Cardiology 3
Session: Cardiology 3
168 - Novel Role of Thymus Cell Antigen-1(THY-1) in primary Endocardial Fibroelastosis (pEFE)
Friday, April 25, 2025
5:30pm - 7:45pm HST
Publication Number: 168.5613
Angela C. Zeigler, UCLA Mattel Childrens Hospital, Santa Monica, CA, United States; Marlin Touma, UCLA_David Geffen School of Medicine, Los Angeles, CA, United States
.jpg)
Angela C. Zeigler, MD PhD (she/her/hers)
Pediatric Critical Care Fellow
UCLA Mattel Childrens Hospital
Santa Monica, California, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Primary EFE (pEFE) is a congenital cardiac pathology characterized by a thick layer of elastin-rich fibrosis usually in the left ventricle that usually results in death or need for heart transplantation. The primary cause is unclear although it’s thought to be driven by endothelial to mesenchymal transition which results in activated fibroblasts and elastin-rich extracellular matrix (ECM) production. Our lab previously performed whole exome sequencing and RNA-seq on fibroblasts from a patient with pEFE and a control patient, which associated the pEFE phenotype with a null mutation in ALMS1.
Objective: We sought to use this dataset to identify potential genetic drivers for the pathogenesis of pEFE.
Design/Methods: Using the RNA-seq data, which included three technical replicates from control dermal fibroblasts and three from pEFE dermal fibroblasts, I performed a principal components analysis in order to identify genes that contribute to the discrimination between the control and pEFE patients. I used Cytoscape and the StringApp to identify experimentally identified connections between our genes of interest.
Results: Several genes, including THY1, had high loading scores along principal component one (Fig. 1) which implies they account for most of the variance between the control and pEFE gene expression. THY1 has previously been associated with decreased collagen deposition and fibroblast activation in the heart and lungs, which is consistent with our dataset where THY1 expression was decreased in our patient with pEFE compared to control. In contrast, elastin (ELN), several elastin-associated associated proteins (fibulin5, FBLN5; fibrillin1, FBN1), and periostin (POSTN), a maker of fibroblast activation, were all upregulated (Fig.1). The StringApp identified genes with a published connection to THY1 (Fig. 2), which included several genes important to the pathogenesis of pEFE such as elastin (ELN) and periostin (POSTN).
