Neonatal Neurology 1
Session: Neonatal Neurology 1
338 - Intra- and Inter-Observer Reproducibility of Neonatal Brain Measures of Growth and Maturation Using Cranial Ultrasonography
Friday, April 25, 2025
5:30pm - 7:45pm HST
Publication Number: 338.5281
Lucia McLean, The Royal Women's Hospital, Carlton, Victoria, Australia; Brett J. Manley, Mercy Hospital for Women, Melbourne, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia; Louise S. Owen, Royal Women's Hospital, Melbourne, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia; Peter Davis, Royal Women's Hospital, Melbourne, Victoria, Australia; Rocco Cuzzilla, The Royal Women's Hospital, Parkville, Victoria, Australia
.jpg)
Lucia McLean, BSc (Hons), MD (she/her/hers)
Neonatal Fellow
The Royal Women's Hospital
Carlton, Victoria, Australia
Presenting Author(s)
Background: Extreme preterm birth and its sequelae are associated with altered postnatal brain development. Several linear brain measures on neuroimaging have been shown to reliably assess brain development and predict neurodevelopmental outcomes. Data on the reproducibility of brain measures of maturation are lacking.
Objective: This sub-study of infants born at < 28 weeks’ gestational age or < 1000 g aimed to assess the intra- and inter-observer reproducibility of neonatal brain measures of growth and maturation using cranial ultrasonography (cUS).
Design/Methods: Retrospective observational study. Linear brain measures (Figure) reflecting growth and maturation were made on cUS performed as part of clinical care. Brain measures were chosen for their potential clinical relevance and ease of recognition of anatomical landmarks on standard imaging planes. Measurements were performed independently by two observers and repeated by one observer after one month. Intra- and inter-observer reproducibility were assessed by interclass correlation coefficients (ICC) using two-way mixed effects and random effects modelling, respectively. ICC relate to consistency of agreement.
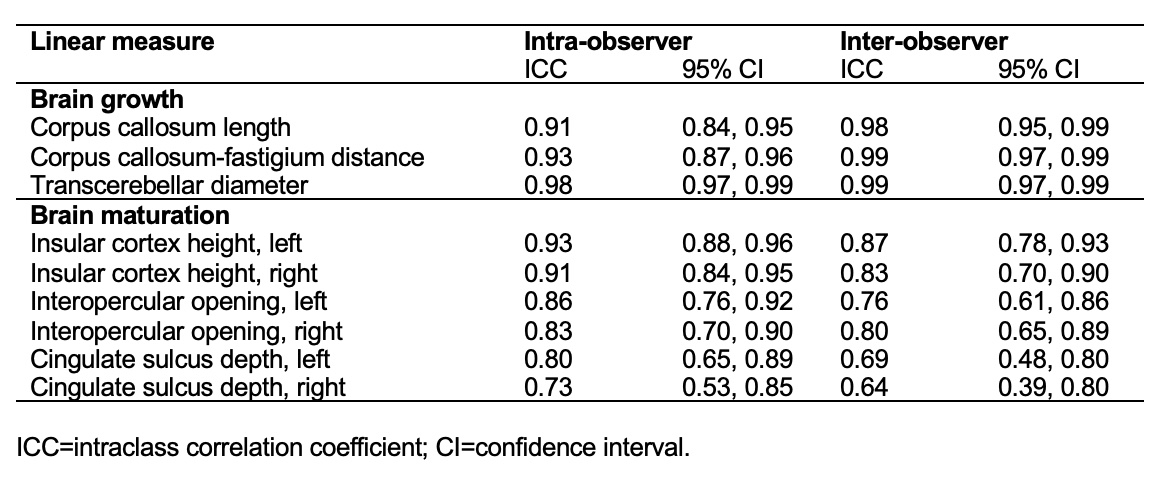
Results: Brain measures were made from 50 cUS scans performed for 13 infants. Brain measures of growth showed excellent intra- and inter-observer reproducibility (all measures ICC >0.90) (Table). Brain measures of maturation showed moderate to excellent intra- and inter-observer reproducibility. Measurements of the insular cortex (IC) height and interopercular (IO) opening showed higher agreement between, and within, observers, compared with cingulate sulcus (CS) depth.
Conclusion(s): Simple, readily identifiable linear brain measures of growth and maturation on cUS were shown to be highly reproducible. Measurements of the IC height and IO opening should be explored further as potential markers of brain maturation and neurodevelopmental outcome.
Reproducibility of cranial ultrasonography linear measures
Brain measures made on cranial ultrasonography
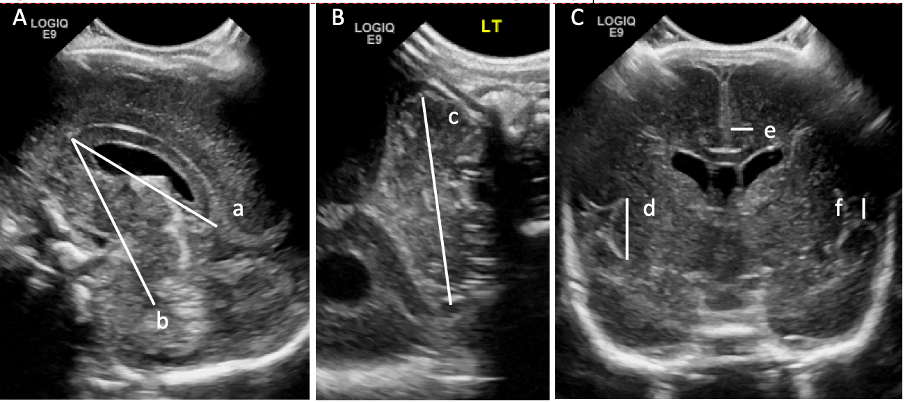 Cranial ultrasound linear measures of brain growth (A and B) and maturation (C). Images taken through the anterior fontanelle in the midsagittal plane (A) and coronal plane at the level of the foramina of Monro (C) and through the mastoid fontanelle in the coronal plane (B). a=corpus callosum length, b=corpus callosum-fastigium distance, c=transcerebellar diameter, d=insular cortex height, e=cingulate sulcus depth and f=interopercular opening
Cranial ultrasound linear measures of brain growth (A and B) and maturation (C). Images taken through the anterior fontanelle in the midsagittal plane (A) and coronal plane at the level of the foramina of Monro (C) and through the mastoid fontanelle in the coronal plane (B). a=corpus callosum length, b=corpus callosum-fastigium distance, c=transcerebellar diameter, d=insular cortex height, e=cingulate sulcus depth and f=interopercular opening
