Neonatal Pulmonology - Clinical 4: Common Acute Clinical Concerns
Session: Neonatal Pulmonology - Clinical 4: Common Acute Clinical Concerns
350 - Assessment of pulsatile perfusion in preterm infants with pulmonary hypertension
Monday, April 28, 2025
7:00am - 9:15am HST
Publication Number: 350.3993
Katelyn G. Enzer, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, CO, United States; Nilton Barbosa da Rosa Junior, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, United States; Omid Rajabi Shishvan, University at Albany, SUNY, Albany, NY, United States; Gary J.. Saulnier, University at Albany, SUNY, Albany, NY, United States; Jonathan C.. Newell, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Slingerlands, NY, United States; David Isaacson, RPI, Troy, NY, United States; Christopher D. Baker, University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora, CO, United States; Jennifer L. Mueller, Colorado State University, Fort Collins, CO, United States

Jennifer L. Mueller, PhD (she/her/hers)
Professor
Colorado State University
Fort Collins, Colorado, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) is the most common lung disease in preterm infants, with 10–15,000 premature infants diagnosed yearly in the USA. Alveolar simplification and pulmonary vascular hypoplasia are characteristic of BPD. Up to 28% of infants with moderate to severe BPD also have pulmonary hypertension (PH). Infants with BPD exhibit ventilation/perfusion (V/Q) mismatch, but the V/Q relationship in infants with BPD-PH is poorly understood. Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) is a non-ionizing, non-invasive bedside imaging technology. The ACT 5 EIT system can provide ventilation and pulsatile perfusion images in real-time without contrast agents.
Objective: To study the potential of EIT images of pulsatile perfusion to assess regional differences in perfusion in infants with BPD-PH.
Design/Methods: EIT ventilation, perfusion, and echocardiogram data were collected with the ACT 5 EIT system (using 16 circumferential chest electrodes) for preterm supine infants in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) at Children’s Hospital Colorado (CHCO). Dynamic images of conductivity and susceptivity in the plane of the electrodes corresponding to pulsatile pulmonary perfusion and ventilation were computed using a linearized reconstruction algorithm. An EIT-derived ventilation/perfusion index (VQI) was calculated from these images. Infants were imaged at approximately 4-week intervals for up to 5 visits or until discharged.
Results: 22 infants were studied, 15 with BPD, 8 with BPD-PH, and 6 controls. The images reveal heterogeneous ventilatory and pulsatile perfusion patterns consistent with their clinical condition. The average VQI from visit 1 for infants diagnosed with PH was found to be 3.0 compared to 1.9 for infants with BPD but no PH and 2.5 for the control subjects (Fig 1). Fig 2 highlights EIT images from a male infant with Grade 2 BPD with PH and left ventricular dysfunction. His clinical course is outlined in Fig 3.
Conclusion(s): EIT is a promising real-time bedside imaging technology for the heterogenous parenchymal and vascular disease in infants with BPD-PH. The higher VQI for infants with BPD-PH may be indicative of more severe pulmonary vascular disease. Regional visualization of ventilation and pulmonary perfusion may aid in detection of V/Q mismatch in BPD-PH, inform ventilation strategies, and guide the use of medications.