Conclusion(s): Together, this data suggests that the downregulation of THY1 in pEFE could be a driver for the increase in elastin-rich ECM production and fibroblast activation. Further studies in our lab will investigate whether the addition of soluble THY1 to control and pEFE patient-derived fibroblasts will reduce ECM production and fibroblast activation thereby reversing the pEFE phenotype.
Fig. 1: Transcriptome landscape in pEFE dermal fibroblasts compared to control fibroblasts.
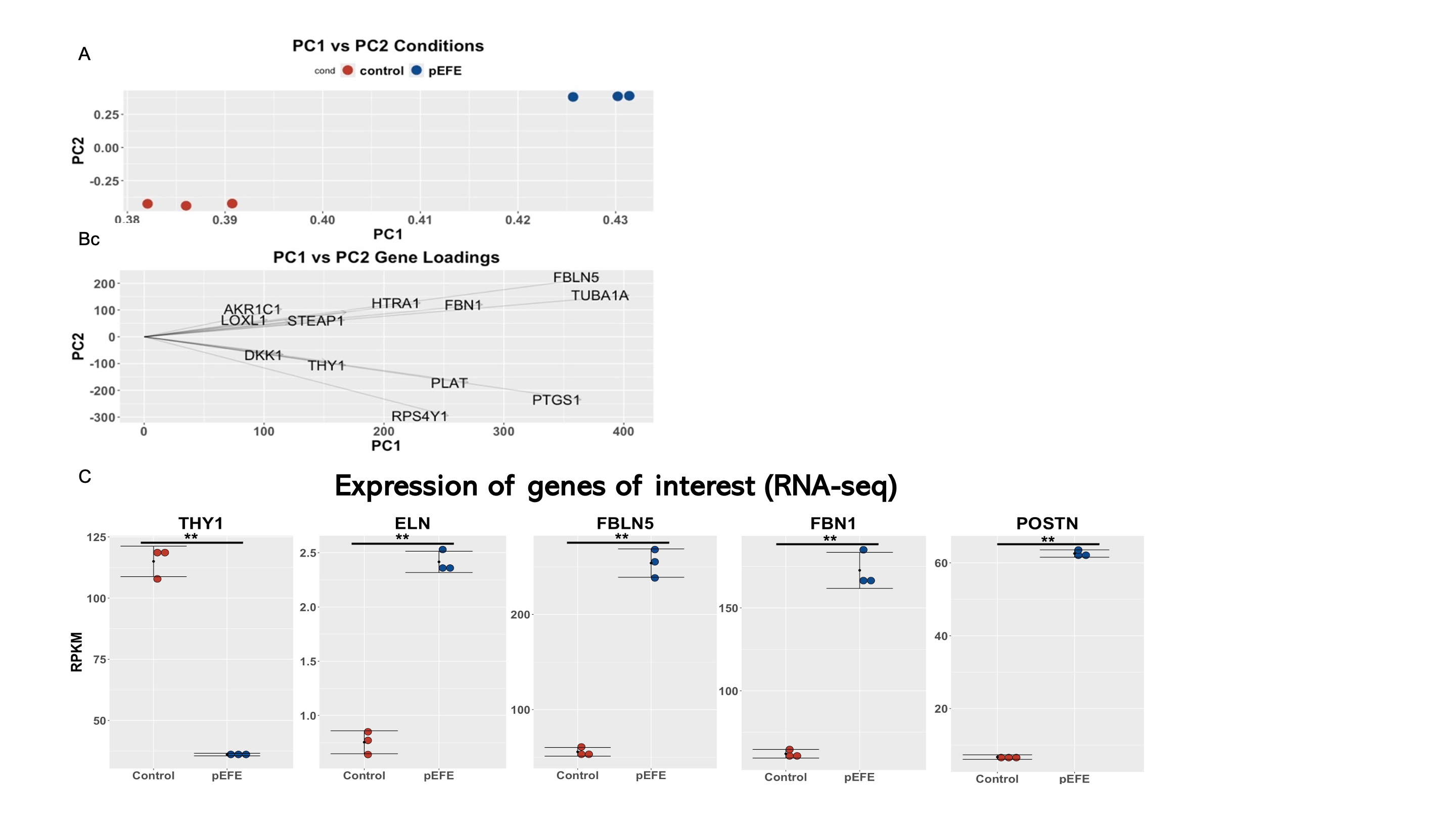 A. Each of the control and pEFE patient samples plotted along the first two principal components (PC). B. Loadings of genes along the first two PCs. Longer lines indicate more influence on the PC. C. Pair-wise comparison (pEFE vs control) of expression values of the differentially genes that drives the variance. Error bars show mean and standard deviation of three technical replicates. PC1, PC2 (principal component 1 and 2, respectively). RPKM: Reads per KB per Million Mapped Reads. ** adjusted p value < 0.01
A. Each of the control and pEFE patient samples plotted along the first two principal components (PC). B. Loadings of genes along the first two PCs. Longer lines indicate more influence on the PC. C. Pair-wise comparison (pEFE vs control) of expression values of the differentially genes that drives the variance. Error bars show mean and standard deviation of three technical replicates. PC1, PC2 (principal component 1 and 2, respectively). RPKM: Reads per KB per Million Mapped Reads. ** adjusted p value < 0.01Fig. 2: THY-1 regulated network.
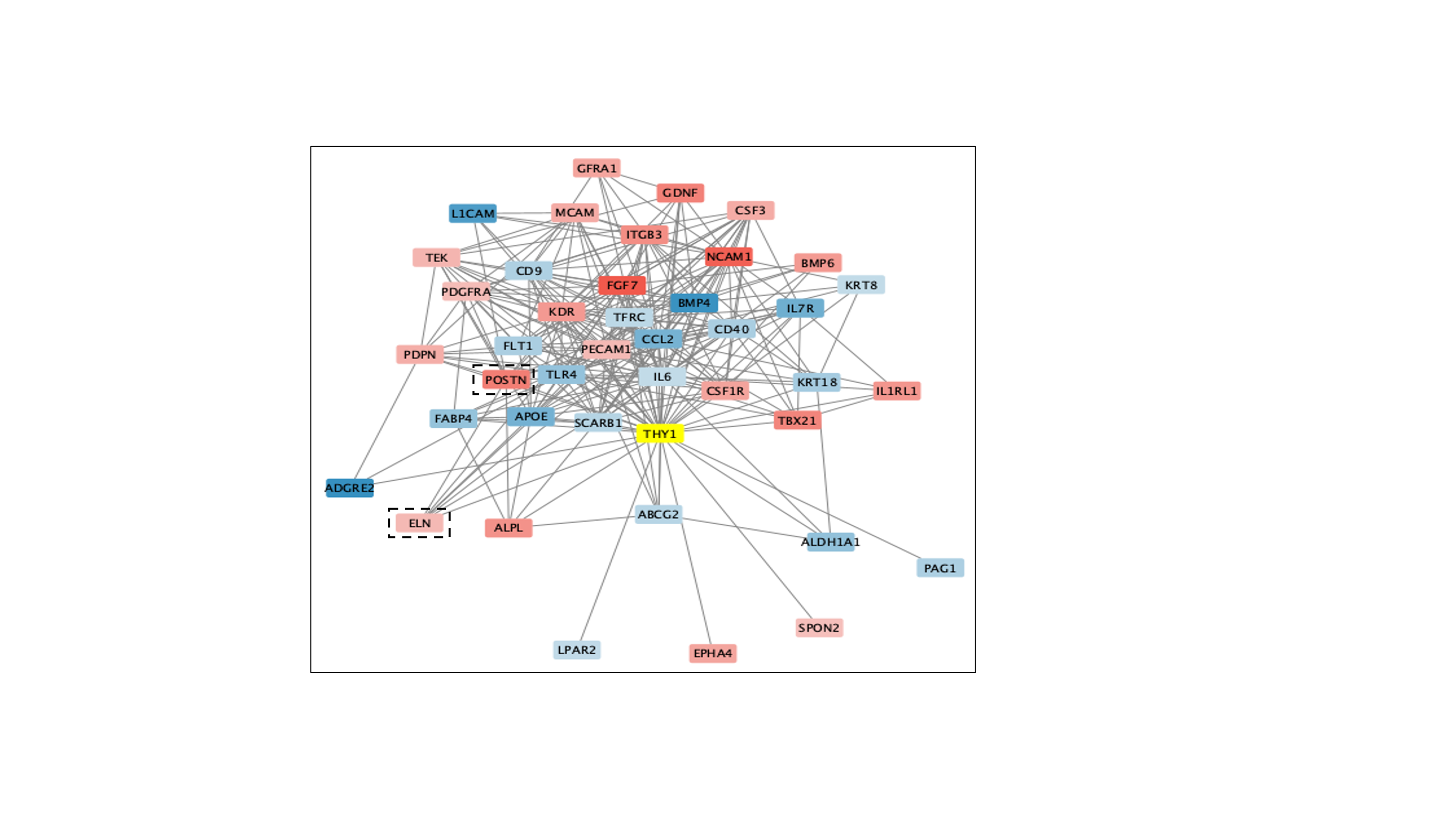 THY-1 and all genes significantly differentially expressed between control and pEFE that have known connections to THY-1 as identified by stringApp. Network visualization generated using Cytoscape. The color of each gene is defined by it’s up- (red) or down- (blue) regulation in the differential expression analysis of control vs pEFE fibroblasts except for THY-1 which is highlighted in yellow. ELN and POSTN are highlighted with a dashed rectangle.
