Neonatal/Infant Resuscitation 1
Session: Neonatal/Infant Resuscitation 1
291 - Cardiopulmonary Transition at Birth in Spontaneously Breathing Lambs With a Diaphragmatic Hernia
Friday, April 25, 2025
5:30pm - 7:45pm HST
Publication Number: 291.4264
Paige J. Riddington, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria, Australia; Philip DeKoninck, Erasmus MC, Rotterdam, Zuid-Holland, Netherlands; Marta Thio, The Royal Women's Hospital Melbourne, Albert Park, Victoria, Australia; Indya M. Davies, Hudson Institute of Medical Research, Clayton, Victoria, Australia; Ebony R. Cannata, The Ritchie Centre, Hudson Institute of Medical Research, Noble Park, Victoria, Australia; Emily Horn-Oudshoorn, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, Zuid-Holland, Netherlands; Alison Thiel, Hudson Institute of Medical Research, clayton, Victoria, Australia; Ilias Nitsos, Hudson Institute, Clayton, Victoria, Australia; Stuart B. Hooper, Monash University, Black Rock, Victoria, Australia; Kelly J. Crossley, The Ritchie Centre, Clayton, Victoria, Australia

Paige J. Riddington, BSc(Hons) (she/her/hers)
PhD Student
Monash University
Clayton, Victoria, Australia
Presenting Author(s)
Background: It is currently recommended that infants with a congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) are intubated and mechanically ventilated (MV) at birth, irrespective of the degree of lung hypoplasia (LH). However, CDH infants with mild LH may only require non-invasive respiratory support to assist their spontaneous breathing (SB) efforts, but it is unknown how this impacts their cardiopulmonary transition. We hypothesised that SB with non-invasive respiratory support would facilitate a successful cardiopulmonary transition at birth in diaphragmatic hernia (DH) lambs with mild LH.
Objective: To investigate the cardiopulmonary transition at birth in SB lambs with a DH.
Design/Methods: SB lambs (n=10) had a left sided DH surgically induced at 103 days of gestational age (GA; term ~147d GA) and implanted with catheters and blood flow probes at ~137d GA. At ~139d GA lambs were delivered via caesarean section under spinal anaesthesia. MV lambs (n=9) had a left sided DH surgically induced at 89d GA and were implanted with catheters and blood flow probes at ~138d GA before they were delivered via caesarean section under general anaesthesia. In SB DH lambs, the umbilical cord was clamped once regular breathing was achieved and pulmonary blood flow (PBF) had increased; subsequent respiratory support was escalated and weaned as required for 2hr. In MV DH lambs, the umbilical cord was clamped after achieving a tidal volume of 4 ml/kg, with a maximum delay of 10 min, then ventilated for 2hr. Data is presented as mean±SEM.
Results: The degree of LH varied in both SB and MV DH lambs. SB DH lambs with mild LH were able to generate the largest intrathoracic pressure changes and tidal volumes (Figure 1), largely because the diaphragmatic defect had repaired spontaneously. SB lambs with a severe LH generated greater intrathoracic pressure changes and tidal volumes than SB lambs with moderate LH (Figure 1). However severe LH lambs spent only 32% of the time spontaneously breathing, compared to 95% in moderate LH lambs (Figure 2). Following cord clamping (10.5±1.6min in SB DH lambs and 8.3±1.2min in MV DH lambs, p=0.3), the increase in PBF (per gram of tissue) and decrease in pulmonary vascular resistance was similar in SB and MV DH lambs (Figure 3).
Conclusion(s): Despite only receiving non-invasive respiratory support, the cardiopulmonary transition was similar in SB DH lambs with a mild or moderate LH compared to MV DH lambs during the first 2 hours after birth. This study suggests that SB and non-invasive respiratory support may be a viable approach for assisting CDH infants with less severe LH transition at birth.
Figure 1. Change in intrathoracic pressure with tidal breathing in spontaneously breathing (SB) diaphragmatic hernia (DH) lambs with different degrees of lung hypoplasia (LH).
