Neonatal GI Physiology & NEC 3
Session: Neonatal GI Physiology & NEC 3
688 - Hyperoxia Decreases Stem Cells, Increases Inflammation, and Impairs Transcriptional Programs Underlying Digestion in the Premature Intestine
Monday, April 28, 2025
7:00am - 9:15am HST
Publication Number: 688.5200
Comfort Adegboye, Boston Children's Hospital, Lanham, MD, United States; Yu-Syuan Wu, Boston Children's Hospital, Malden, MA, United States; Luiz Fernando Silva Oliveira, Boston Children's Hospital, Boston, MA, United States; Liza Konnikova, Yale School of Medicine, North Haven, CT, United States; Kent A.. Willis, The University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, AL, United States; Amy E.. O'Connell, Boston Children's Hospital, Boston, MA, United States
- AO
Amy E. O'Connell, MD, PhD
Assistant Professor
Boston Children's Hospital
Harvard Medical School
Boston, Massachusetts, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Prematurely born infants are exposed to higher postnatal oxygen than they would be if development had continued in utero. This is known to contribute to a range of prematurity-related diseases, including bronchopulmonary dysplasia and retinopathy of prematurity. However, the effects of hyperoxia on the intestine are not well studied.
Objective: To evaluate whether hyperoxia impacts the premature intestinal epithelium.
Design/Methods: We generated epithelial organoids, self-organizing stem cell-derived tissue cultures, from immature (7 day) and mature (2 month) mouse ileum, and immature (22 week) and mature (37 week) human small intestine. We then exposed the organoids to 12 hours of normoxia (0.21 FiO2), hypoxia (0.05 O2) or hyperoxia (0.95 FiO2), and evaluated the effects by microscopy. We used RNASeq to compare transcriptomic differences between exposure groups. We confirmed these findings with qRT-PCR and immunofluorescence. Notable findings were evaluated in the human organoids. C57Bl/6 mice were also treated with hyperoxia (0.75 FiO2) for 8 days starting at P1 and ileum tissue was evaluated by histology and qRT-PCR.
Results: Hyperoxia had a more profound effect on the transcriptome of immature organoids than hypoxia, and immature organoids were more significantly affected than mature ones (Fig. 1). The expression of intestinal stem cell (ISC) markers and transit amplifying (TA) cell markers was significantly decreased in hyperoxia conditions in immature organoids, while markers of differentiated epithelial cells were increased (Fig. 2A, 2B). ISC markers were also significantly decreased in 22-week human organoids after hyperoxia but not in 37-week organoids (Fig. 2C, 2D). Hyperoxia significantly increased IL-6 expression in human immature organoids and caused decreased expression of key epithelial digestion genes including sucrase isomaltase (Sis), Glut1 (Slc1a1), and Glut2 (Slc1a2) (Fig. 2E). Treating newborn mice with 75% hyperoxia for 8 days caused decreased intestinal length and decreased ISC expression with significantly increased expression of Alpi, a marker of differentiated enterocytes (Fig. 3).
Conclusion(s): Here we demonstrate that hyperoxia significantly impacts the immature intestine. Hyperoxia may contribute to nutritional impairment in the premature neonate by direct impacts on the intestine. Furthermore, the decrease in stem cells and increase in inflammation caused by hyperoxia may leave the intestine vulnerable to injury, which could be meaningful in the context of necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC).
Figure 1. Immature ileum transcriptome is significanctly altered by hyperoxia.
