Neo-Perinatal Health Care Delivery: Epidemiology/Health Services Research 3
Session: Neo-Perinatal Health Care Delivery: Epidemiology/Health Services Research 3
374 - Opioid-associated mortality in reproductive-age females and infant mortality in regions of socioeconomic deprivation
Saturday, April 26, 2025
2:30pm - 4:45pm HST
Publication Number: 374.5676
Matthew Loop, Auburn University, Auburn, AL, United States; Namasivayam Ambalavanan, University of Alabama School of Medicine, Birmingham, AL, United States; Waldemar Carlo, UAB School of Medicine, Birmingham, AL, United States; Vivek Shukla, University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL, United States
- ML
Matthew Loop, PhD
Assistant Professor
Auburn University
Auburn, Alabama, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Infants are vulnerable populations that are affected by the growing opioid crisis in the US, including opioid use during pregnancy. It is not known whether the relationship between opioid-associated mortality among females of child-bearing age and infant mortality is stronger in areas with worse socioeconomic deprivation.
Objective: Among US counties, estimate how much the relationship between infant mortality and opioid mortality among females of child-bearing age depends upon socioeconomic deprivation.
Design/Methods: Using CDC WONDER, we conducted an ecological correlation study of county-level infant ( < 365 days), early neonatal ( < 7 days), neonatal ( < 28 days), and post-neonatal (28 - 264 days) mortality rates per 1,000 births from 2007 to 2020 and county-level opioid-associated mortality rates per 100,000 females age 15 to 44 years. We identified opioid-associated mortality using the multiple causes of death ICD-10 codes T40.0 (Opium), T40.1 (Heroin), T40.2 (Other opioids), T40.3 (Methadone), and T40.4 (Other synthetic narcotics). We measured county-level socioeconomic deprivation using the county-level mean 2015 area deprivation index (ADI). We used Poisson regression to predict the number of infant deaths as a function of opioid-associated mortality rates among females of child-bearing age, mean ADI, and their interaction.
Results: From 2007 to 2020 the median (quartile 1, quartile 3) county-level infant death rate was 6.4 (5.2, 8.0) per 1,000 births. The median county-level opioid mortality rate among women of child-bearing age was 10.8 (5.1, 16.7) per 100,000. The relationships between county-level infant, early neonatal, neonatal, and post-neonatal (among term and all infants) mortality and opioid mortality were stronger among counties with higher ADI (Figure 1). Counties with ADI > 75th percentile that currently have < 5 opioid deaths per 100,000 were concentrated in the Deep Southern and Midwestern states (Figure 2A). Counties with ADI > 75th percentile that currently have > 20 opioid deaths per 100,000 were concentrated in Appalachia (Figure 2B).
Conclusion(s): Opioid-associated mortality among females of child-bearing age is more strongly associated with neonatal and infant mortality in counties with high versus low socioeconomic deprivation.
Figure 1
.png) Estimated county-level infant mortality rates per 1,000 births, as a function of county-level mortality rates with opioid poisoning as a contributing cause of death per 100,000 females aged 15 - 44 years. Associations are presented by mean county-level Area Deprivation Index (ADI) quartile.