Fig. 1
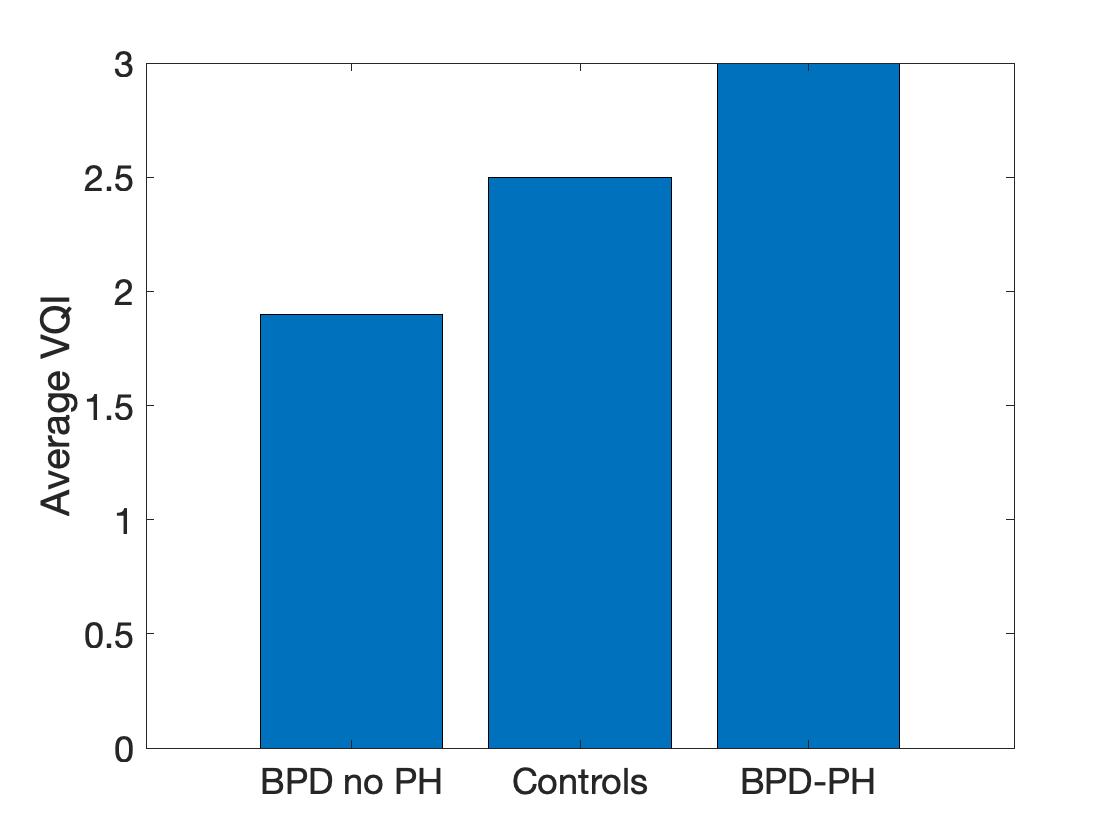 Comparison of the average EIT-derived VQ index for each group
Comparison of the average EIT-derived VQ index for each groupFig. 2
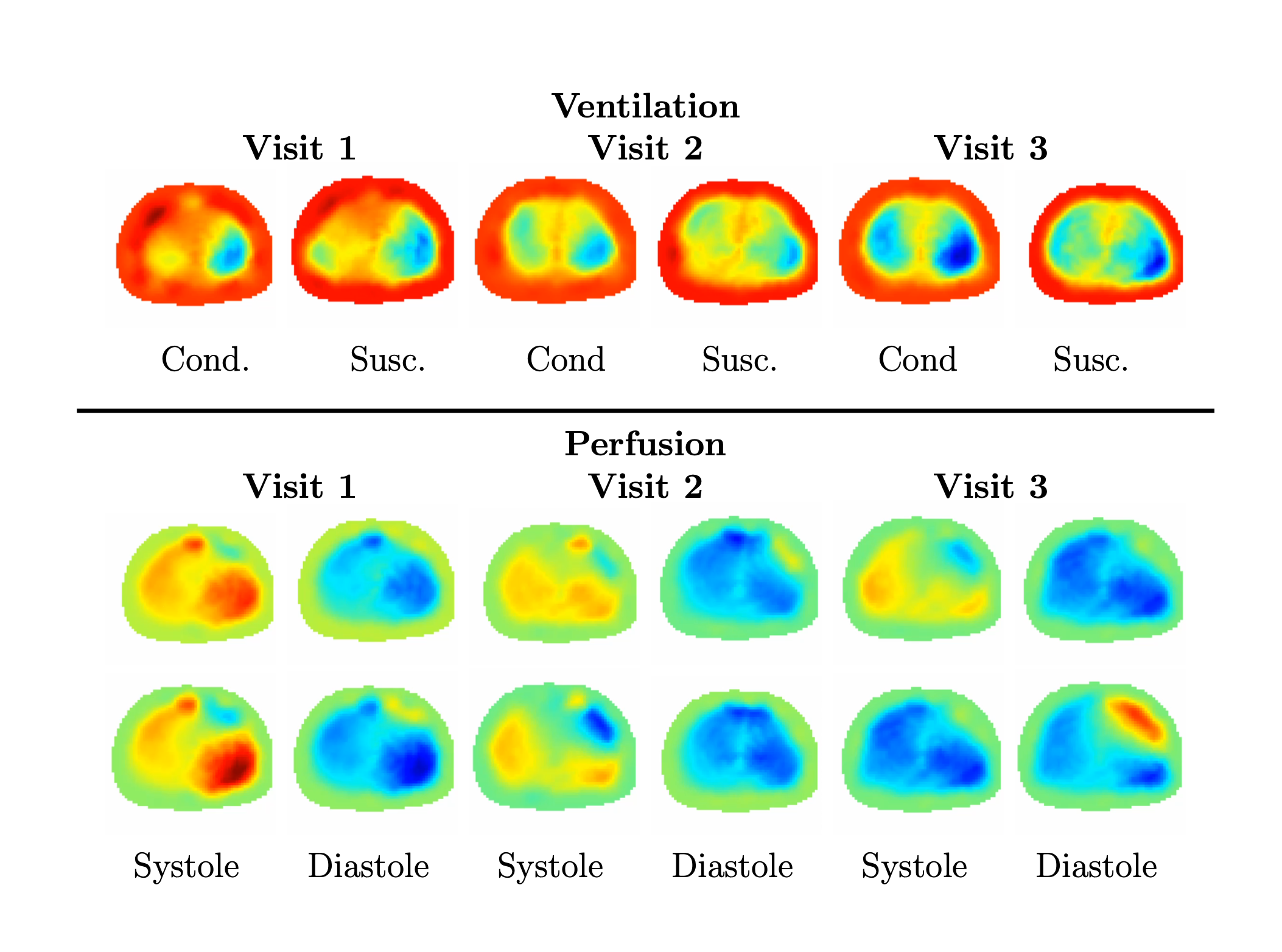 Top: Time snapshots of ventilatory EIT difference images at full inspiration of the infant at each visit. All are displayed on the same scale. Regions of low conductivity and susceptivity indicate regions containing more air than those of higher conductivity and susceptivity values. Bottom: Time snapshots of EIT images of pulsatile perfusion of the infant at each visit. Upper row is conductivity, all displayed on the same scale. Bottom row is susceptivity, all displayed on the same scale. Regions of high conductivity and susceptivity indicate regions containing more blood than those of lower conductivity and susceptivity values.
Top: Time snapshots of ventilatory EIT difference images at full inspiration of the infant at each visit. All are displayed on the same scale. Regions of low conductivity and susceptivity indicate regions containing more air than those of higher conductivity and susceptivity values. Bottom: Time snapshots of EIT images of pulsatile