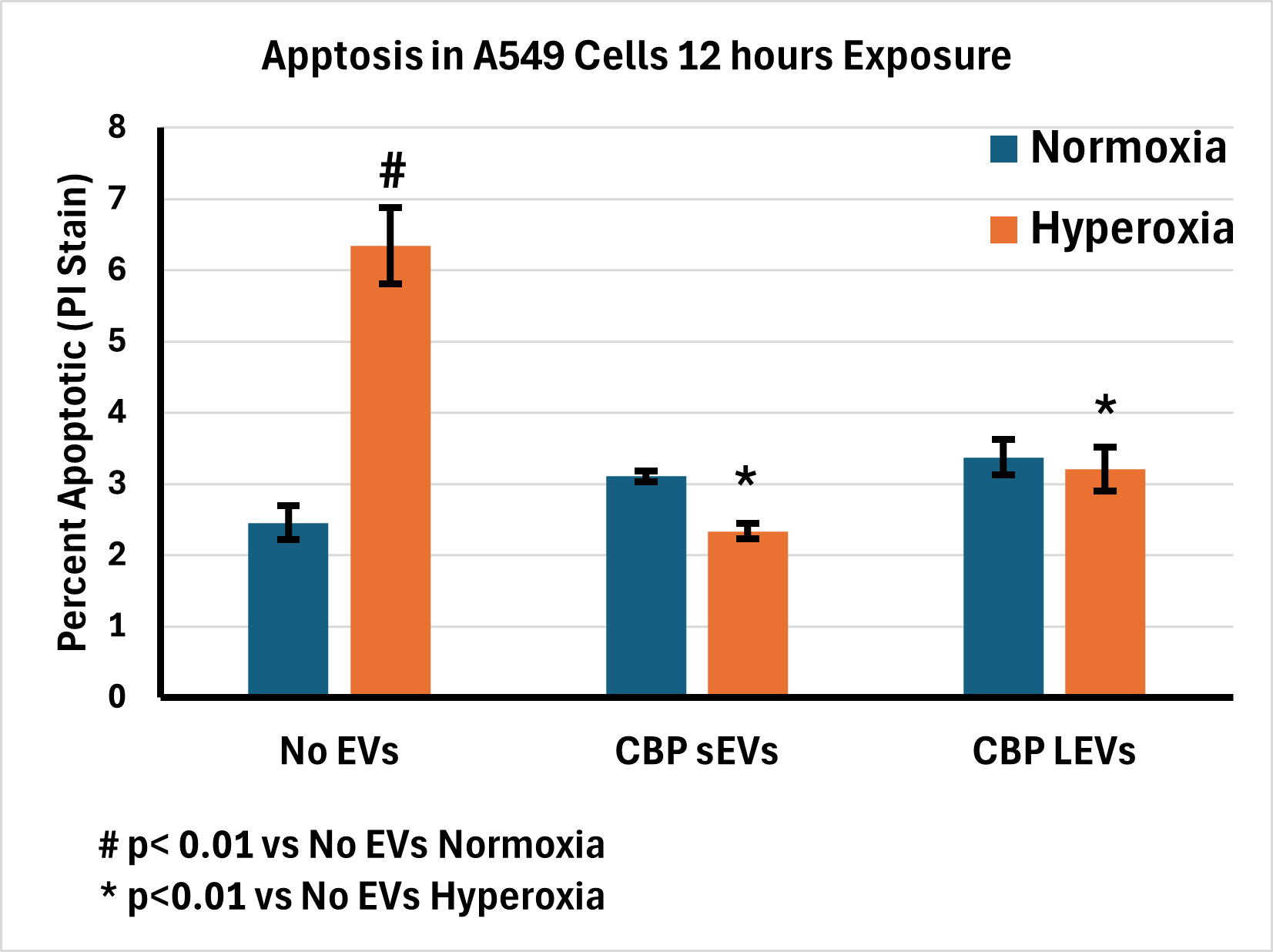 Nuclear fragmentation by Propidium Iodide staining shows increased apoptosis of A549 cells in hyperoxic condition when compared to normoxic condition. Treatment of A 549 cells with CBP derived sEVS and LEVS significantly decreased apoptosis in hyperoxic conditions when compared to normoxic condition. Statistics were done by ANOVA, Tukey posttest.
Nuclear fragmentation by Propidium Iodide staining shows increased apoptosis of A549 cells in hyperoxic condition when compared to normoxic condition. Treatment of A 549 cells with CBP derived sEVS and LEVS significantly decreased apoptosis in hyperoxic conditions when compared to normoxic condition. Statistics were done by ANOVA, Tukey posttest.