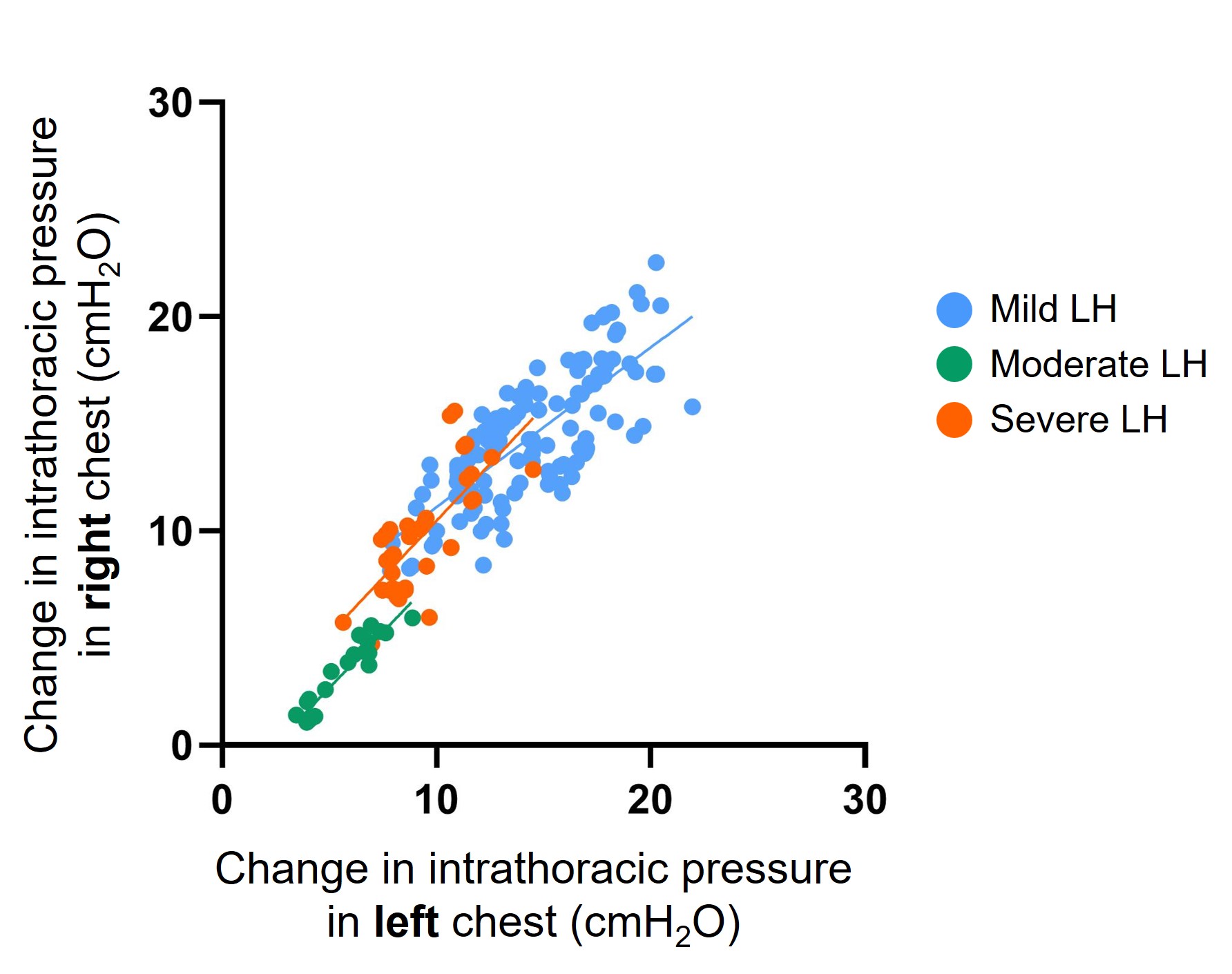 SB DH lambs with mild lung hypoplasia had a spontaneous repair of the diaphragmatic defect (closed defect). SB DH lambs with moderate and severe DH had a patent (open) defect. Intrathoracic pressure was measured with a saline filled latex balloon tipped catheter placed within the left and right intrapleural space of each lamb.