THY-1 and all genes significantly differentially expressed between control and pEFE that have known connections to THY-1 as identified by stringApp. Network visualization generated using Cytoscape. The color of each gene is defined by it’s up- (red) or down- (blue) regulation in the differential expression analysis of control vs pEFE fibroblasts except for THY-1 which is highlighted in yellow. ELN and POSTN are highlighted with a dashed rectangle. Fig. 1: Transcriptome landscape in pEFE dermal fibroblasts compared to control fibroblasts.
 A. Each of the control and pEFE patient samples plotted along the first two principal components (PC). B. Loadings of genes along the first two PCs. Longer lines indicate more influence on the PC. C. Pair-wise comparison (pEFE vs control) of expression values of the differentially genes that drives the variance. Error bars show mean and standard deviation of three technical replicates. PC1, PC2 (principal component 1 and 2, respectively). RPKM: Reads per KB per Million Mapped Reads. ** adjusted p value < 0.01
A. Each of the control and pEFE patient samples plotted along the first two principal components (PC). B. Loadings of genes along the first two PCs. Longer lines indicate more influence on the PC. C. Pair-wise comparison (pEFE vs control) of expression values of the differentially genes that drives the variance. Error bars show mean and standard deviation of three technical replicates. PC1, PC2 (principal component 1 and 2, respectively). RPKM: Reads per KB per Million Mapped Reads. ** adjusted p value < 0.01Fig. 2: THY-1 regulated network.
 THY-1 and all genes significantly differentially expressed between control and pEFE that have known connections to THY-1 as identified by stringApp. Network visualization generated using Cytoscape. The color of each gene is defined by it’s up- (red) or down- (blue) regulation in the differential expression analysis of control vs pEFE fibroblasts except for THY-1 which is highlighted in yellow. ELN and POSTN are highlighted with a dashed rectangle.
THY-1 and all genes significantly differentially expressed between control and pEFE that have known connections to THY-1 as identified by stringApp. Network visualization generated using Cytoscape. The color of each gene is defined by it’s up- (red) or down- (blue) regulation in the differential expression analysis of control vs pEFE fibroblasts except for THY-1 which is highlighted in yellow. ELN and POSTN are highlighted with a dashed rectangle. 
