Neonatal Infectious Diseases/Immunology 1: Improving antibiotic use in NICU
Session: Neonatal Infectious Diseases/Immunology 1: Improving antibiotic use in NICU
571 - Impact Of An Antimicrobial Stewardship Program On Late Onset Sepsis And Healthcare Associated Infections in a South American Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
Friday, April 25, 2025
5:30pm - 7:45pm HST
Publication Number: 571.5502
Soledad Urzua, Universidad Catolica de Chile, Santiago, Region Metropolitana, Chile; Andrea Maccioni, Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile and Complejo Asistencial Dr. Sótero del Río, Santiago, Region Metropolitana, Chile; Liliana Marcela. Leguizamón, Hospital Clinico Universidad Católica de Chile, Santiago, Region Metropolitana, Chile; Alberto Toso, Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile, Santiago, Region Metropolitana, Chile; Rocio Inojosa, Complejo Asistencial Dr Sotero del Rio, Santiago, Region Metropolitana, Chile; Claudia Toro, Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile, Las Condes, Region Metropolitana, Chile; Javiera F. Campos, Hospital Clínico UC-Christus, Santiago, Region Metropolitana, Chile; Elisa Jimenez, Universidad Diego Portales, Santiago, Region Metropolitana, Chile
- SU
Soledad Urzúa, Dr. (she/her/hers)
Neonatologist
Universidad Catolica de Chile
Santiago, Region Metropolitana, Chile
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Late-onset sepsis (LOS) and healthcare-associated infections (HAI) contribute to higher morbidity and mortality. Implementing an antimicrobial stewardship program (ASP) in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) can promote changes in clinical practice and improve infection-related outcomes.
Objective: To assess the impact of an ASP on the incidence of LOS and culture-negative sepsis (CNS) in very low birth weight infants (VLBWI), as well as on HAIs and antibiotic use in all patients in a NICU.
Design/Methods: Retrospective cohort study comparing 2 periods, before (P1, 2016-2019) and after (P2, 2020-2023) implementation of an ASP. The ASP was developed at the end of 2019 under the supervision of a university hospital with an established ASP. The purpose of this program was to develop and oversee strategies for the prevention and control of infections, as well as the rational use of antimicrobials. Several guidelines and bundles were incorporated into clinical practice, and personnel were trained to ensure acceptable compliance. Data for VLBWI were obtained from the Neocosur database, and from the unit’s own database. Baseline population characteristics and infectious episodes were analyzed for both periods. Additionally, HAIs and days of antibiotic therapy standardized by hospital occupancy rates (DOTst) were analyzed for all hospitalized newborns. A simple statistical analysis was used to compare both periods, with differences considered significant at p < 0.05.
Results: A total of 497 hospitalized VLBWI were analyzed, 288 were born in P1 and 209 in P2. No differences were found in most of baseline characteristics (Table 1). Prenatal corticosteroids use increased between P1 and P2 (91.6 vs 96.1%, p=0.032). A total of 111 episodes of LOS and 296 of CNS occurred in P1 versus 44 episodes of LOS and 136 of CNS in P2. The incidence of LOS and CNS per 1000 patient-days between P1 and P2 significantly decreased from 6.1 to 2.85 (p < 0.01) and from 16.2 to 8.8 (p < 0.001) respectively. There was no difference in the mortality rate. Analyzing HAIs in all hospitalized newborns, there was a significant decrease in Central Line-Associated Bloodstream Infection (CLABSI) from 3.7 (P1) to 1.7 (P2) per 1000 days of central line use (p=0.003), as well as in Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (VAP) (from 5.4 to 2.1 per 1000 days of mechanical ventilation, p=0.01) (Table 1). DOTst for most antibiotics decreased significantly (Table 2).
Conclusion(s): Implementation of an ASP in a single NICU was associated with a decreased incidence of LOS and CNS in VLBWI. CLABSI, VAP, and antibiotics use decrease in all hospitalized newborns.
Table 1. Baseline population characteristics, infection episodes and rates.