SB DH lambs with mild lung hypoplasia had a spontaneous repair of the diaphragmatic defect (closed defect). SB DH lambs with moderate and severe DH had a patent (open) defect. Intrathoracic pressure was measured with a saline filled latex balloon tipped catheter placed within the left and right intrapleural space of each lamb.Figure 2. Individual heat maps depicting the type of respiratory support required in each spontaneously breathing (SB) diaphragmatic hernia (DH) lamb.
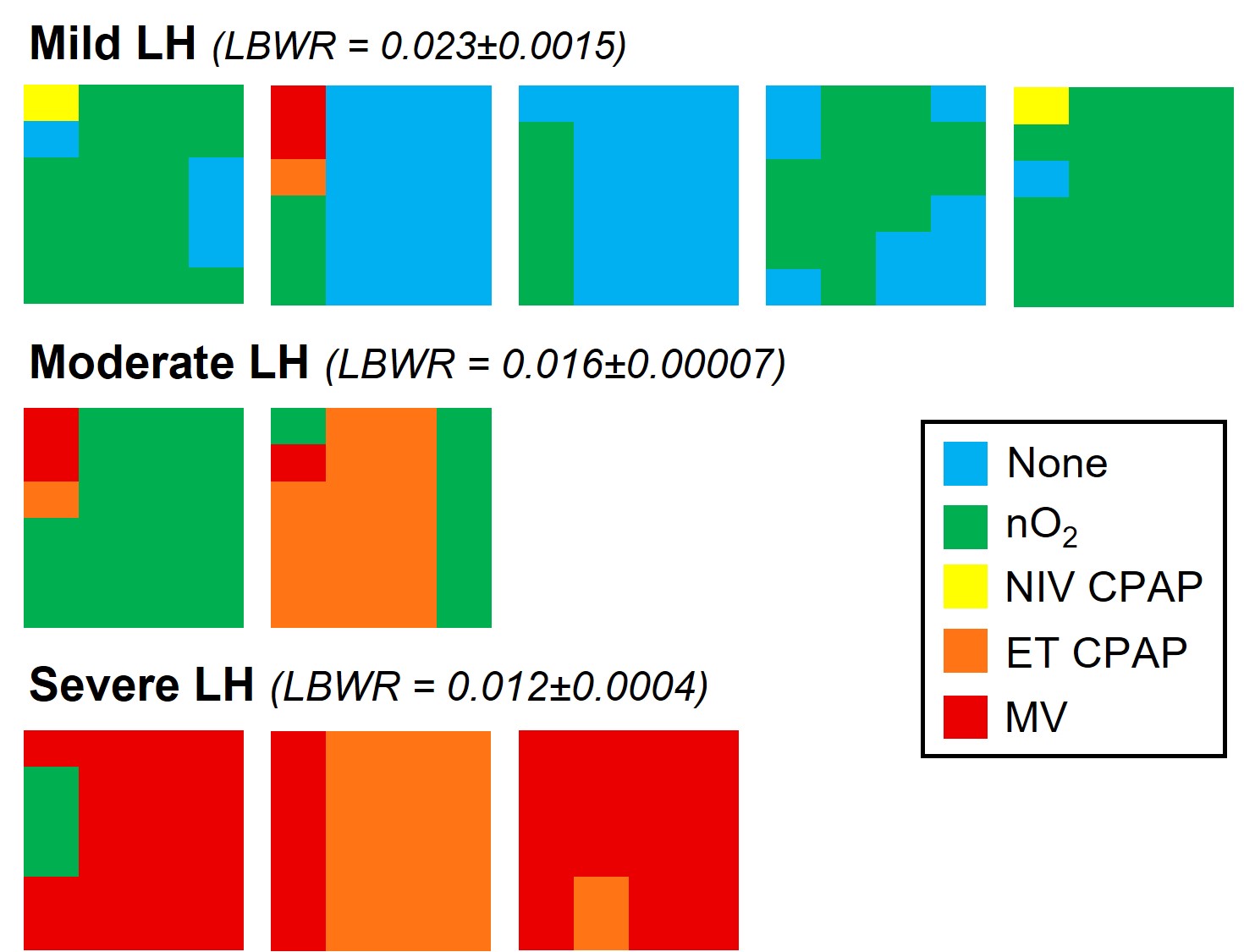 Types of respiratory support graded according to decreasing intensity of support. Blue = no respiratory support, Green = nasal gas flow (with oxygen; nO2), Yellow = Non-invasive CPAP (delivered via face mask or laryngeal mask; NIV CPAP), Orange = intubated with continuous positive airway pressure (ET CPAP), Red = Intubated with mechanical ventilation (MV). Individual lambs with Mild LH, Moderate LH and Severe LH are presented in left-to-right in order of delivery. The 2 hours of respiratory support are represented in columns from left to right with each column presenting the proportion of time spent on any form of respiratory support for that 30-minute interval. LH = lung hypoplasia, LBWR = lung-to-body weight ratio (a proxy for LH; healthy lungs = 0.033±0.004).