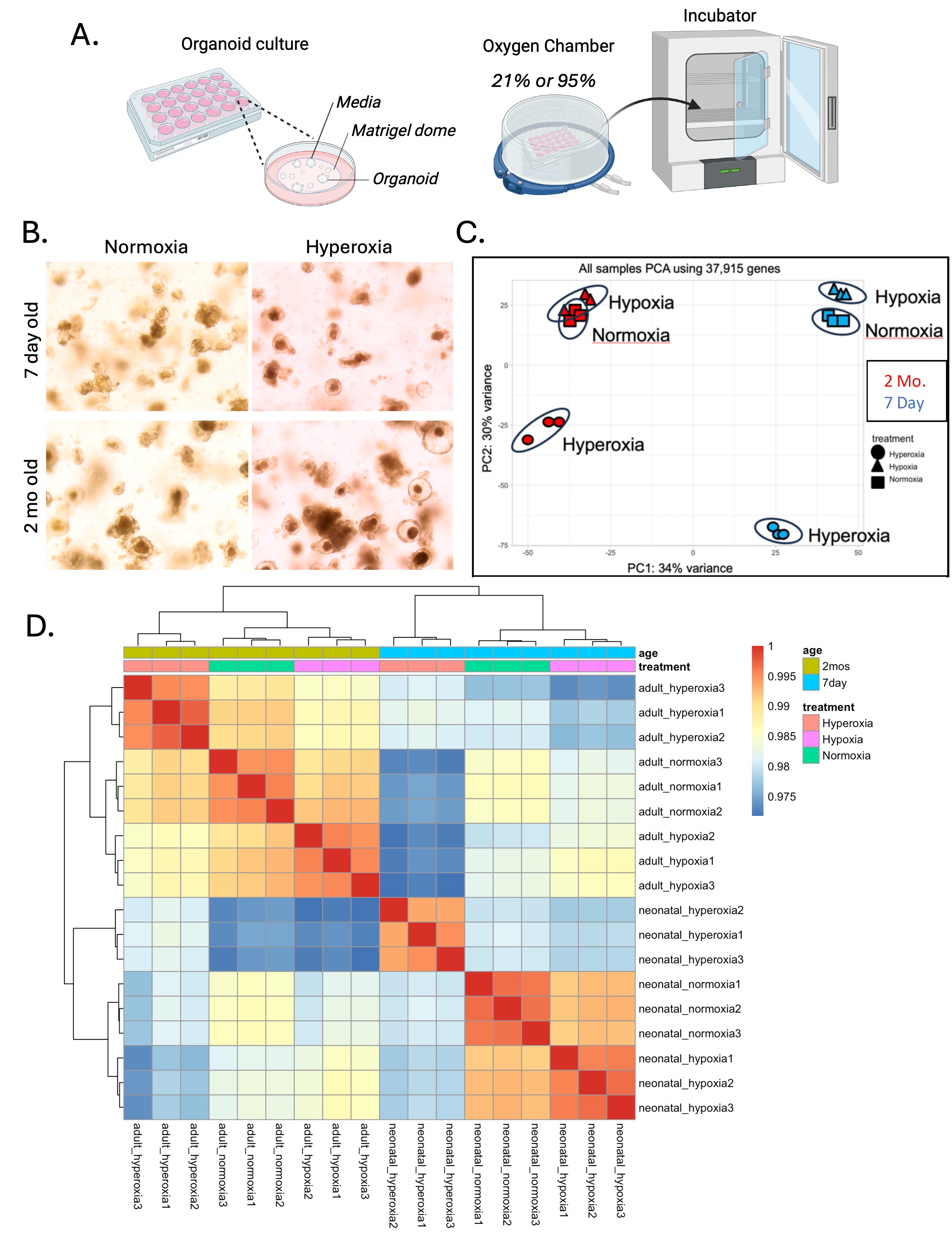 A.) Morphology of organoids in culture after 12 hours of normoxia or hyperoxia. B.) Principal component analysis of RNASeq data for ileum organoids from 7-day-old mice (blue) versus 2 month-old mice (red) under normoxia (squares), hypoxia (triangles) or hyperoxia (circles). C.) Hierarchical clustering of RNASeq data shows that immature hyperoxia samples clustered independently of all other groups.
A.) Morphology of organoids in culture after 12 hours of normoxia or hyperoxia. B.) Principal component analysis of RNASeq data for ileum organoids from 7-day-old mice (blue) versus 2 month-old mice (red) under normoxia (squares), hypoxia (triangles) or hyperoxia (circles). C.) Hierarchical clustering of RNASeq data shows that immature hyperoxia samples clustered independently of all other groups. Figure 2. Epithelial cell differentiation is altered by hyperoxia.
.jpg) A.) Heat maps of key epithelial subset genes form RNASeq in 7-day-old and 2-month-old ileal organoids treated with normoxia (NO) or hyperoxia (HO). B.) qRT-PCR confirmation of A. for Lgr5 and Lyz1 expression. C. Morphology of human organoids from 22-week fetus or 37-week infant after exposure to 12 hours of normoxia (21%) or hyperoxia (95%). D.) RNA expression in hyperoxia treated human organoids. E.) Heatmap of expression of genes important for nutrient transport and absorption in the intestine after normoxia or hyperoxia (HO) exposure. * indicates p <0.05 (or adjusted p-value <0.005 for A and E), *** p < 0.001.