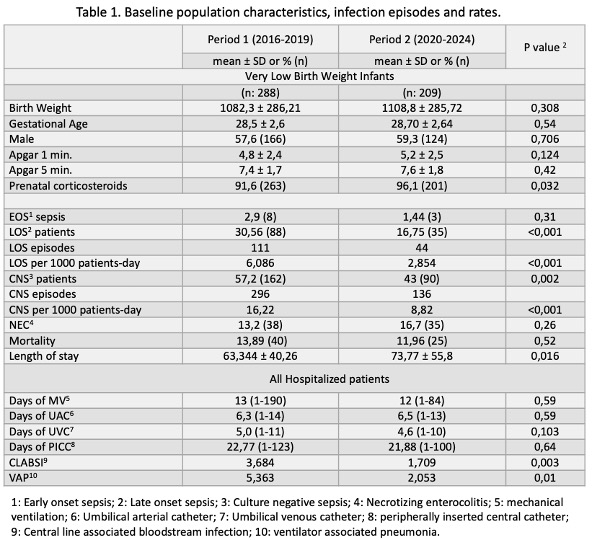 This table presents the demographic characteristics, as well as the incidence of late-onset sepsis (LOS) and culture-negative sepsis (CNS) in VLBWI during both periods. Additionally, it includes the rates of CLABSI and VAP across all hospitalized infants. It is observed that the general characteristics of the VLBWI are similar in both periods; however, there is a significant reduction in LOS and CNS. Regarding healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), there is a decrease in both CLABSI and VAP among all hospitalized patients.
This table presents the demographic characteristics, as well as the incidence of late-onset sepsis (LOS) and culture-negative sepsis (CNS) in VLBWI during both periods. Additionally, it includes the rates of CLABSI and VAP across all hospitalized infants. It is observed that the general characteristics of the VLBWI are similar in both periods; however, there is a significant reduction in LOS and CNS. Regarding healthcare-associated infections (HAIs), there is a decrease in both CLABSI and VAP among all hospitalized patients.Table 2. Days of Therapy indicator standardized by hospital occupancy rates (DOT-std) by period.
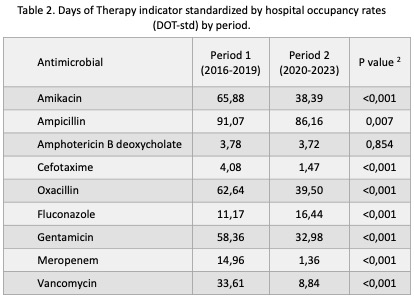 This table presents antibiotic consumption expressed as standardized DOT (Days of Therapy), adjusted for occupancy (per 1,000 patient-days). A significant reduction in DOT is observed for nearly all antimicrobial agents.
This table presents antibiotic consumption expressed as standardized DOT (Days of Therapy), adjusted for occupancy (per 1,000 patient-days). A significant reduction in DOT is observed for nearly all antimicrobial agents.Figure 1. Anual DOT per 1000 bed-days (DOT std) by year.
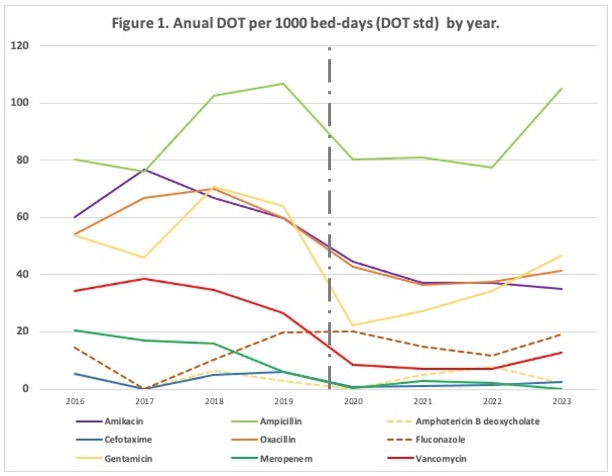 The graph illustrates the trend in standardized DOT for various antimicrobials from 2016 to 2023. The dashed black line marks the point when the ASP was implemented. It shows that the standardized DOT for most antimicrobials has decreased over time.
The graph illustrates the trend in standardized DOT for various antimicrobials from 2016 to 2023. The dashed black line marks the point when the ASP was implemented. It shows that the standardized DOT for most antimicrobials has decreased over time.