Types of respiratory support graded according to decreasing intensity of support. Blue = no respiratory support, Green = nasal gas flow (with oxygen; nO2), Yellow = Non-invasive CPAP (delivered via face mask or laryngeal mask; NIV CPAP), Orange = intubated with continuous positive airway pressure (ET CPAP), Red = Intubated with mechanical ventilation (MV). Individual lambs with Mild LH, Moderate LH and Severe LH are presented in left-to-right in order of delivery. The 2 hours of respiratory support are represented in columns from left to right with each column presenting the proportion of time spent on any form of respiratory support for that 30-minute interval. LH = lung hypoplasia, LBWR = lung-to-body weight ratio (a proxy for LH; healthy lungs = 0.033±0.004).Figure 3. Cardiopulmonary physiology during the first 500 breaths/inflations (~10 min) after cord clamping in spontaneous breathing (SB; blue) or mechanically ventilated (MV) DH lambs.
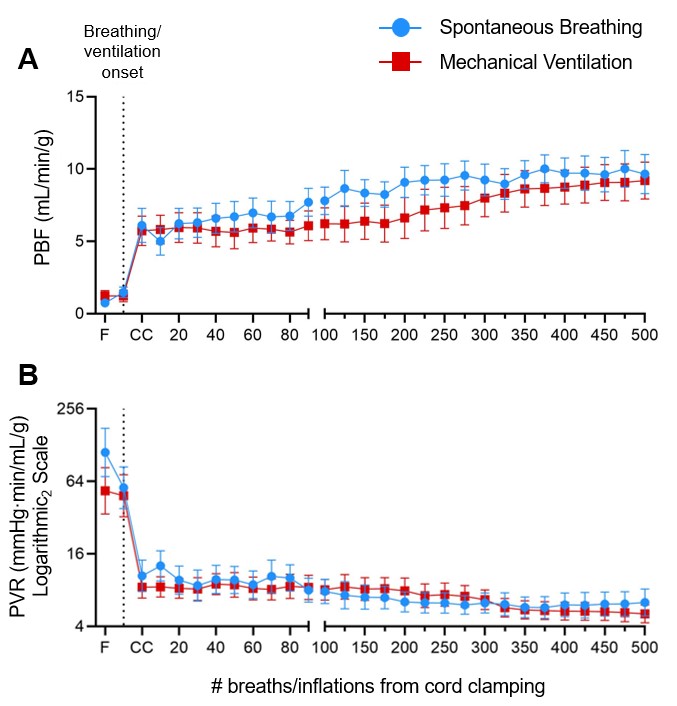 Pulmonary blood flow (PBF; A) and pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR; B) corrected for left lung weight in SB DH lambs (n=10) and MV DH lambs (n=9). Data expressed as mean±SEM. F = Fetal, CC = Cord clamping, PVR = (pulmonary artery pressure – left atrial pressure)/pulmonary blood flow.
Pulmonary blood flow (PBF; A) and pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR; B) corrected for left lung weight in SB DH lambs (n=10) and MV DH lambs (n=9). Data expressed as mean±SEM. F = Fetal, CC = Cord clamping, PVR = (pulmonary artery pressure – left atrial pressure)/pulmonary blood flow. 