A.) Heat maps of key epithelial subset genes form RNASeq in 7-day-old and 2-month-old ileal organoids treated with normoxia (NO) or hyperoxia (HO). B.) qRT-PCR confirmation of A. for Lgr5 and Lyz1 expression. C. Morphology of human organoids from 22-week fetus or 37-week infant after exposure to 12 hours of normoxia (21%) or hyperoxia (95%). D.) RNA expression in hyperoxia treated human organoids. E.) Heatmap of expression of genes important for nutrient transport and absorption in the intestine after normoxia or hyperoxia (HO) exposure. * indicates p <0.05 (or adjusted p-value <0.005 for A and E), *** p < 0.001.Figure 3. Hyperoxia impacts the developing intestine in vivo.
.jpg) A.) Schematic of mouse hyperoxia experiment. B.) Body weights at start and end of experiment, as well as gross organ measurements. C.) RNA expression by qRT-PCR of control normoxia mice (NO) versus hyperoxia exposed mice (HO). ** p <0.01.
A.) Schematic of mouse hyperoxia experiment. B.) Body weights at start and end of experiment, as well as gross organ measurements. C.) RNA expression by qRT-PCR of control normoxia mice (NO) versus hyperoxia exposed mice (HO). ** p <0.01.Figure 1. Immature ileum transcriptome is significanctly altered by hyperoxia.
 A.) Morphology of organoids in culture after 12 hours of normoxia or hyperoxia. B.) Principal component analysis of RNASeq data for ileum organoids from 7-day-old mice (blue) versus 2 month-old mice (red) under normoxia (squares), hypoxia (triangles) or hyperoxia (circles). C.) Hierarchical clustering of RNASeq data shows that immature hyperoxia samples clustered independently of all other groups.
A.) Morphology of organoids in culture after 12 hours of normoxia or hyperoxia. B.) Principal component analysis of RNASeq data for ileum organoids from 7-day-old mice (blue) versus 2 month-old mice (red) under normoxia (squares), hypoxia (triangles) or hyperoxia (circles). C.) Hierarchical clustering of RNASeq data shows that immature hyperoxia samples clustered independently of all other groups. Figure 2. Epithelial cell differentiation is altered by hyperoxia.
.jpg) A.) Heat maps of key epithelial subset genes form RNASeq in 7-day-old and 2-month-old ileal organoids treated with normoxia (NO) or hyperoxia (HO). B.) qRT-PCR confirmation of A. for Lgr5 and Lyz1 expression. C. Morphology of human organoids from 22-week fetus or 37-week infant after exposure to 12 hours of normoxia (21%) or hyperoxia (95%). D.) RNA expression in hyperoxia treated human organoids. E.) Heatmap of expression of genes important for nutrient transport and absorption in the intestine after normoxia or hyperoxia (HO) exposure. * indicates p <0.05 (or adjusted p-value <0.005 for A and E), *** p < 0.001.
A.) Heat maps of key epithelial subset genes form RNASeq in 7-day-old and 2-month-old ileal organoids treated with normoxia (NO) or hyperoxia (HO). B.) qRT-PCR confirmation of A. for Lgr5 and Lyz1 expression. C. Morphology of human organoids from 22-week fetus or 37-week infant after exposure to 12 hours of normoxia (21%) or hyperoxia (95%). D.) RNA expression in hyperoxia treated human organoids. E.) Heatmap of expression of genes important for nutrient transport and absorption in the intestine after normoxia or hyperoxia (HO) exposure. * indicates p <0.05 (or adjusted p-value <0.005 for A and E), *** p < 0.001.Figure 3. Hyperoxia impacts the developing intestine in vivo.
.jpg) A.) Schematic of mouse hyperoxia experiment. B.) Body weights at start and end of experiment, as well as gross organ measurements. C.) RNA expression by qRT-PCR of control normoxia mice (NO) versus hyperoxia exposed mice (HO). ** p <0.01.
A.) Schematic of mouse hyperoxia experiment. B.) Body weights at start and end of experiment, as well as gross organ measurements. C.) RNA expression by qRT-PCR of control normoxia mice (NO) versus hyperoxia exposed mice (HO). ** p <0.01.
