Quality Improvement/Patient Safety 5
Session: Quality Improvement/Patient Safety 5
474 - Improving Asthma Control at a Federally Qualified Health Center
Saturday, April 26, 2025
2:30pm - 4:45pm HST
Publication Number: 474.5324
Cindy Do, NewYork-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital, Brooklyn, NY, United States; Snezana Osorio, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, United States; Prina Amin, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, United States; Kobi Axelrod, NewYork-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital, New York, NY, United States; Nicole Crofton, NewYork-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital, New York, NY, United States; Jessica DeAngelis, NewYork-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital, New York, NY, United States; Kathleen Fan, Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, NY, United States; Arianny Martinez-Beltran, NewYork-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital, New York, NY, United States; Nadia Nikroo, NewYork-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital, New York City, NY, United States; Sandra Rolston, Weill Cornell Medicine, Long Island City, NY, United States; Hanna Swerdin, NewYork-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital, New York, NY, United States; Noemi Charnow, NewYork-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital, Long Island City, NY, United States

Cindy Do, MD (she/her/hers)
Resident Physician
NewYork-Presbyterian Komansky Children’s Hospital
Brooklyn, New York, United States
Presenting Author(s)
Background: The Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) guideline was updated in 2022 with major changes in using inhaled corticosteroids in patients with asthma. In our federally qualified health center, approximately 11.5% of patients are diagnosed with asthma. However, GINA guidelines have not been fully implemented.
Objective: To improve guideline-consistent care in patients ages 3 – 18 years old with asthma at a resident-based clinic to 70% by June 2024. Guideline-consistent care was defined as the percentage of patients who had documentation of receiving the influenza vaccine, the Asthma Action Plan (AAP), Asthma Control Test (ACT), an asthma severity classification.
Design/Methods: This resident-led quality improvement project from 11/2022 - 5/2024 used the model for improvement to define SMART AIM, project measures, and to design the Key Driver Diagram (Figure 1). We used a planned sequential experimentation to test interventions via 7 PDSA cycles. Compliance with each component of “guideline-consistent care” were used as process measures. We used the percentage of patients with body mass index (BMI) reviewed for the balancing measure. Tertiary drivers were used to design interventions (resident education, AAP and ACT in different languages, algorithm of workflow easily visible, organization of asthma resources, and a laminated asthma kit). Data was collected via Electronic Health Record (EHR) review and analyzed using statistical process control “P” charts. API rules were applied to detect special cause variation.
Results: We reviewed total of 170 electronic health records. Flu vaccination rates were high throughout the project at 72%. By June 2024, the percentage of patients with an asthma severity classification increased from 88% to 98%. The percentage of patients who received an AAP increased from 28% to 70%. The percentage of patients with persistent asthma who had the ACT administered increased from 41% to 76%.
Conclusion(s): We successfully implemented GINA guidelines for asthma patients in our clinic as evident by achieving special cause variation in several process measures while maintaining high influenza vaccination rate that exceed national average of 69%. Interventions that supported both resident education and workflow, including availability of the AAP and ACT in different languages, were implemented. Our next steps include assessment of patient outcomes, including the percentage of patients with persistent asthma who score “well-controlled” on the ACT. Future interventions include further patient education on asthma and spacer usage.