Estimated county-level infant mortality rates per 1,000 births, as a function of county-level mortality rates with opioid poisoning as a contributing cause of death per 100,000 females aged 15 - 44 years. Associations are presented by mean county-level Area Deprivation Index (ADI) quartile.Figure 2
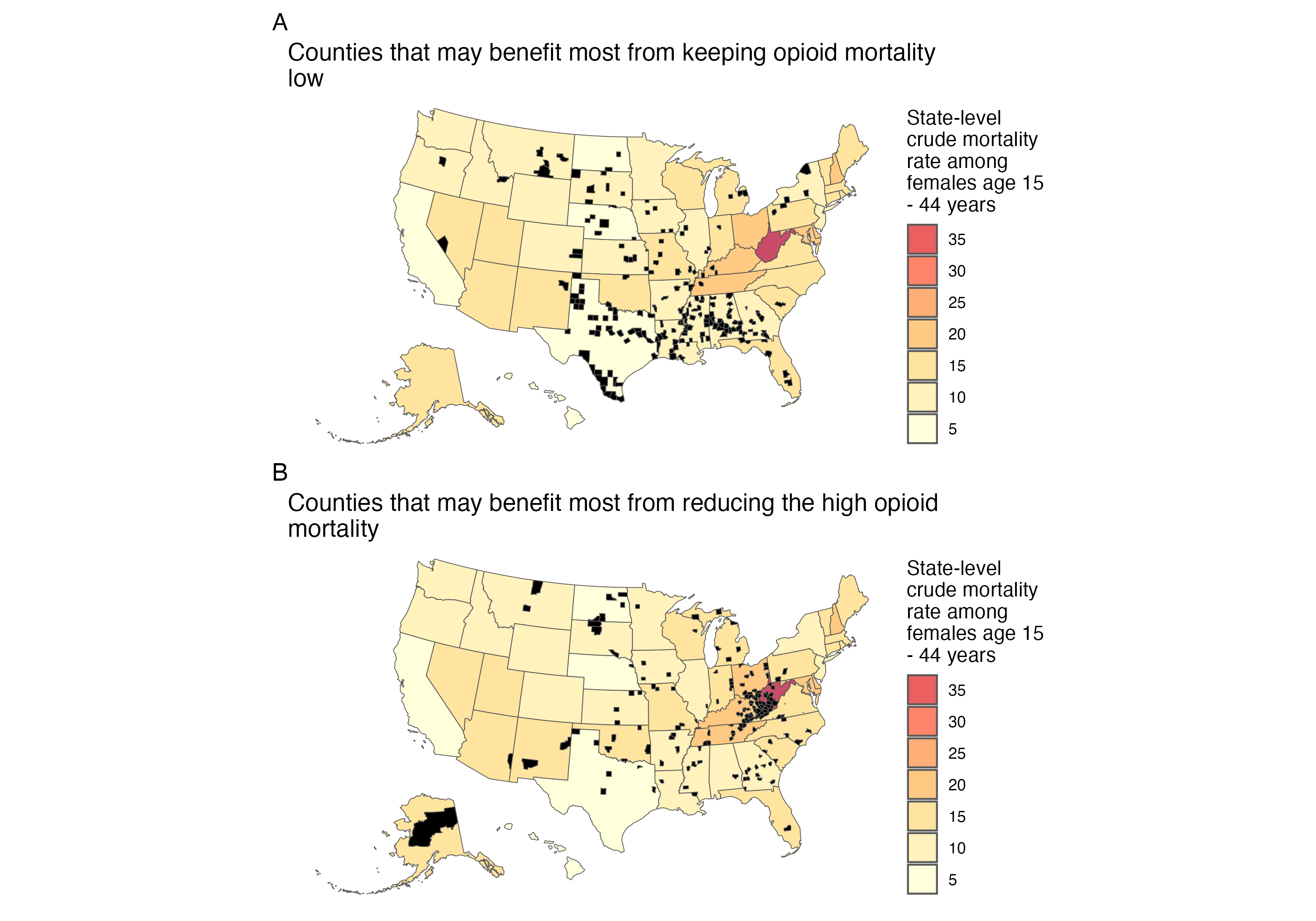 Where could we intervene? (A) Prophylaxis Counties in black are highly deprived (area deprivation index >= 75) but currently have < 5 opioid deaths per 100,000 females aged 15 - 44 years. Higher infant mortality rises the fastest with higher opioid mortality in these counties with high ADI (see Figure 1), so keeping the opioid epidemic from increasing in these counties may prevent the most infant deaths. These counties are concentrated in the Deep South and Midwest. (B) Treatment Counties in black are highly deprived (area deprivation index >= 75) but currently have > 20 opioid deaths per 100,000 females aged 15 - 44 years. Higher infant mortality rises the fastest with higher opioid mortality in these counties with high ADI (see Figure 1), so reducing the opioid epidemic from currently high levels in these counties may prevent the most infant deaths. These counties are concentrated in Appalachia.
Where could we intervene? (A) Prophylaxis Counties in black are highly deprived (area deprivation index >= 75) but currently have < 5 opioid deaths per 100,000 females aged 15 - 44 years. Higher infant mortality rises the fastest with higher opioid mortality in these counties with high ADI (see Figure 1), so keeping the opioid epidemic from increasing in these counties may prevent the most infant deaths. These counties are concentrated in the Deep South and Midwest. (B) Treatment Counties in black are highly deprived (area deprivation index >= 75) but currently have > 20 opioid deaths per 100,000 females aged 15 - 44 years. Higher infant mortality rises the fastest with higher opioid mortality in these counties with high ADI (see Figure 1), so reducing the opioid epidemic from currently high levels in these counties may prevent the most infant deaths. These counties are concentrated in Appalachia.