perfusion of the infant at each visit. Upper row is conductivity, all displayed on the same scale. Bottom row is susceptivity, all displayed on the same scale. Regions of high conductivity and susceptivity indicate regions containing more blood than those of lower conductivity and susceptivity values.Fig. 3
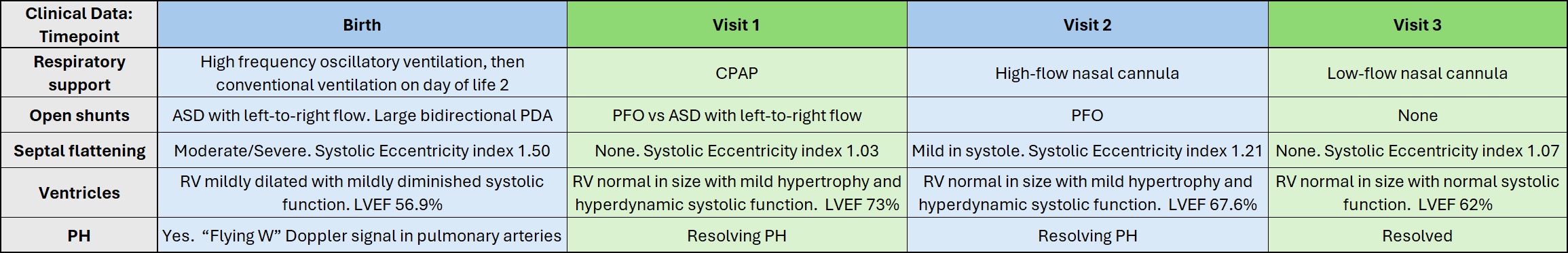 : Clinical course of a mono-di twin male infant born at 29 weeks gestation with pregnancy complicated by fetal hydrops of this twin. Initial course notable for pleural effusions and pneumothoraces requiring chest tubes, hypotension, and severe PH. He was imaged with EIT at 22 days (visit 1), 48 days (visit 2), and 75 days (visit 3) chronological age. Data from the echocardiograms are within 4 days of each EIT visit.
: Clinical course of a mono-di twin male infant born at 29 weeks gestation with pregnancy complicated by fetal hydrops of this twin. Initial course notable for pleural effusions and pneumothoraces requiring chest tubes, hypotension, and severe PH. He was imaged with EIT at 22 days (visit 1), 48 days (visit 2), and 75 days (visit 3) chronological age. Data from the echocardiograms are within 4 days of each EIT visit.