Key Driver Diagram
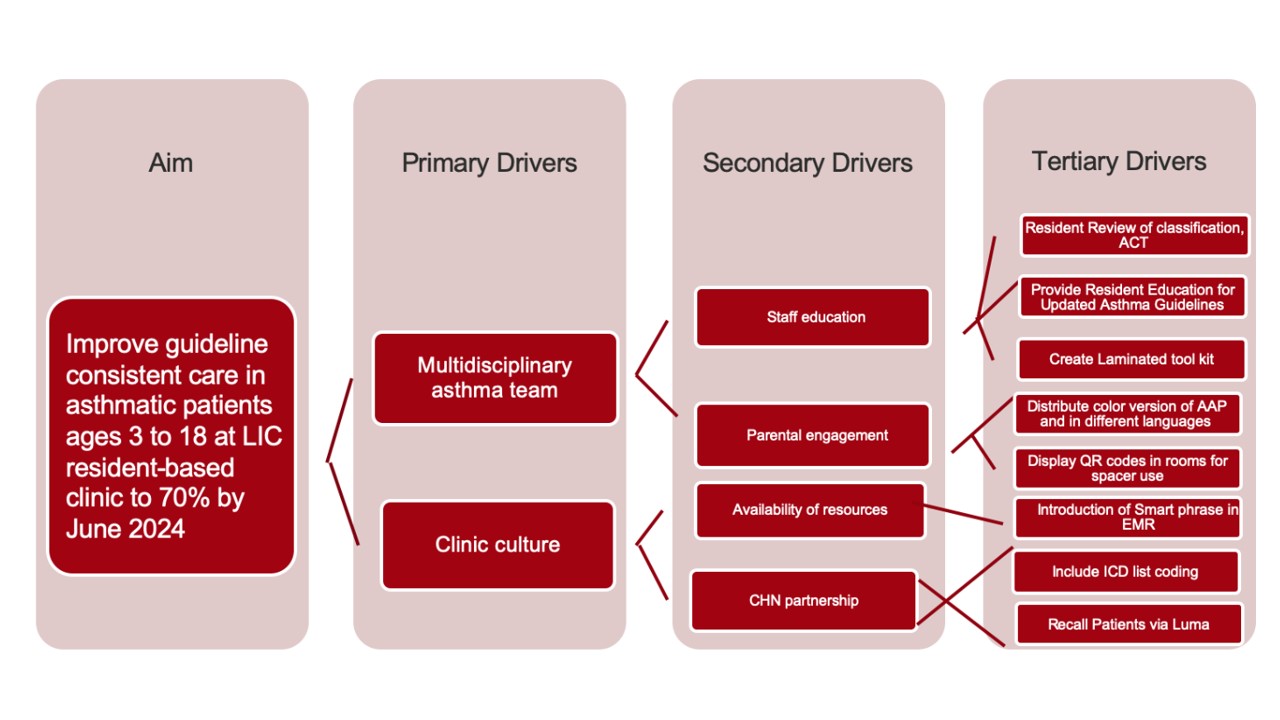 Figure 1. Key Driver Diagram
Figure 1. Key Driver DiagramAsthma Action Plan Given
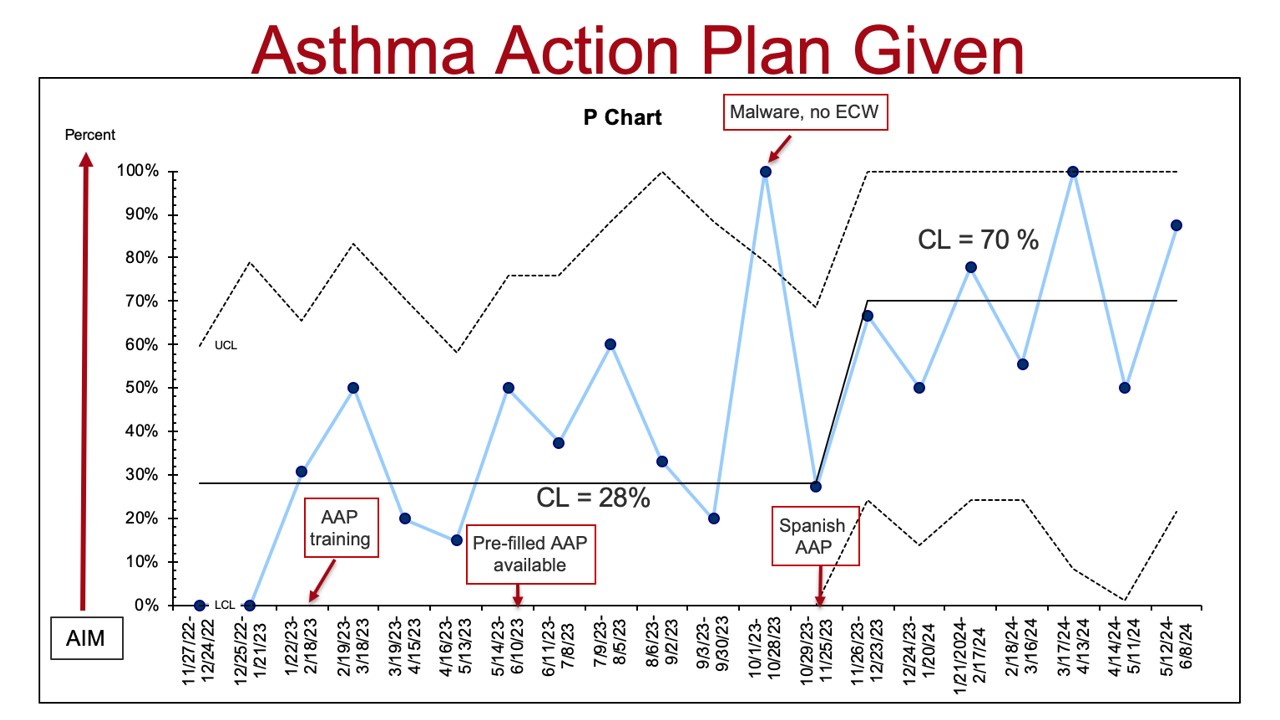 Figure 2. Control chart showing percentage of patients who were given the AAP with center line. Interventions noted in the red boxes. Of note, ECW (eClinicalWorks) is the clinic’s electronic health record system.
Figure 2. Control chart showing percentage of patients who were given the AAP with center line. Interventions noted in the red boxes. Of note, ECW (eClinicalWorks) is the clinic’s electronic health record system. Asthma Control Test Administered to Patients with Persistent Asthma
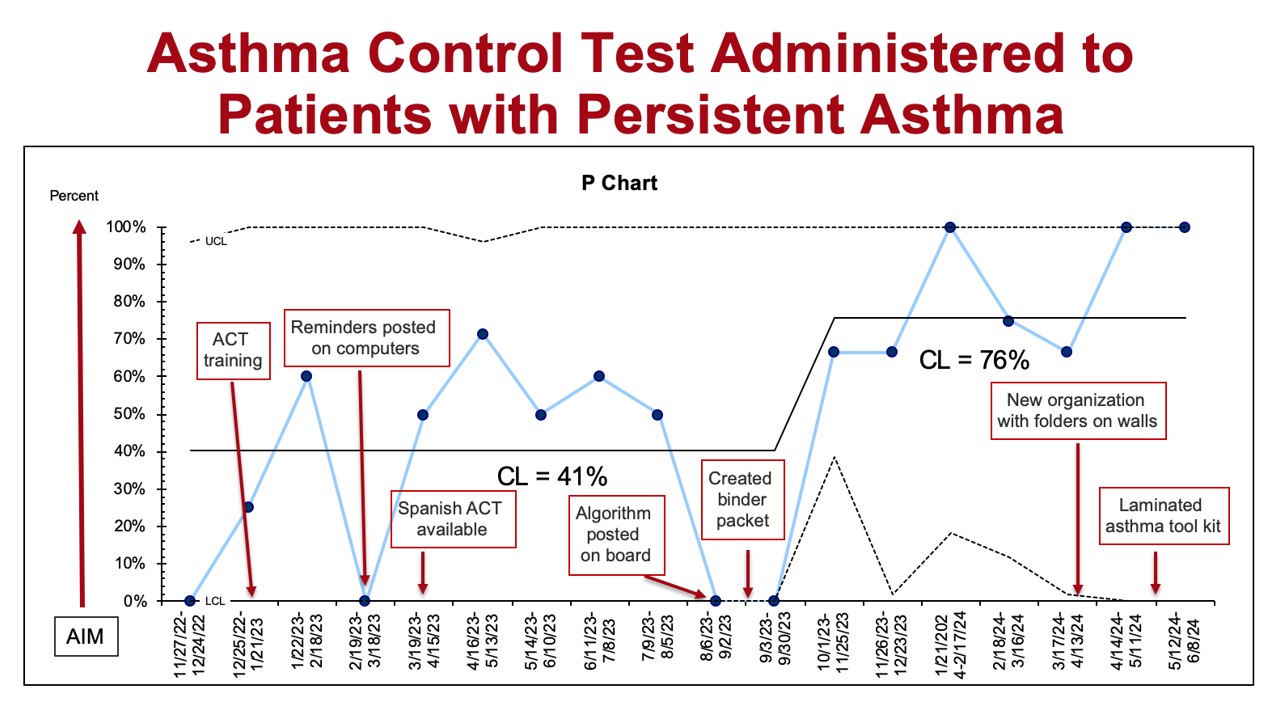 Figure 3. Control chart showing percentage of patients with persistent asthma who were administered the ACT with center line. Interventions noted in the red boxes.
Figure 3. Control chart showing percentage of patients with persistent asthma who were administered the ACT with center line. Interventions noted in the red boxes. 

